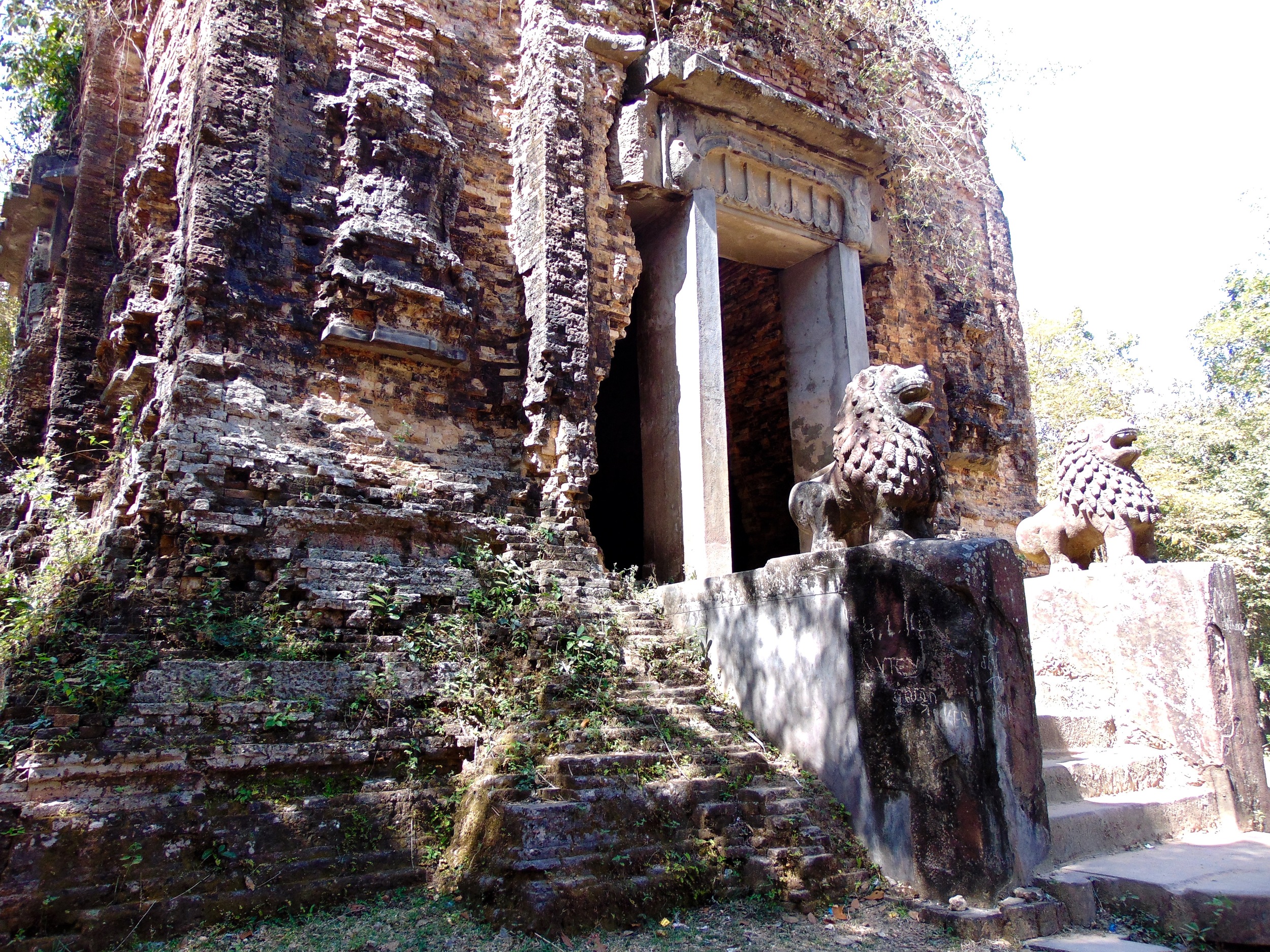
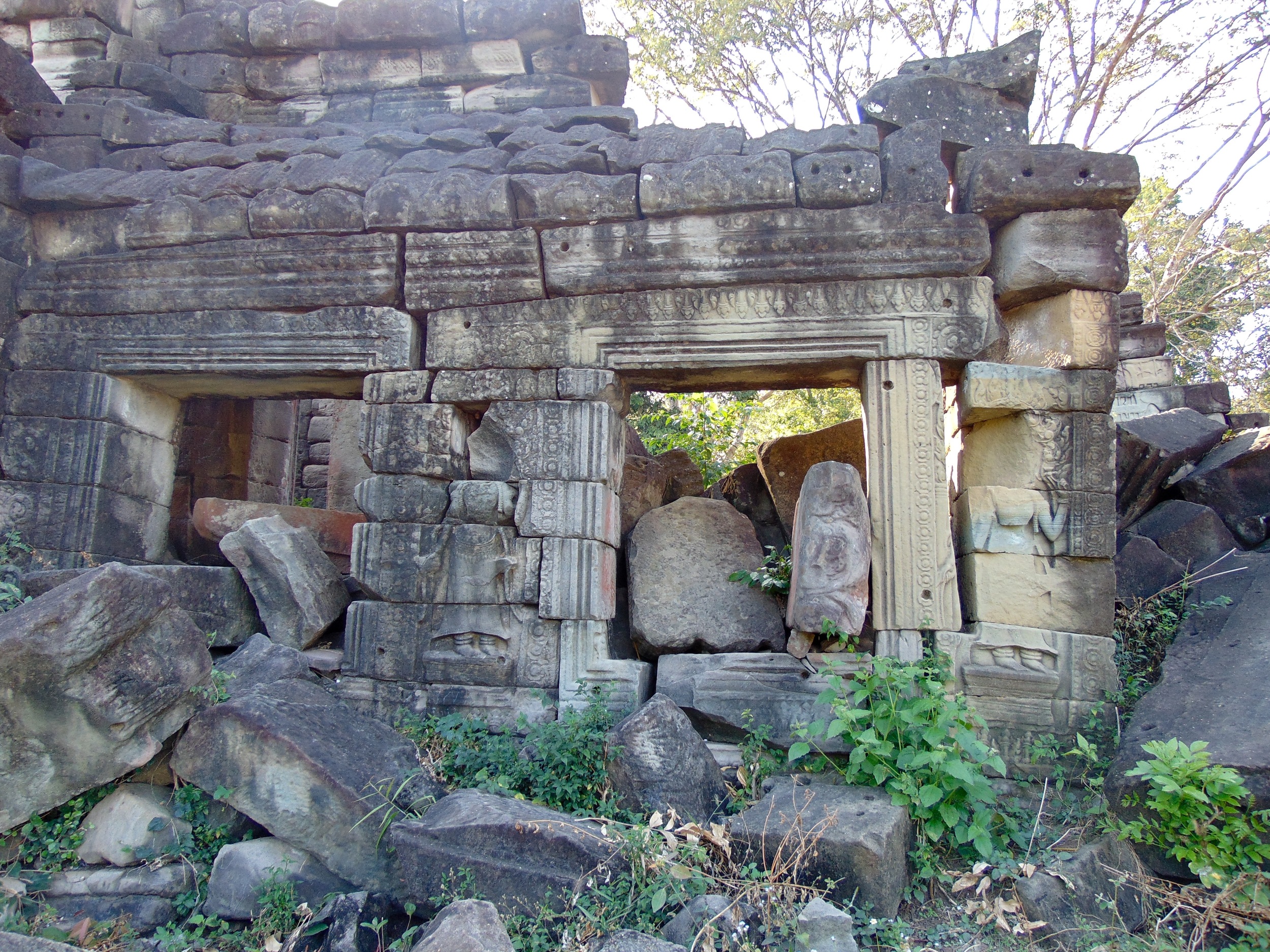
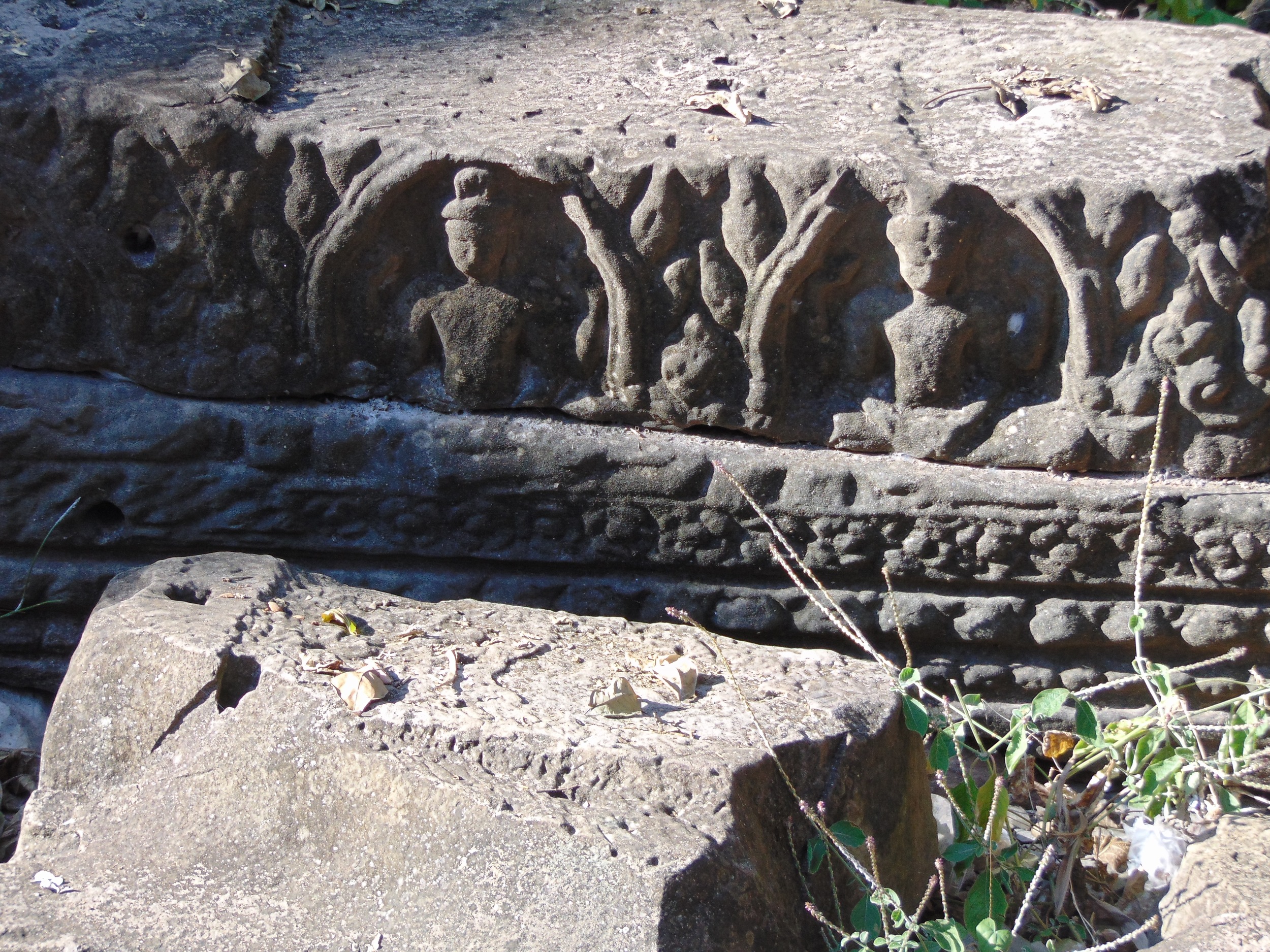
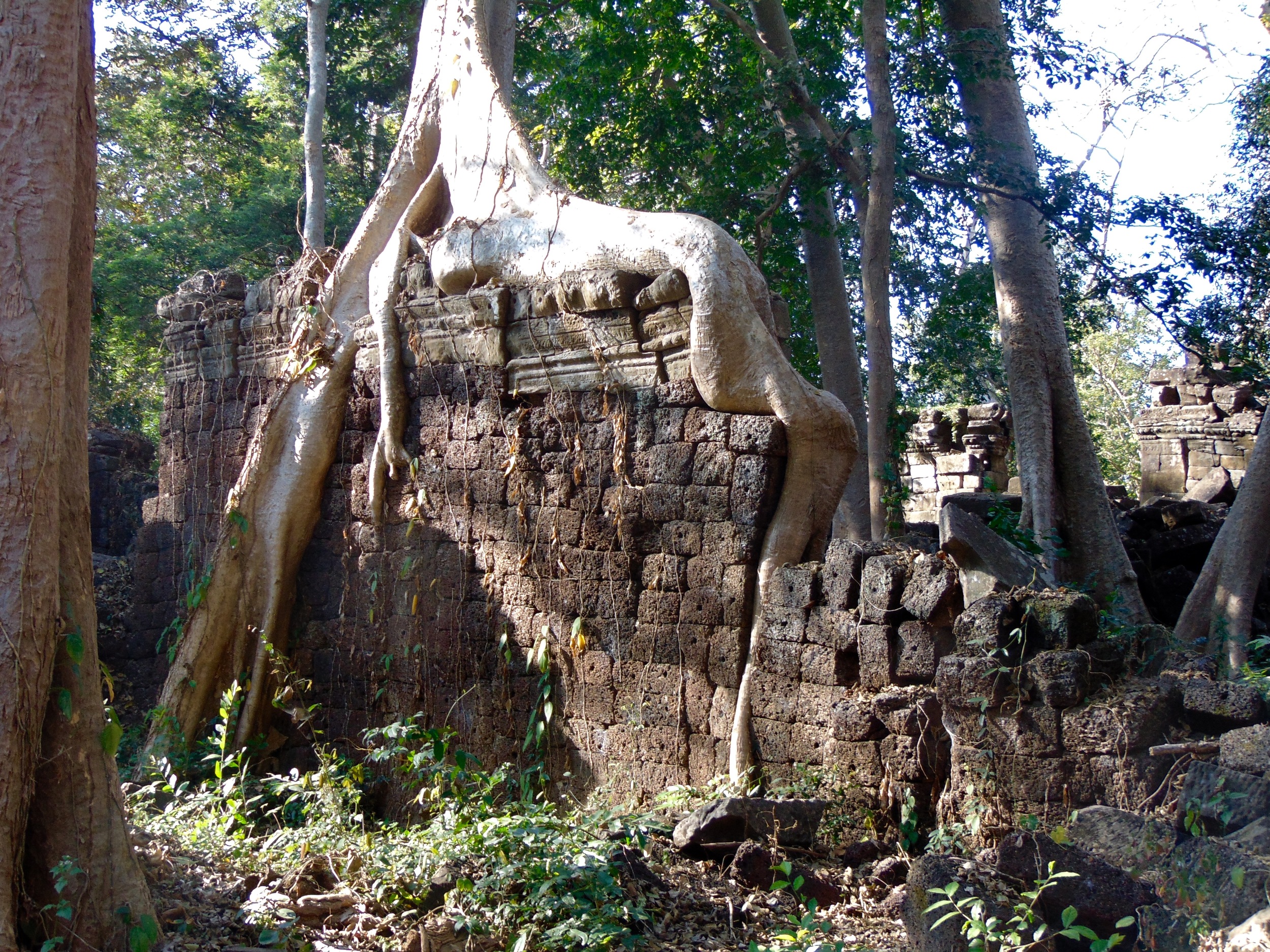
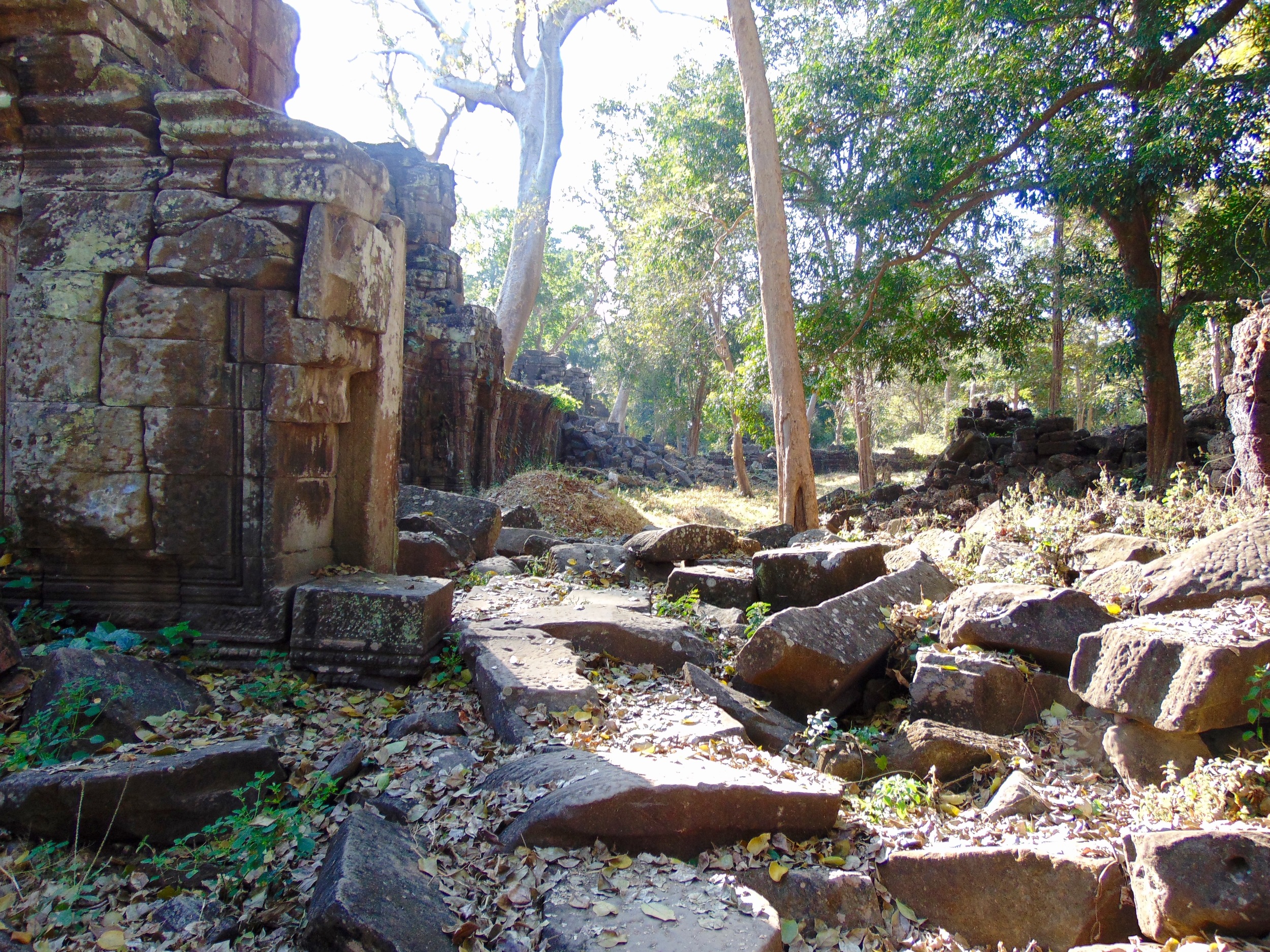
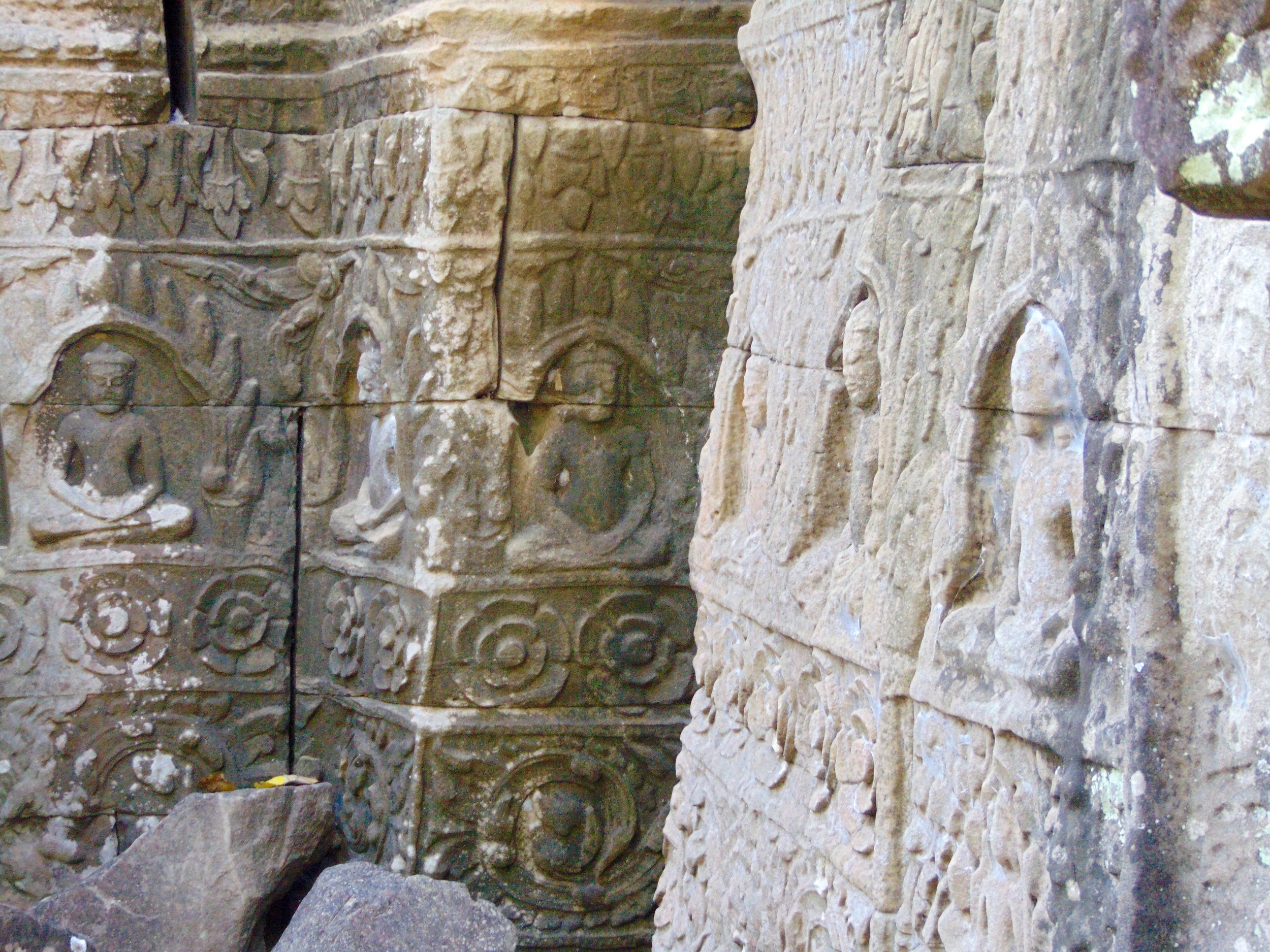
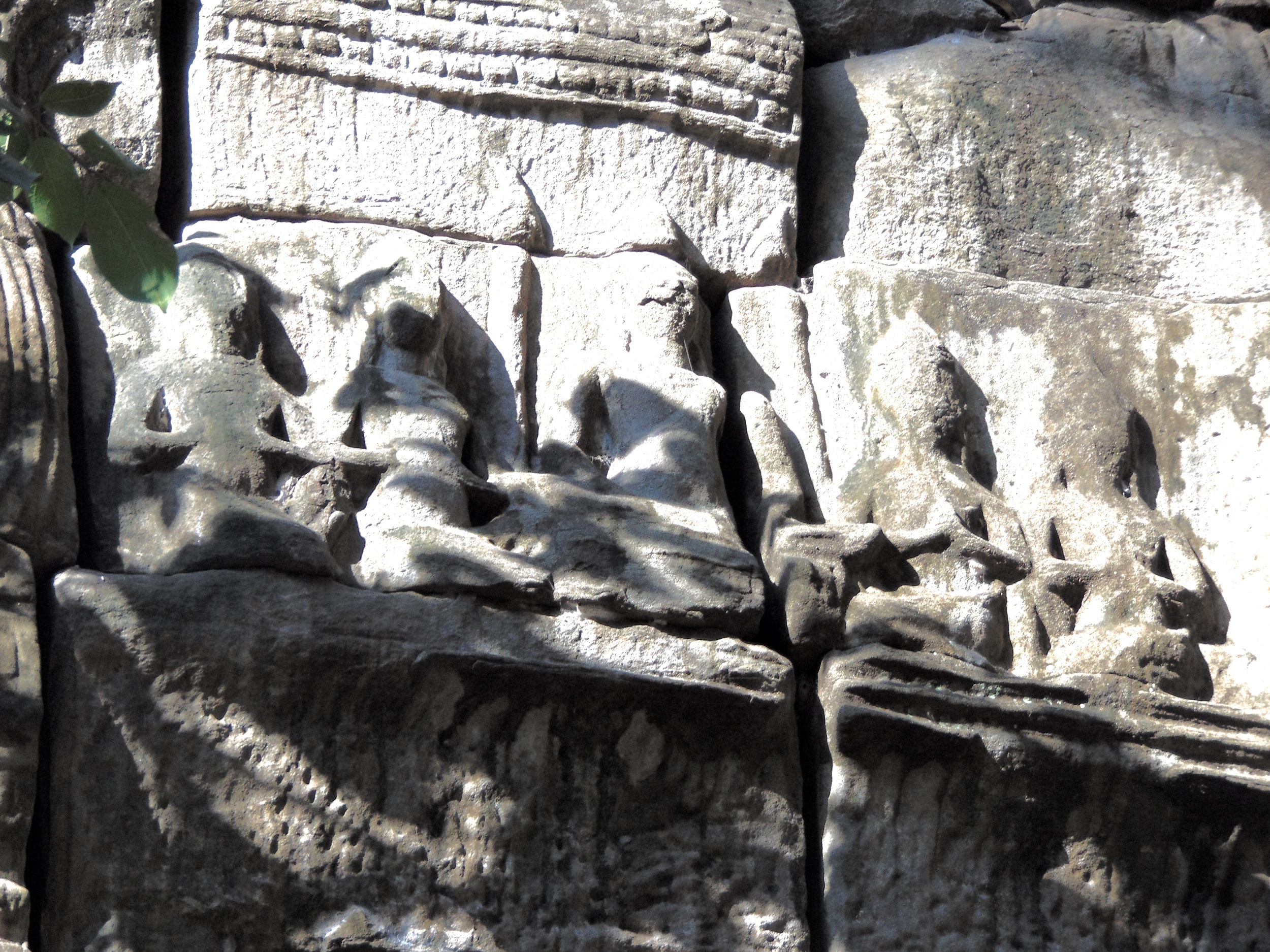
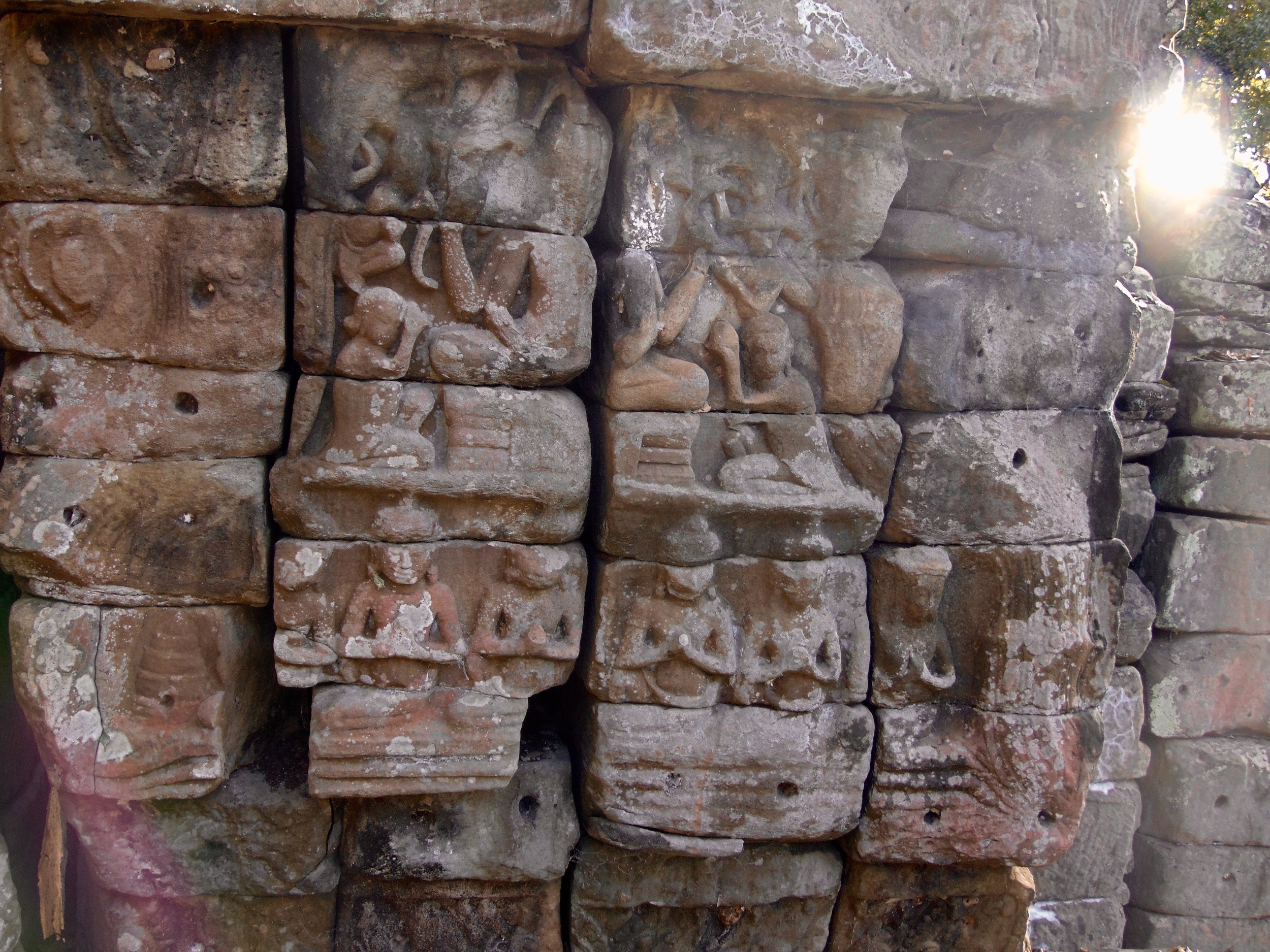
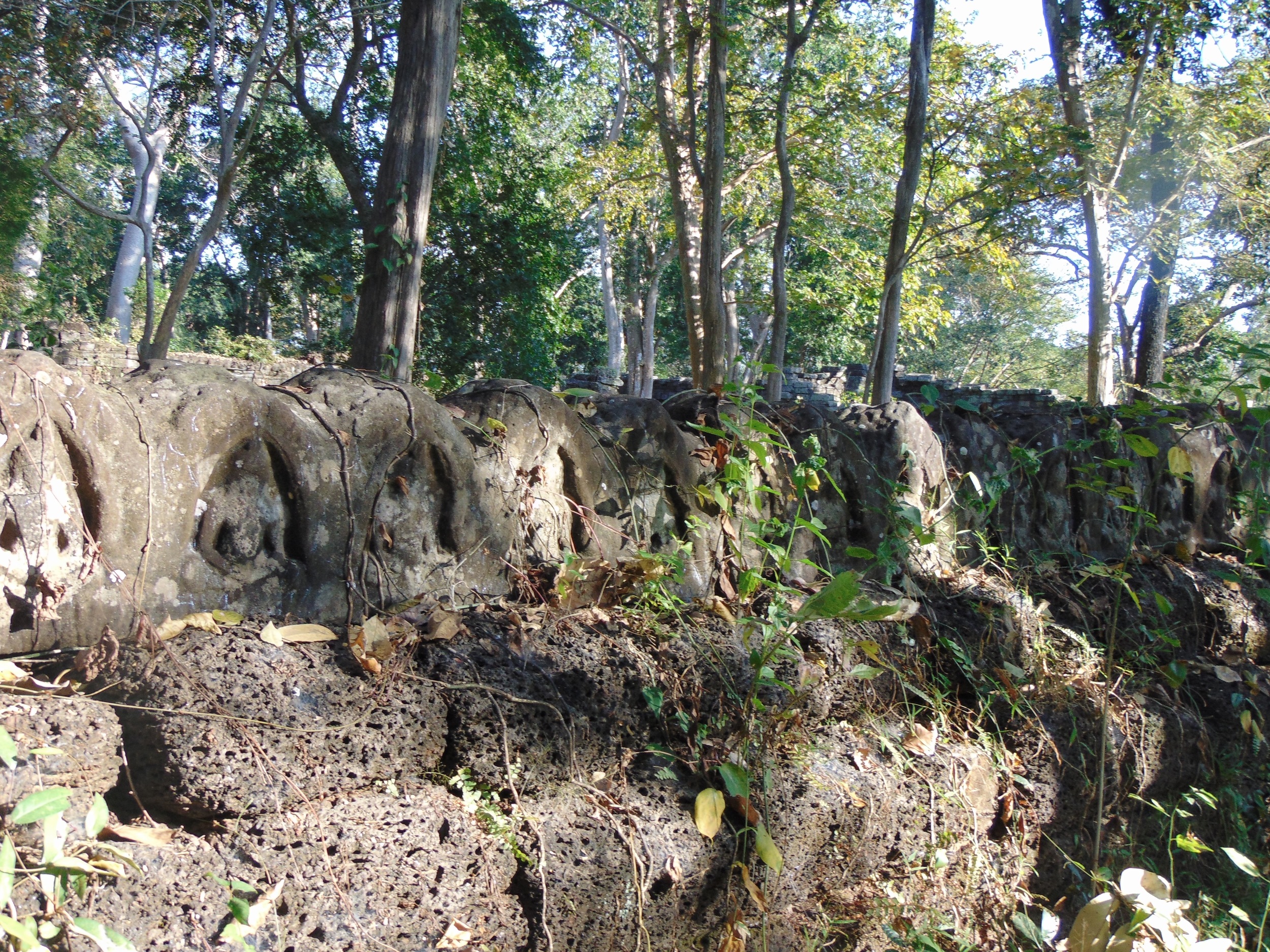
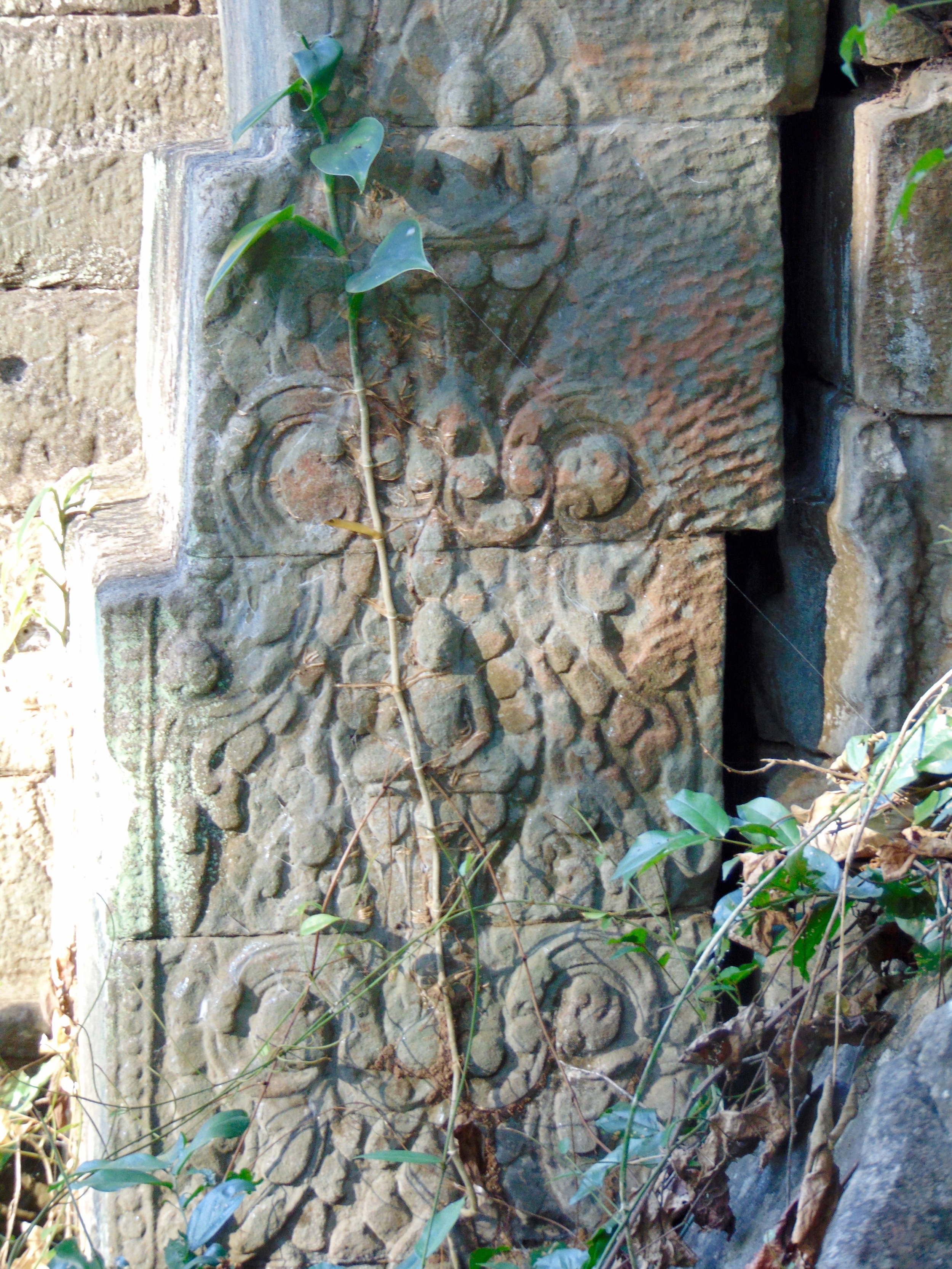
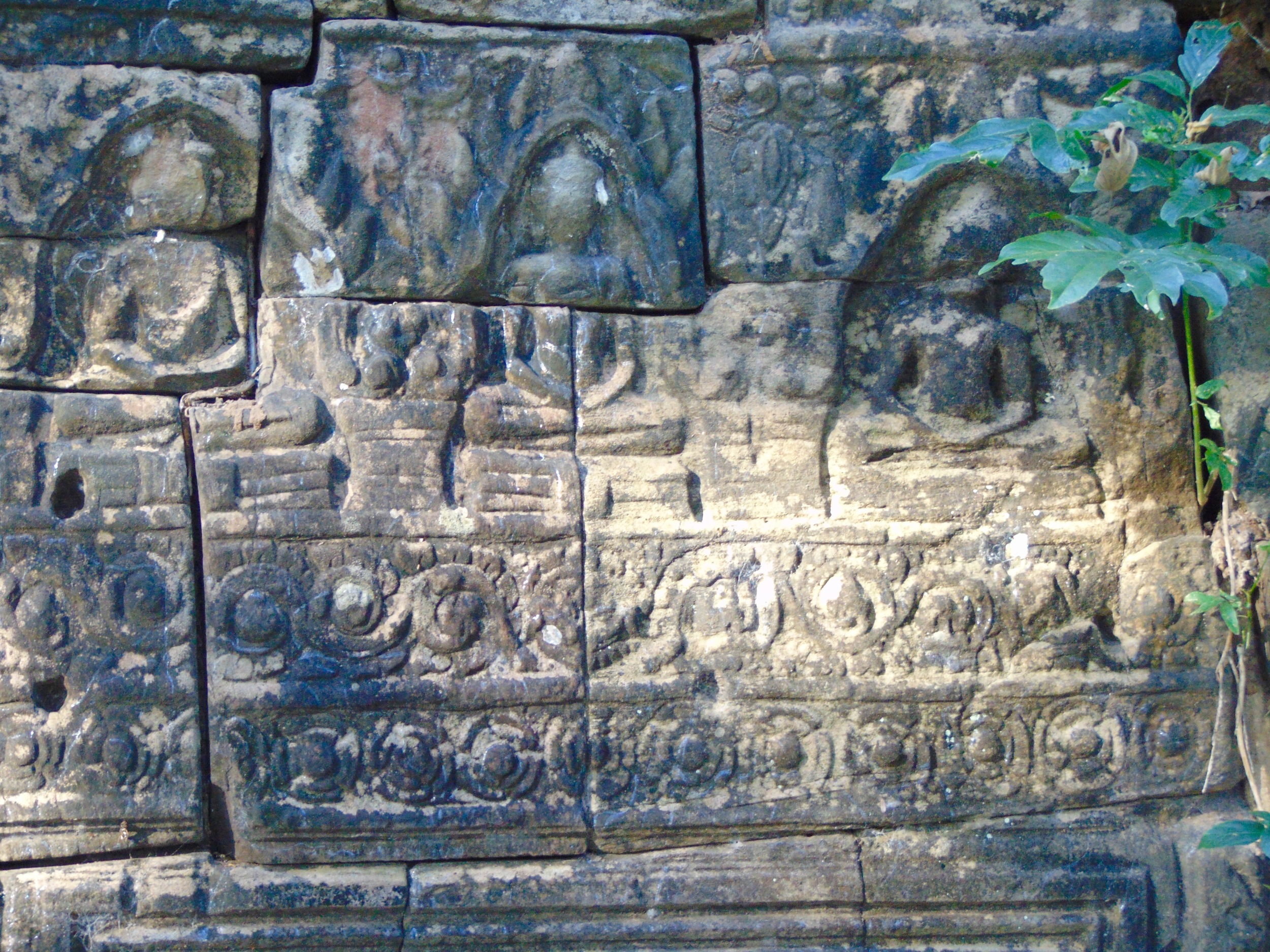
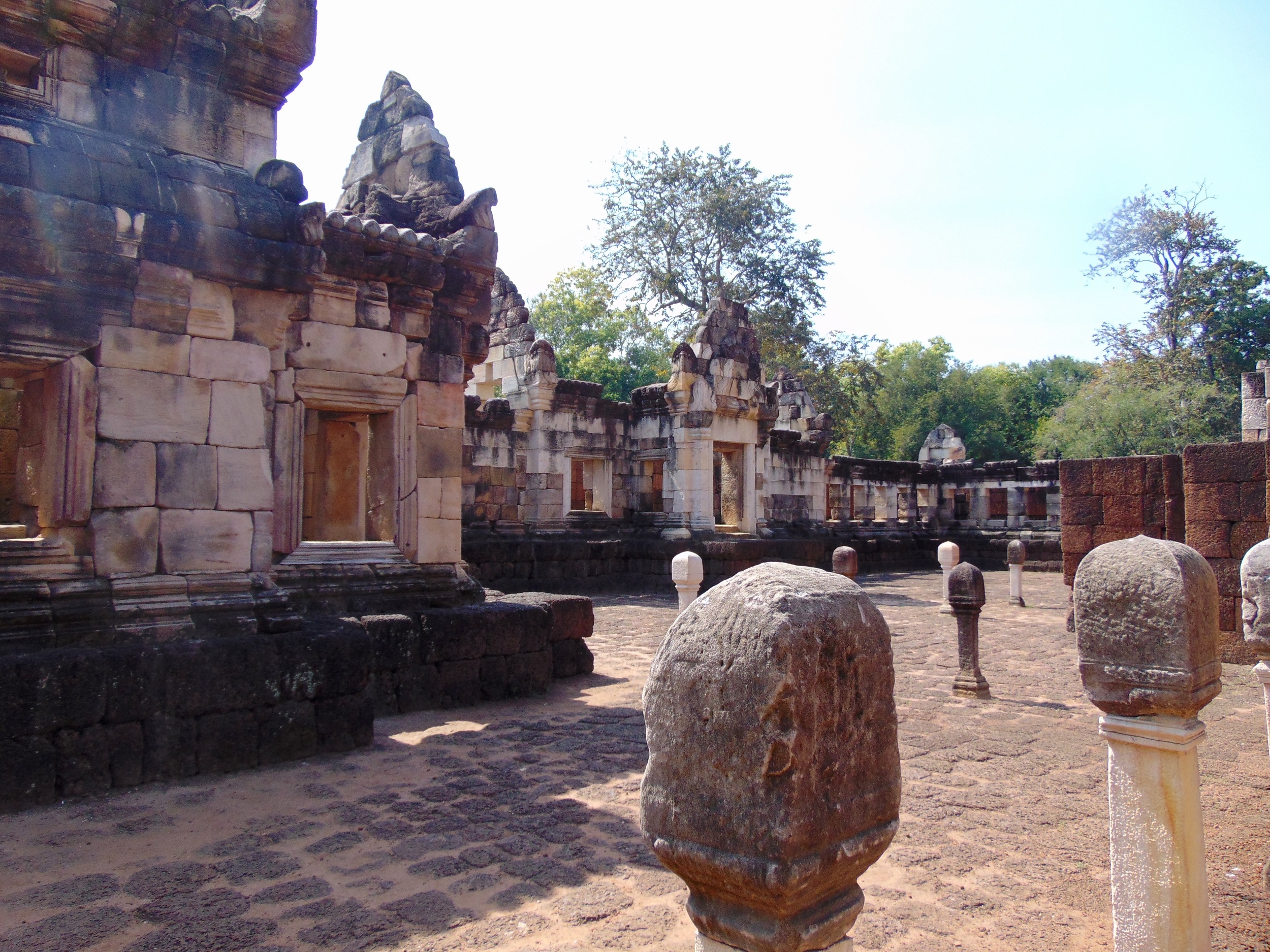
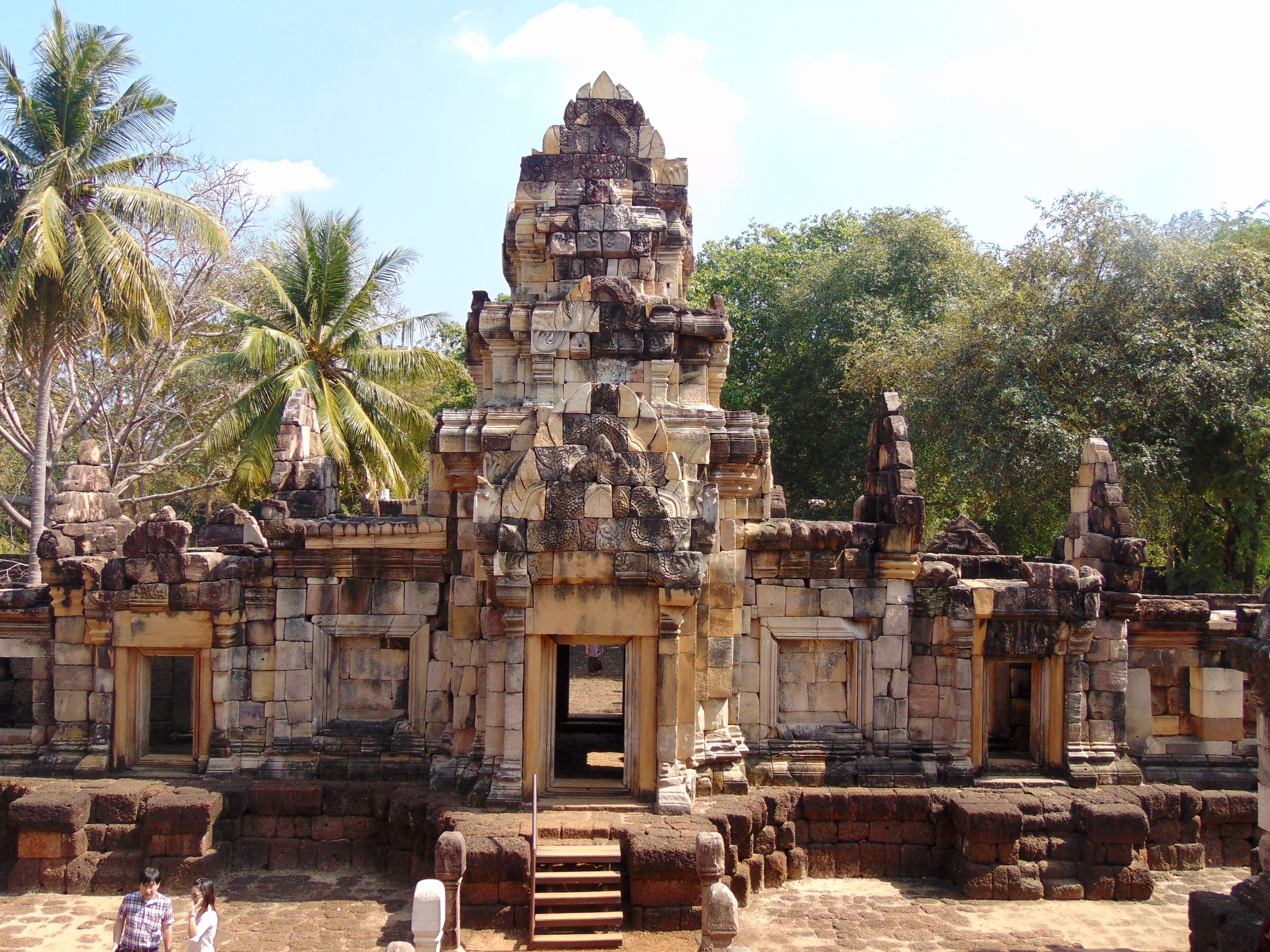
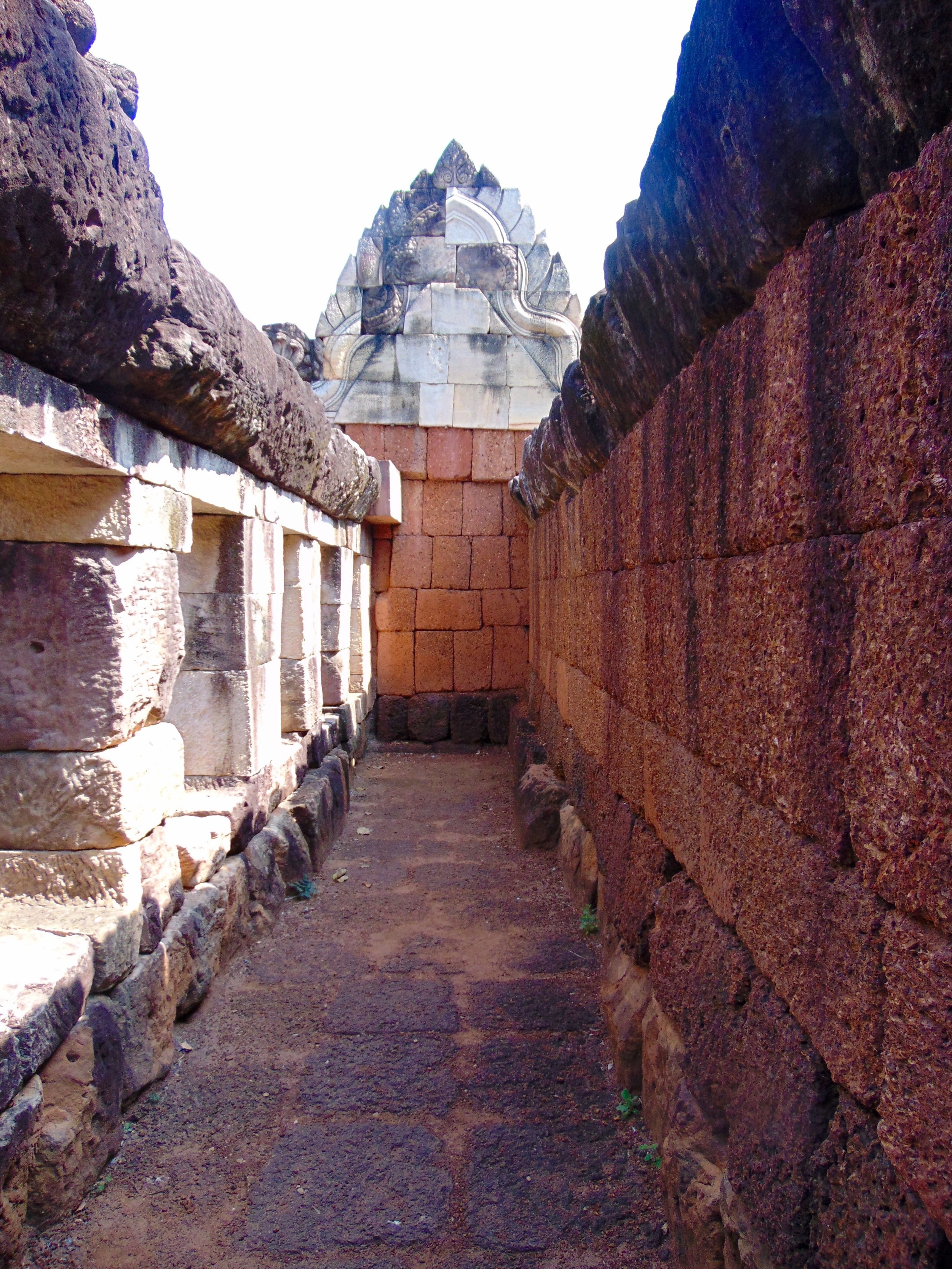
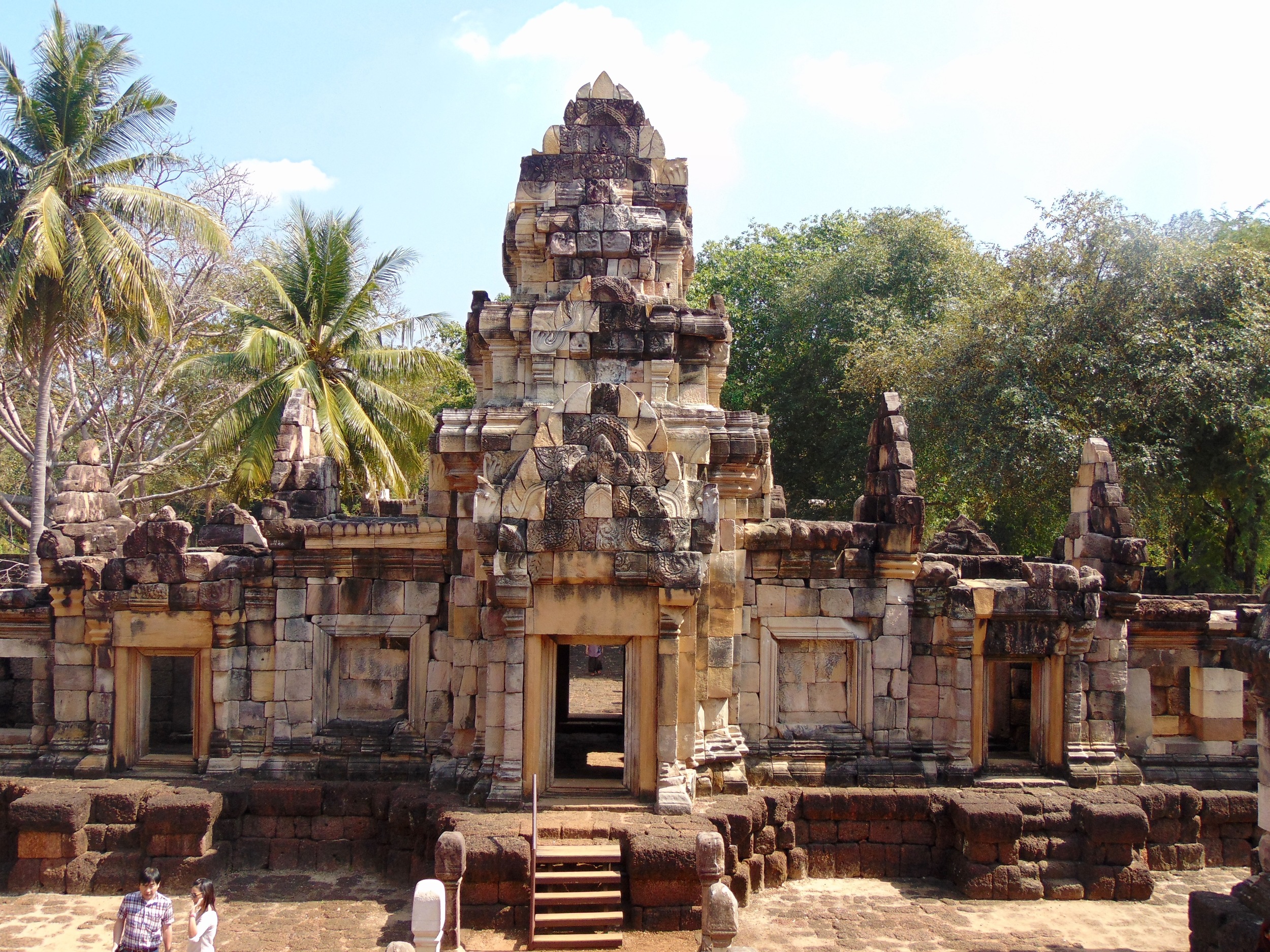
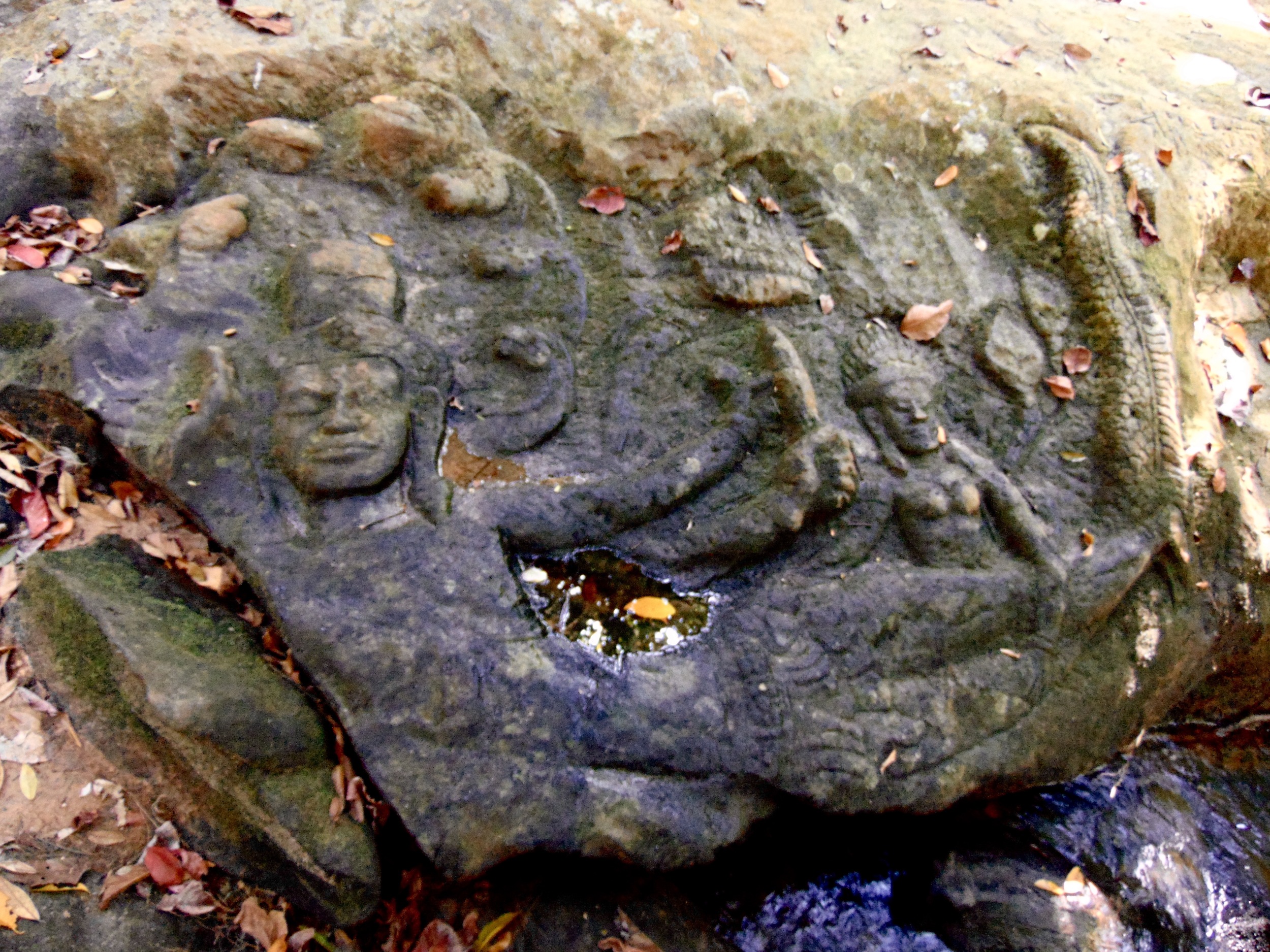
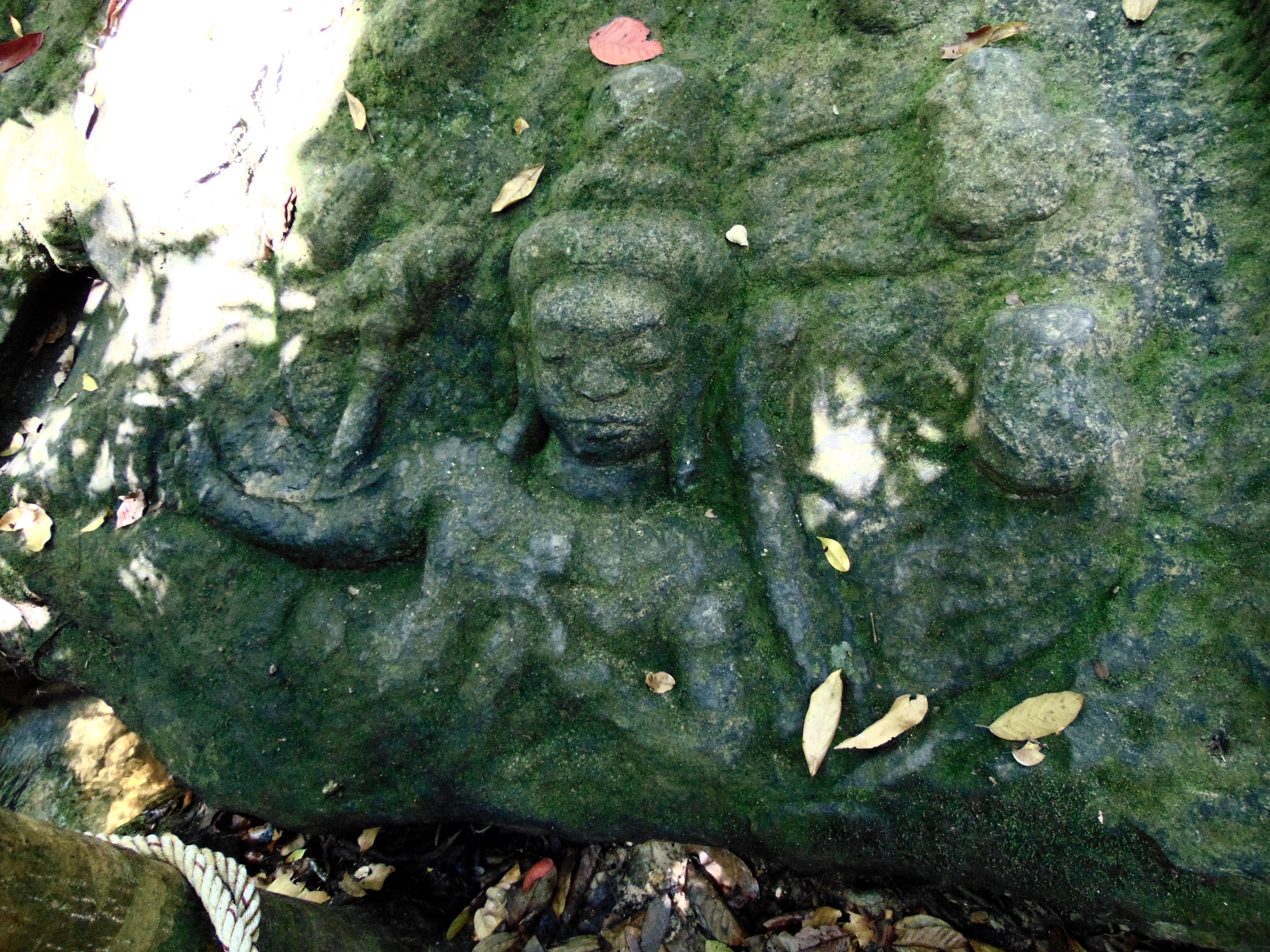
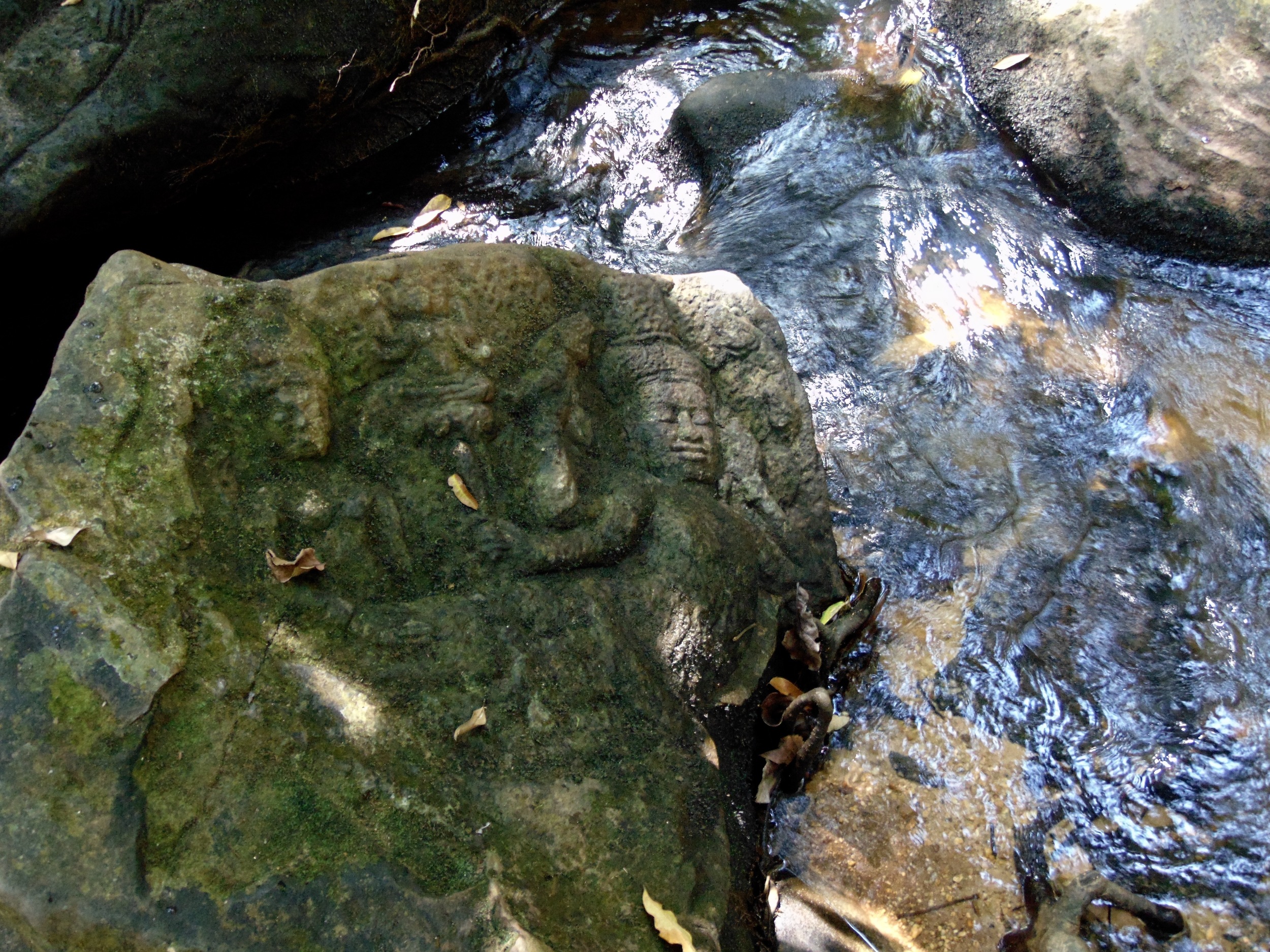
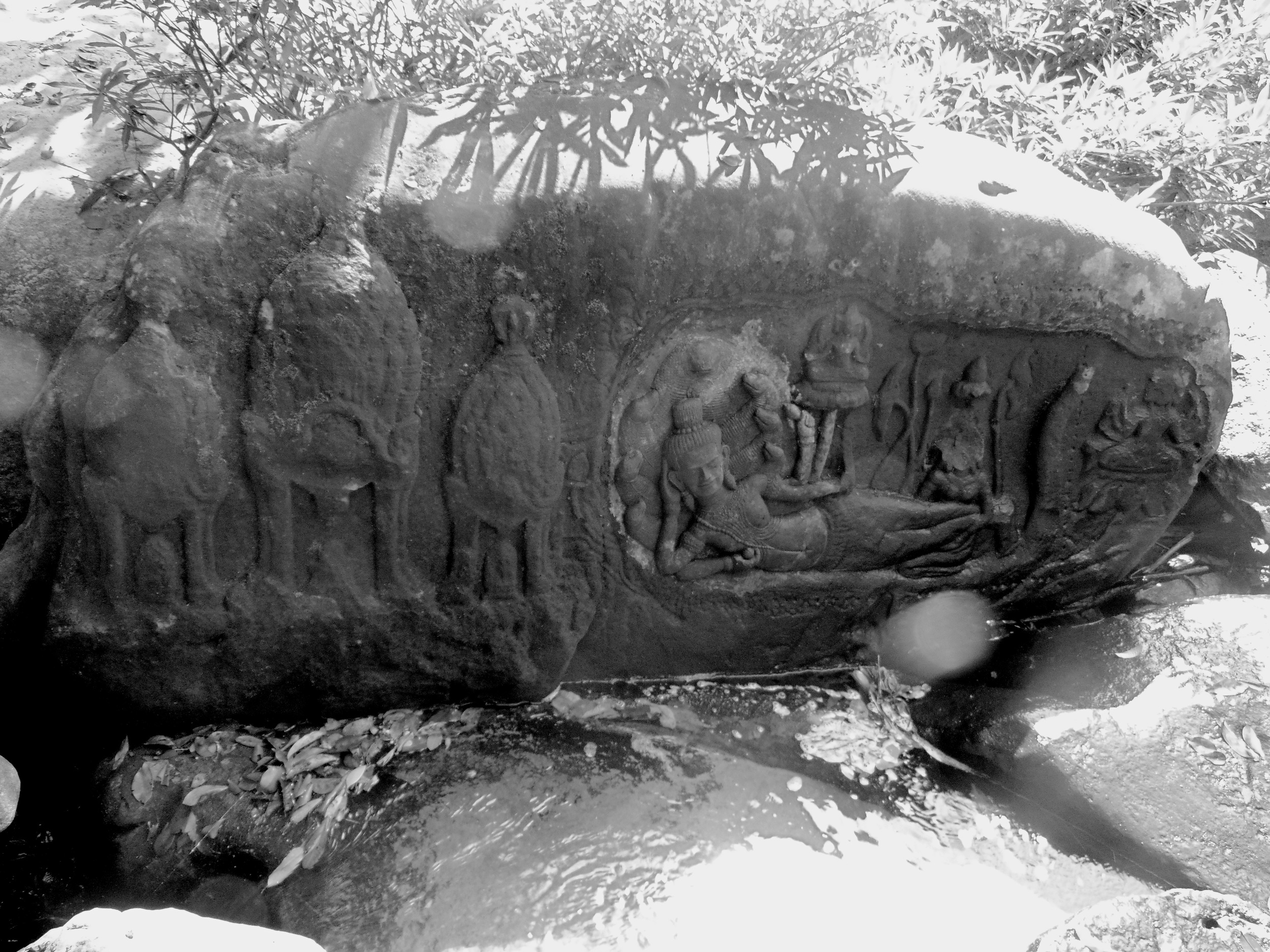
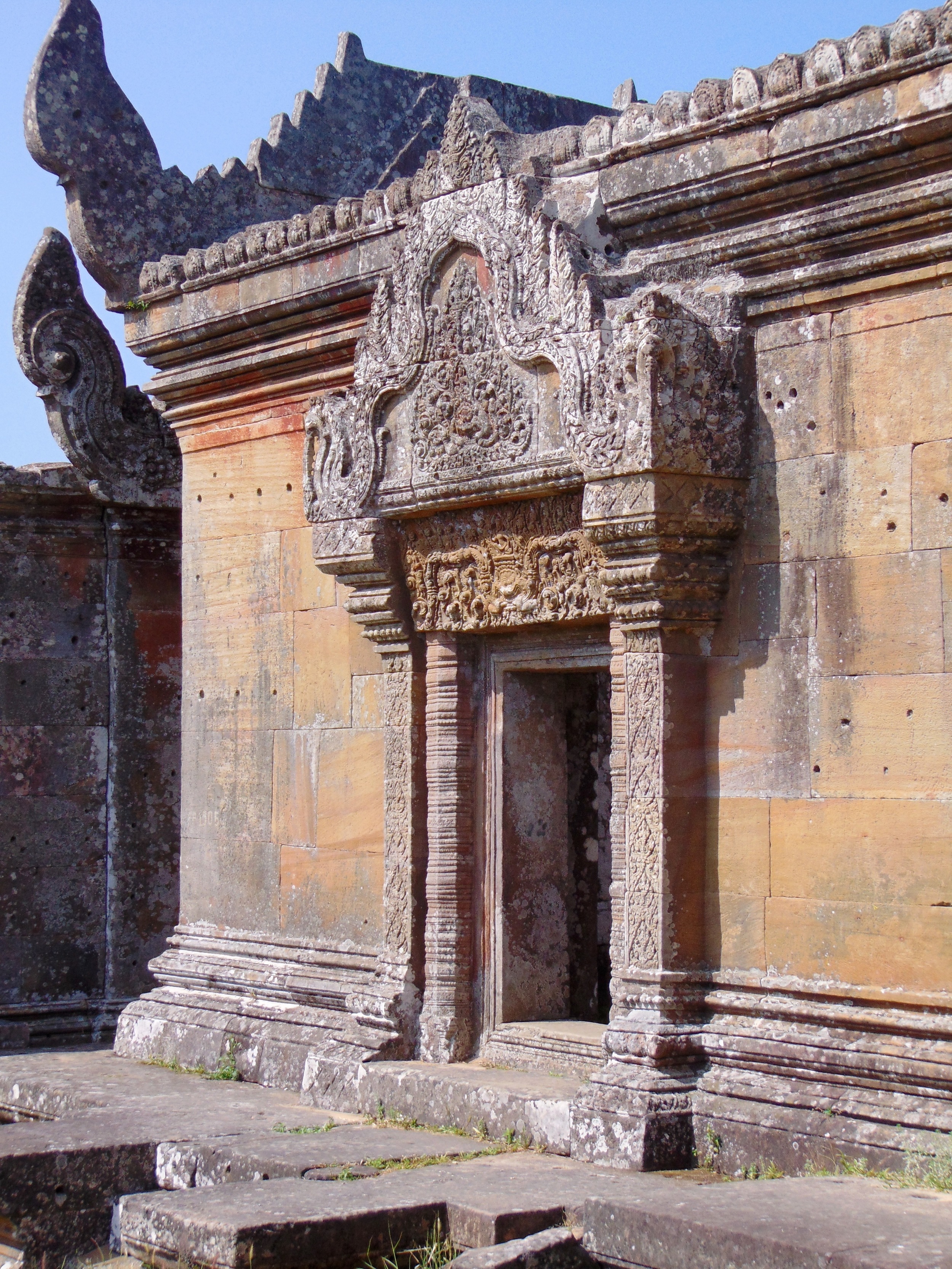
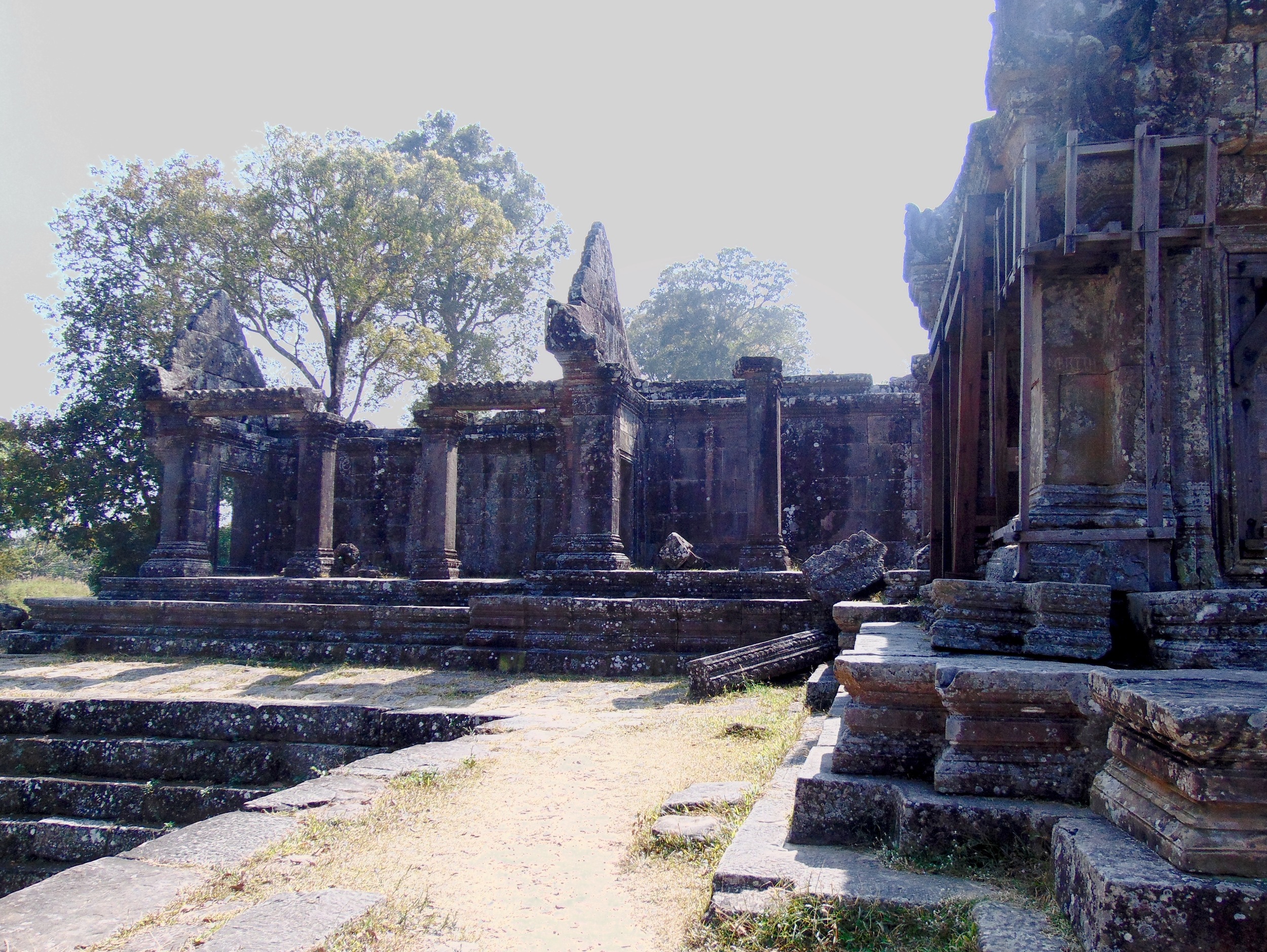
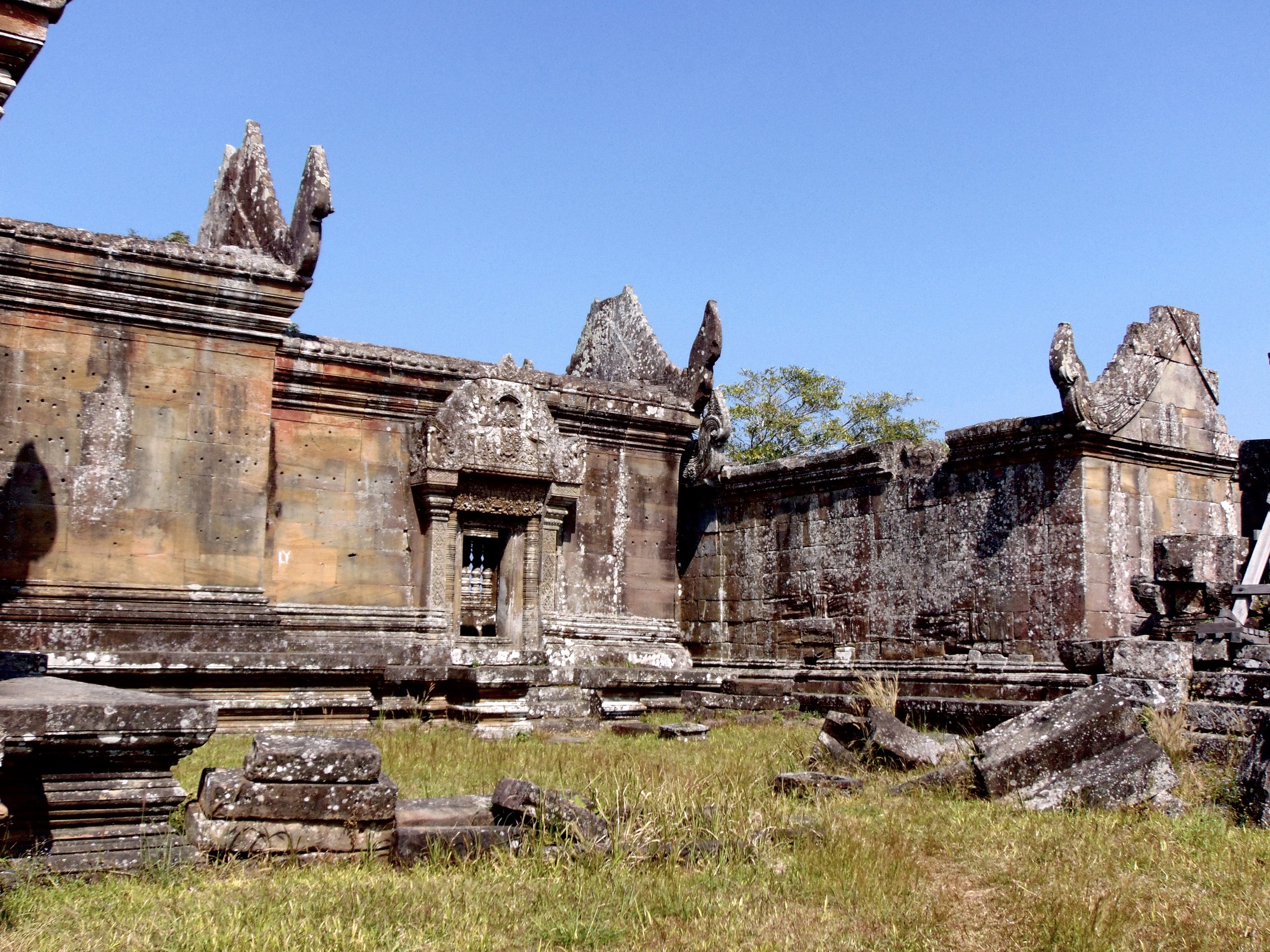
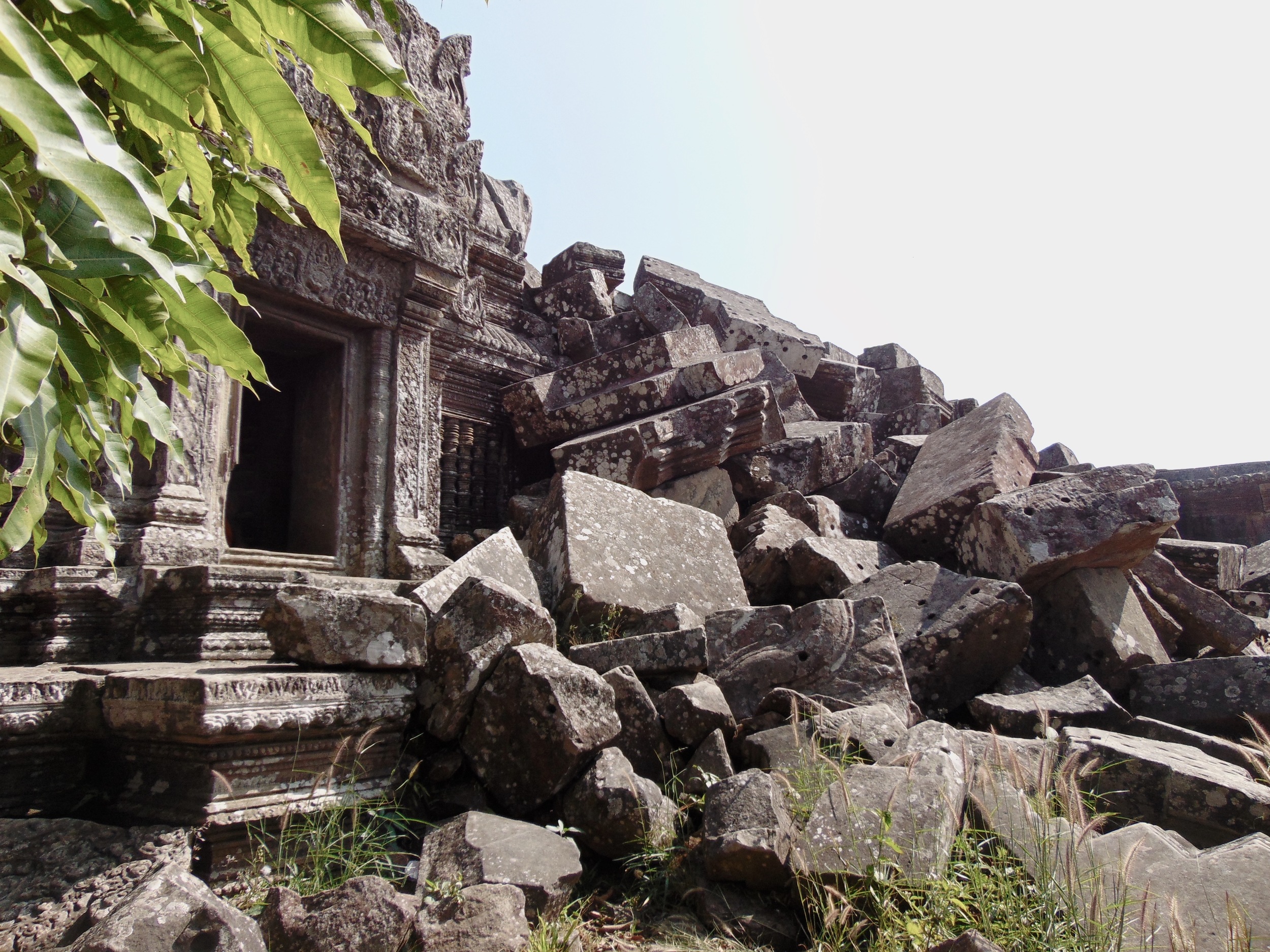
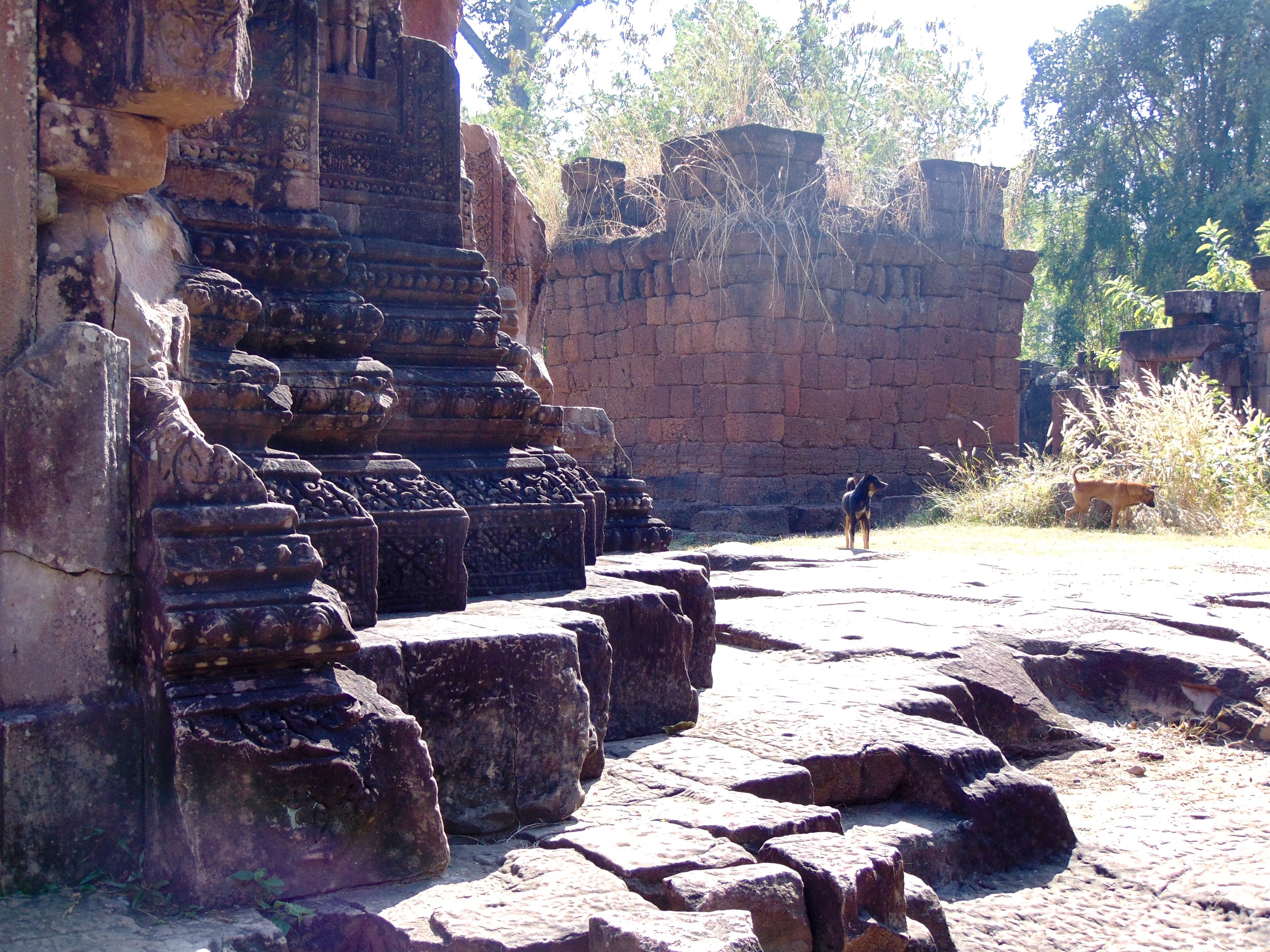
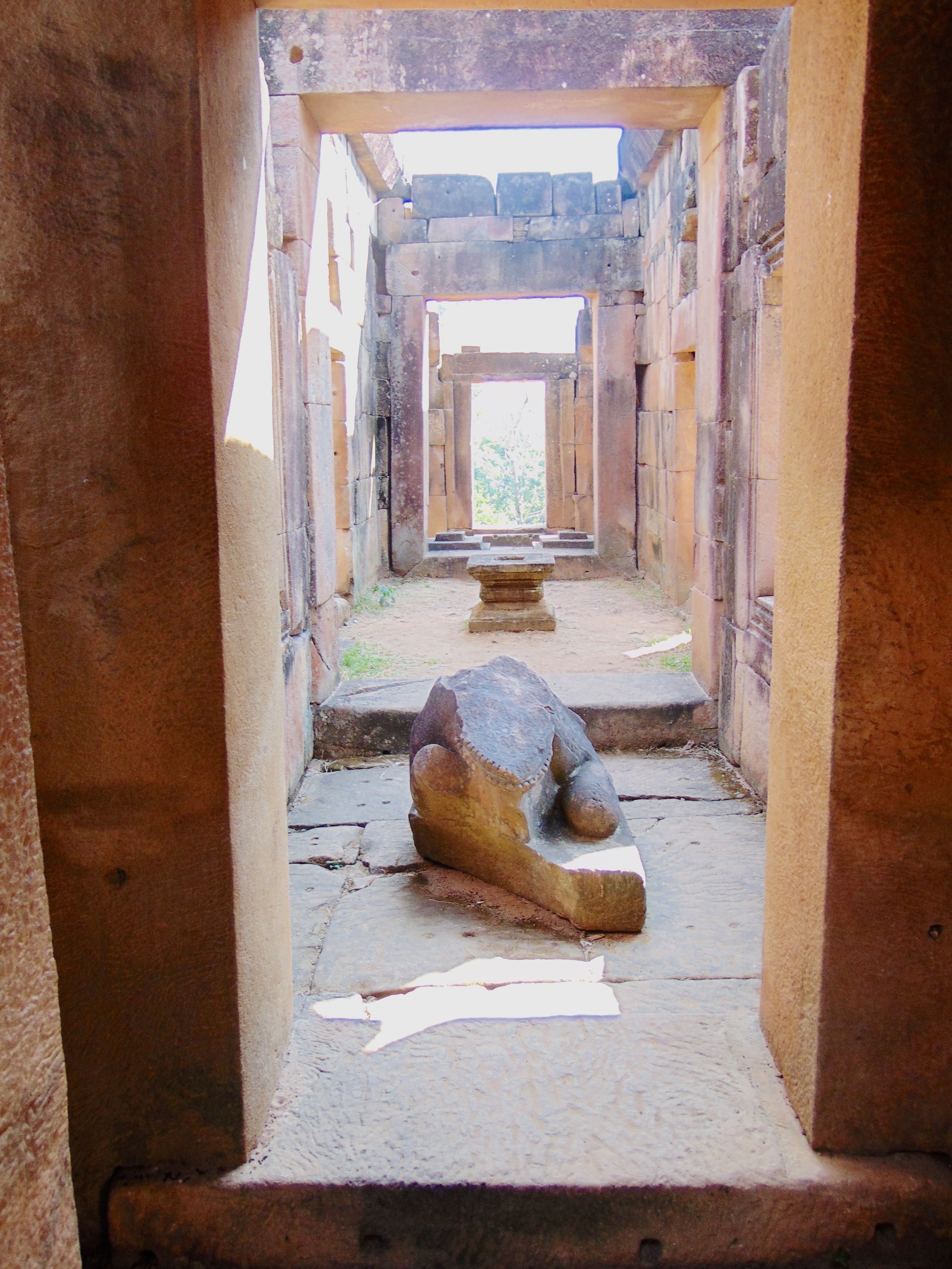
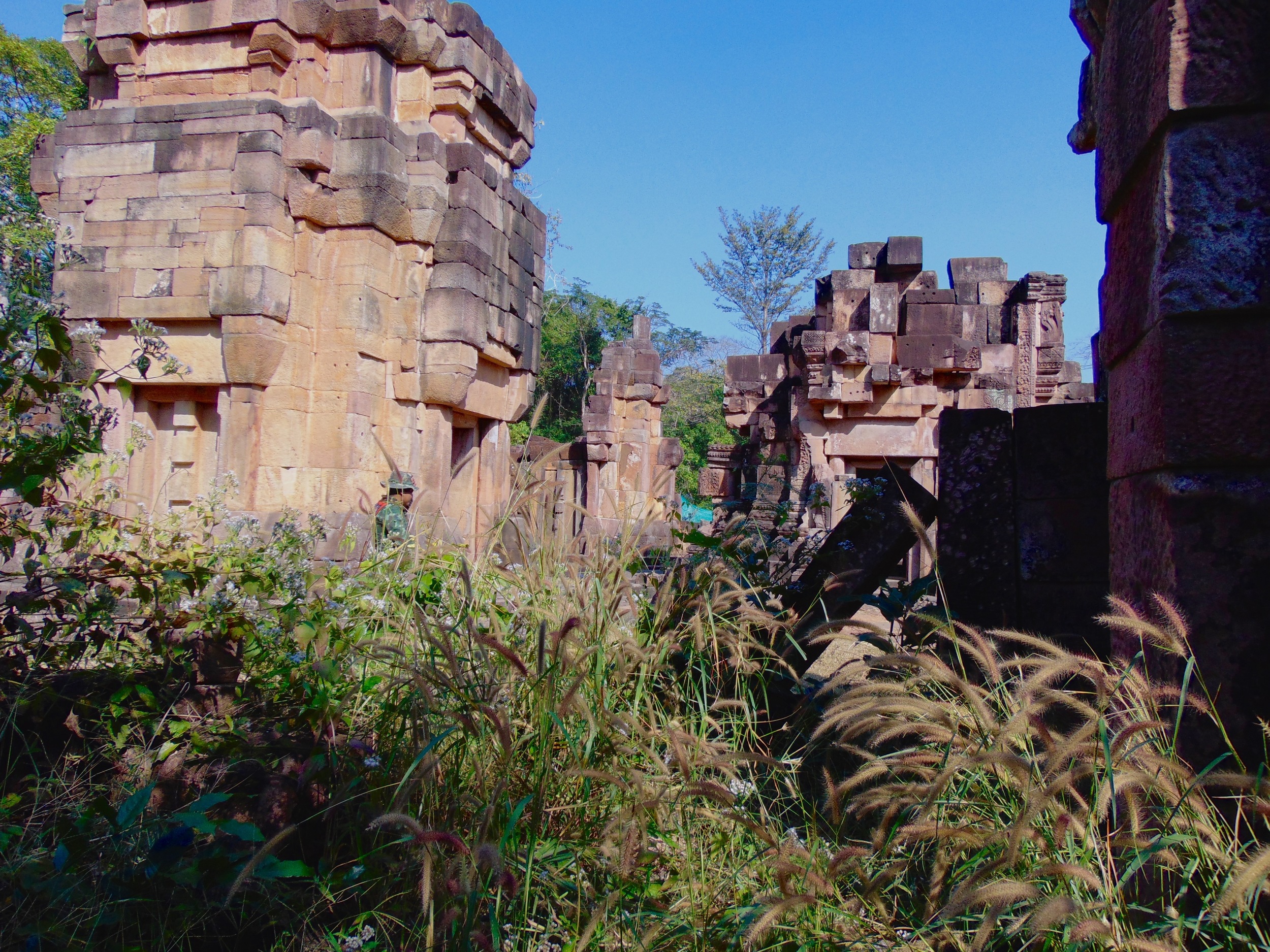
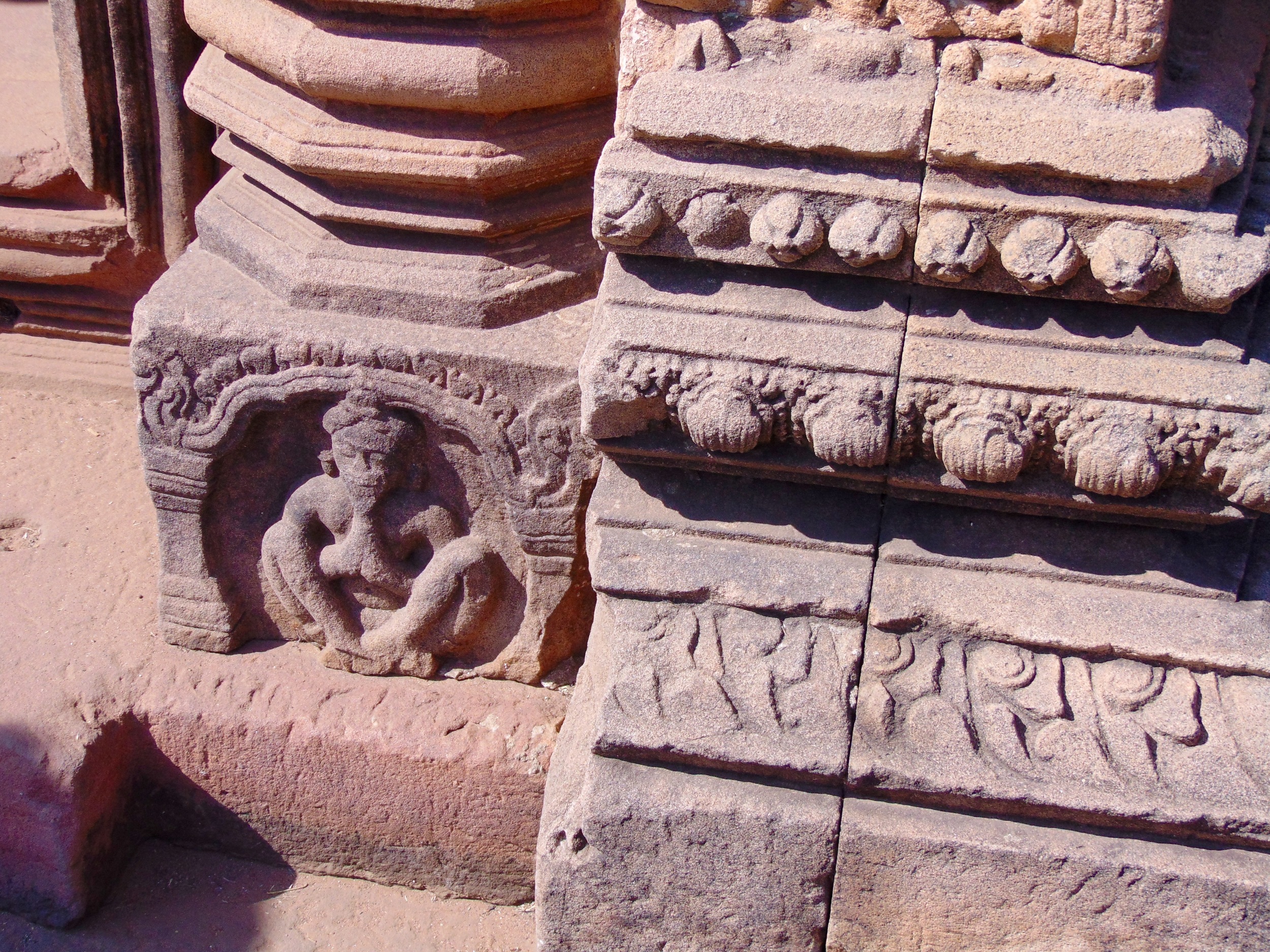
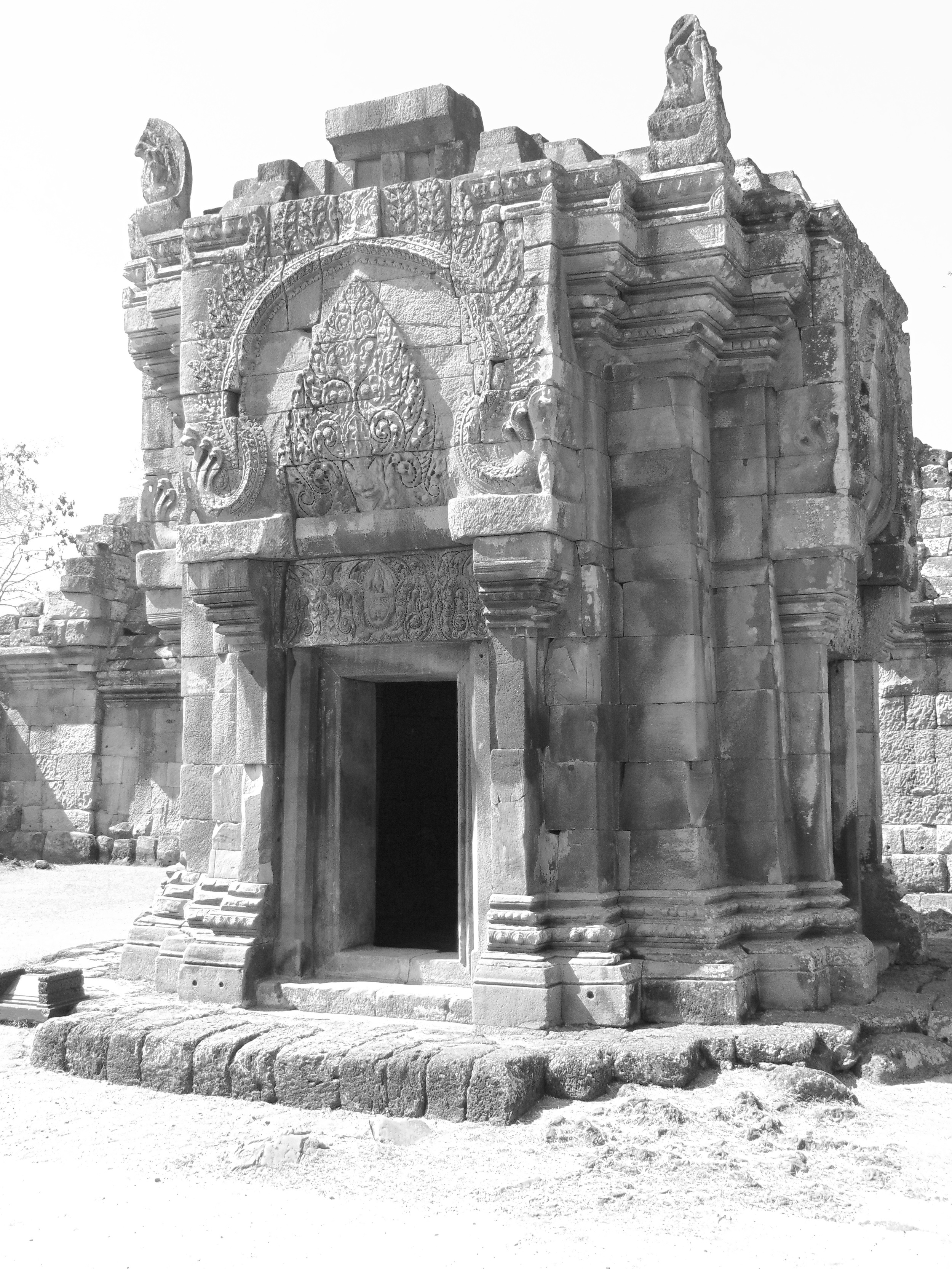
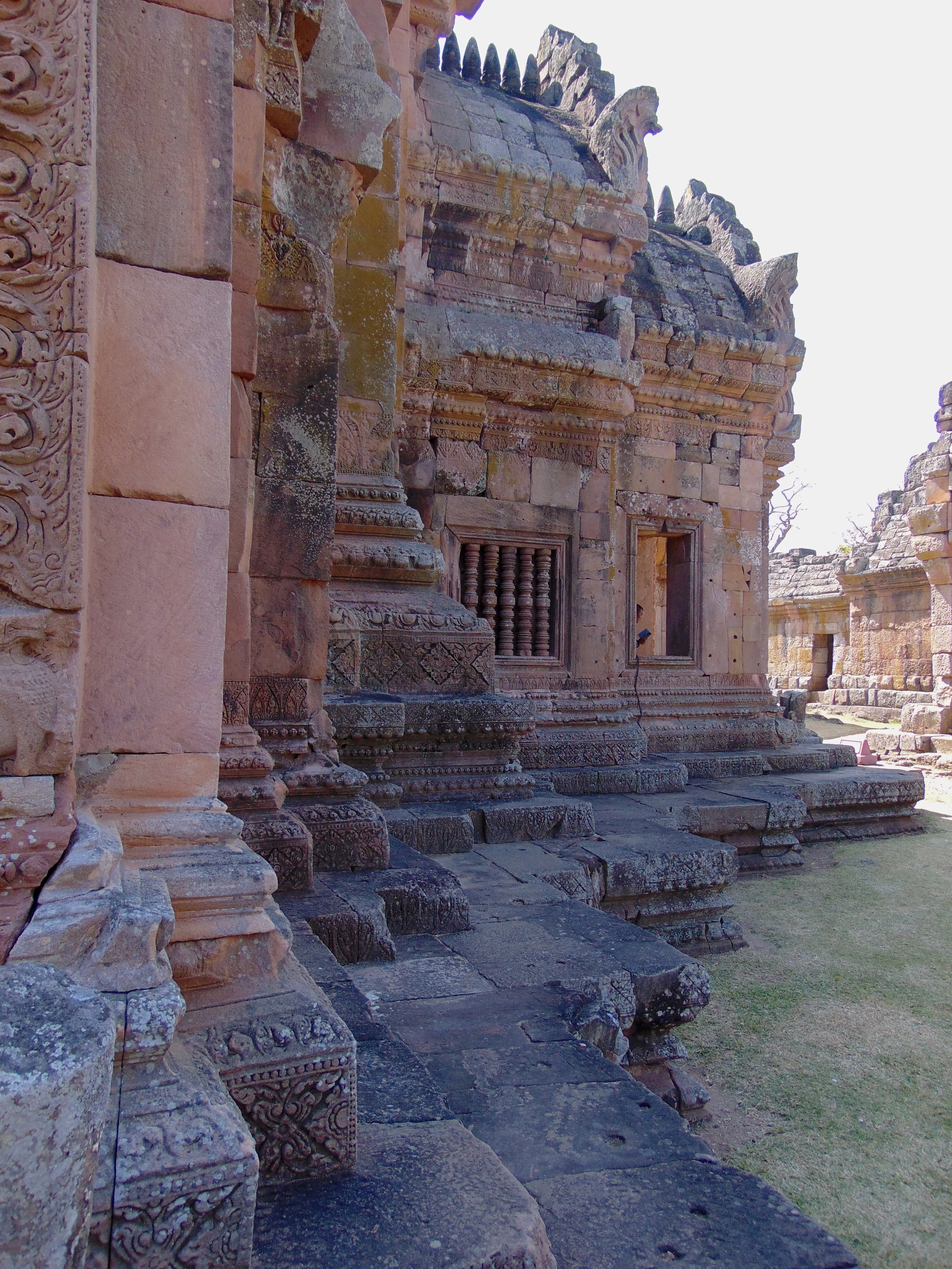
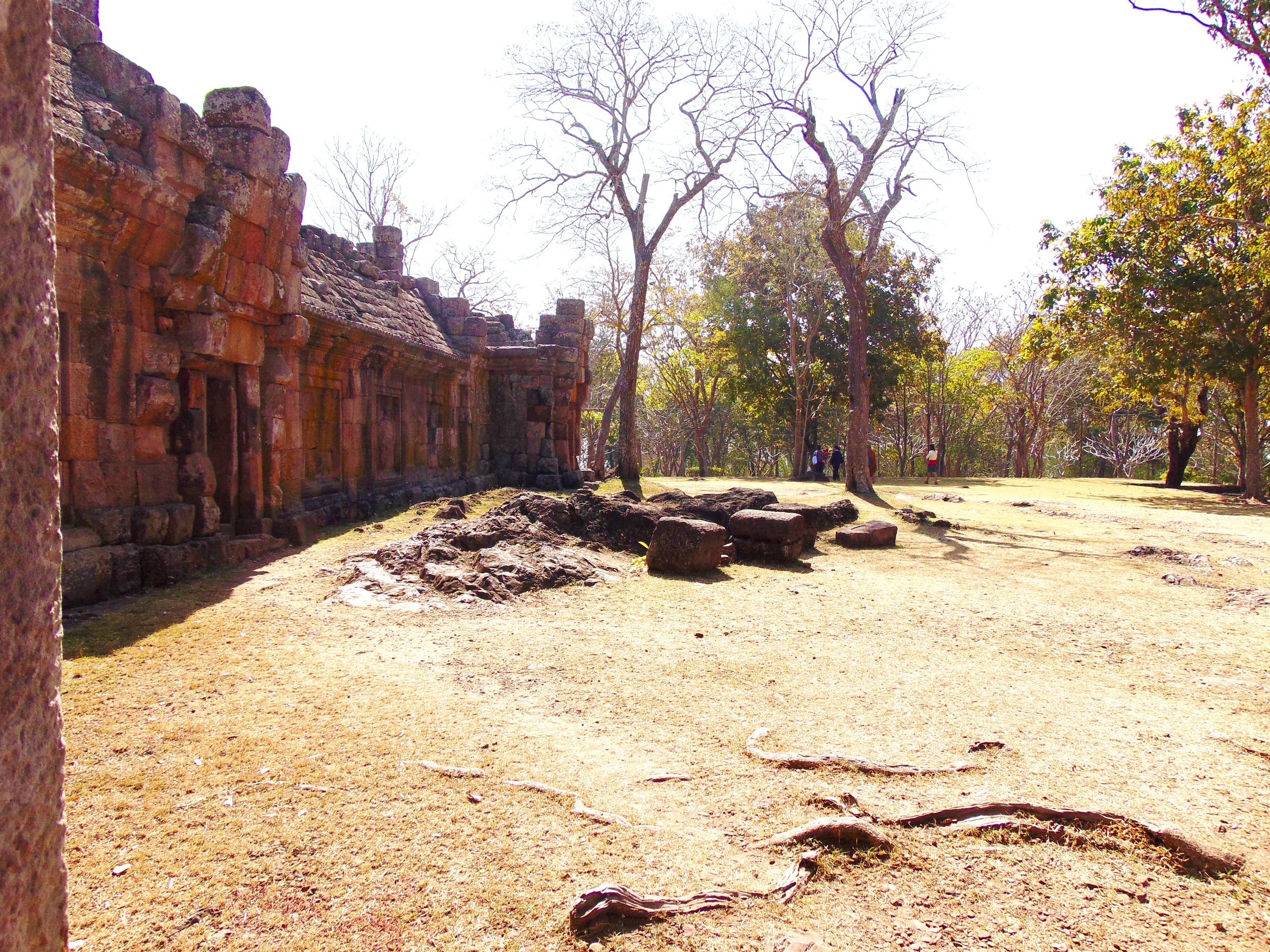
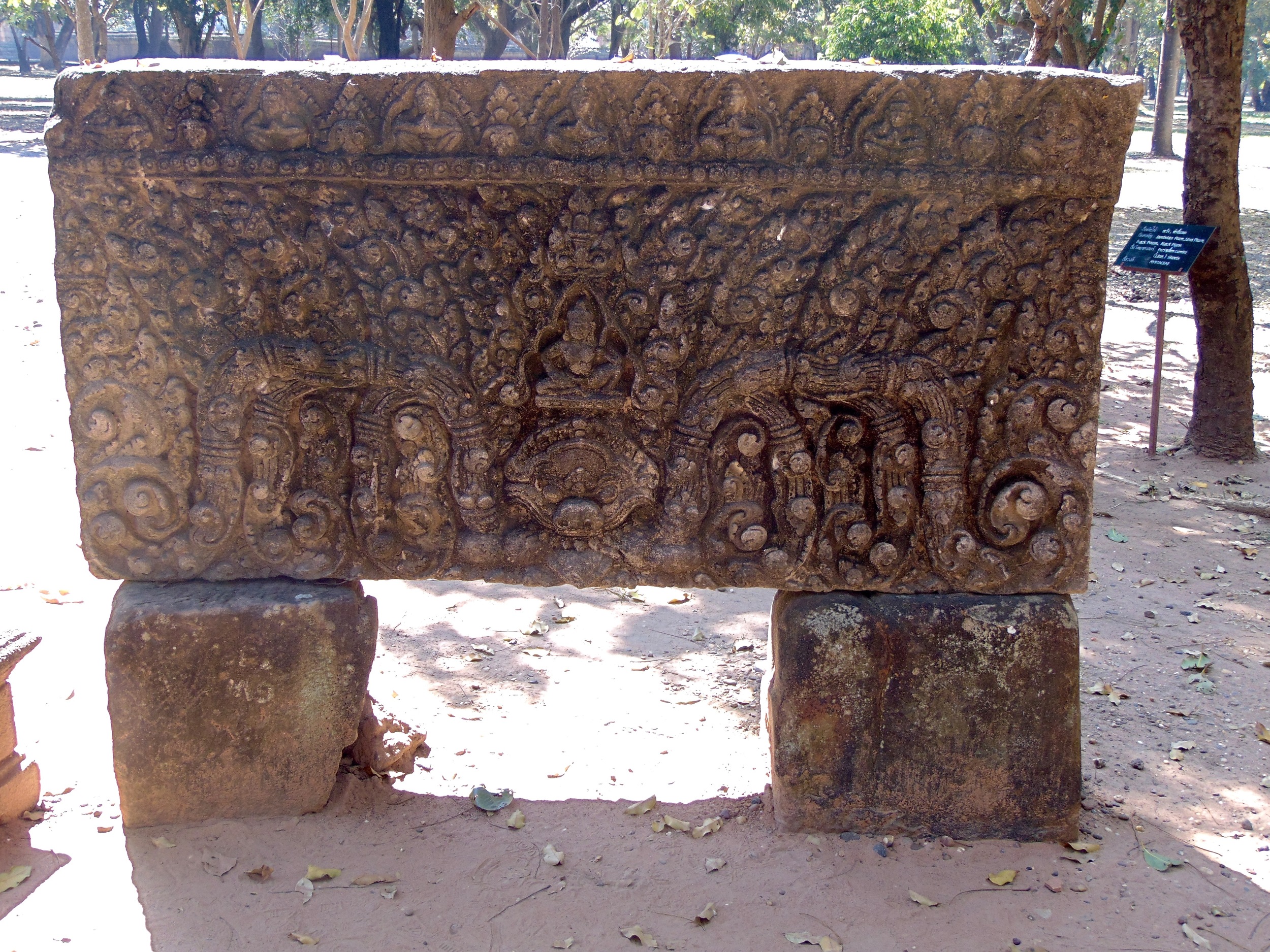
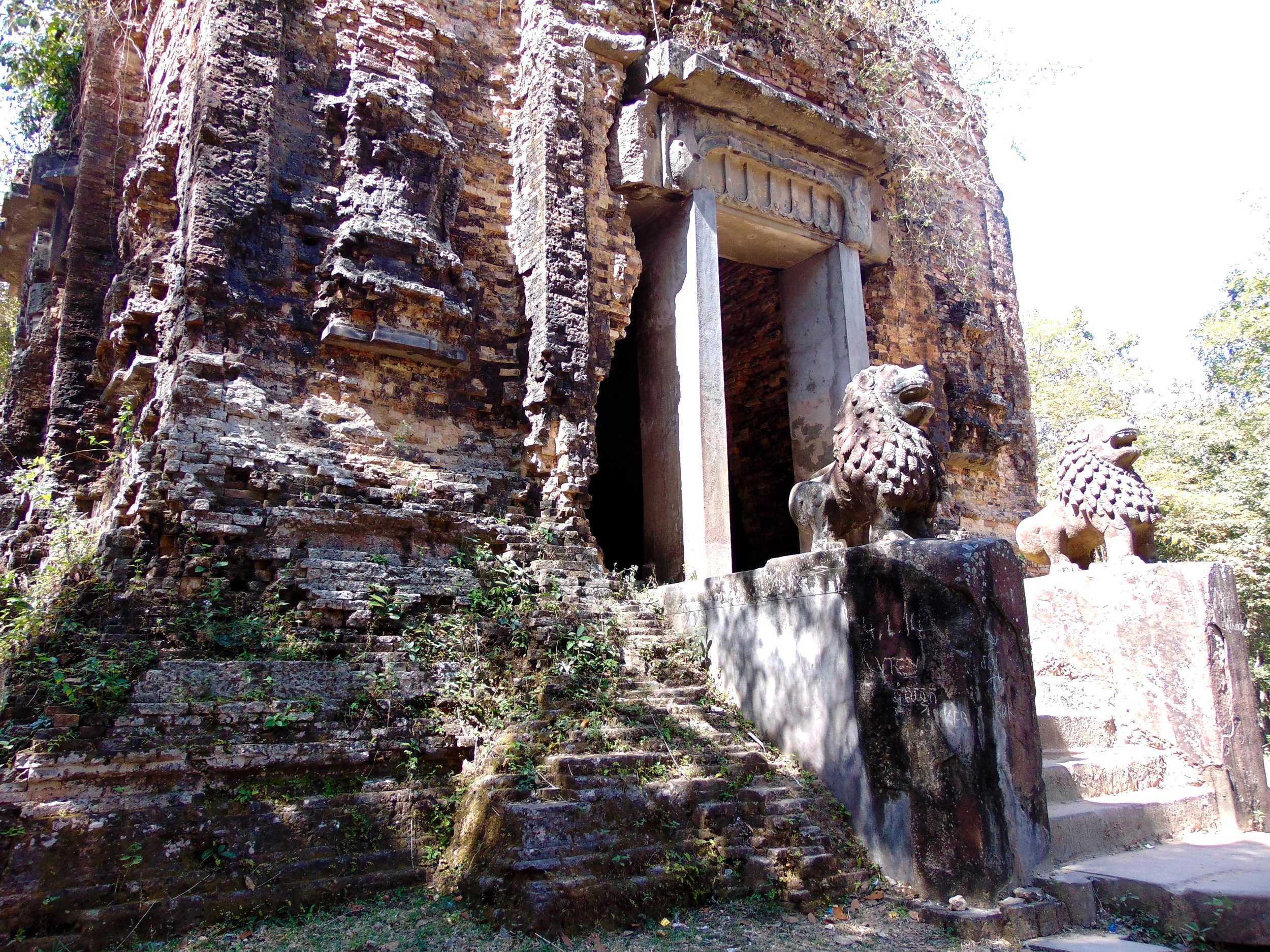
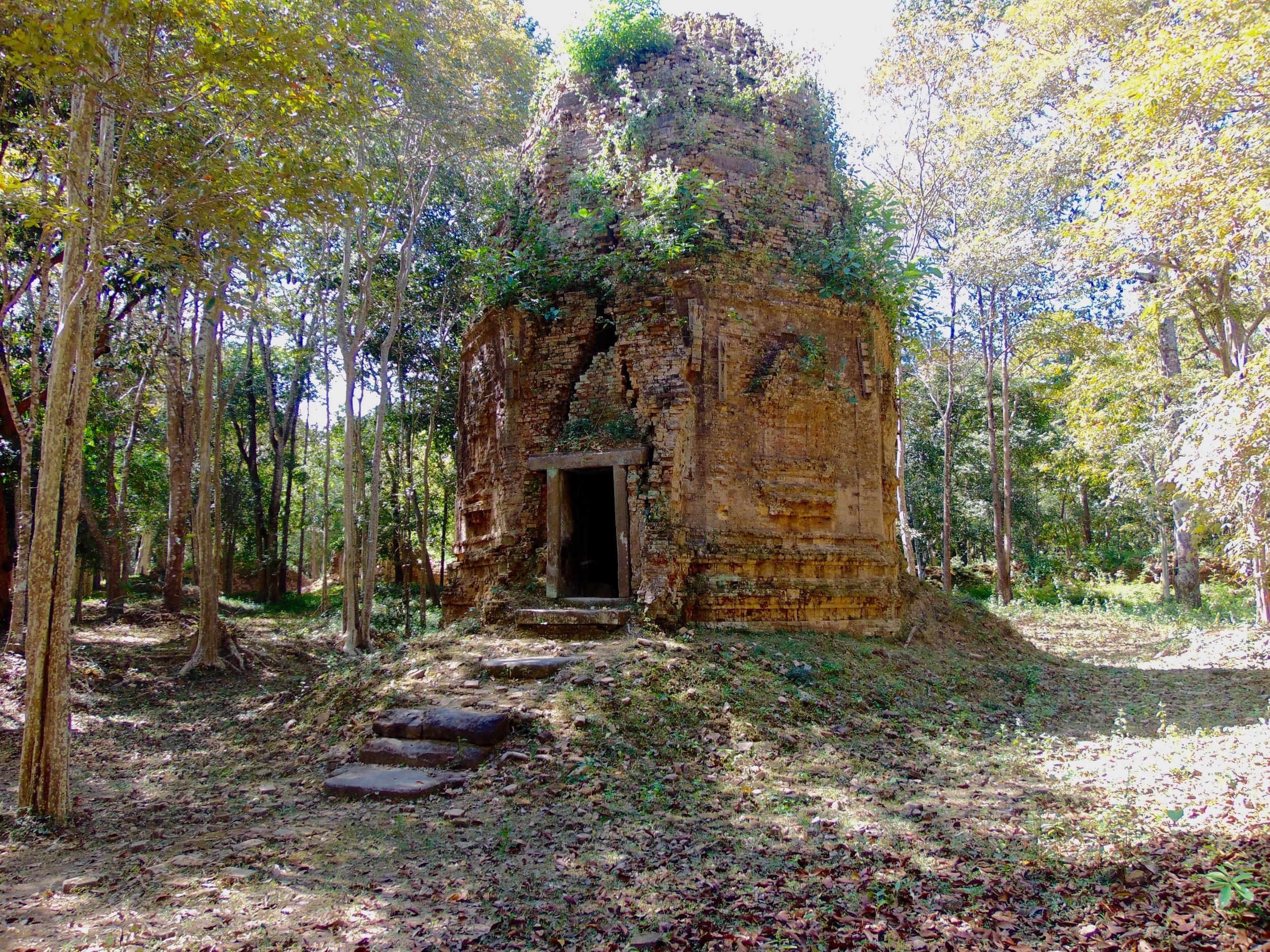
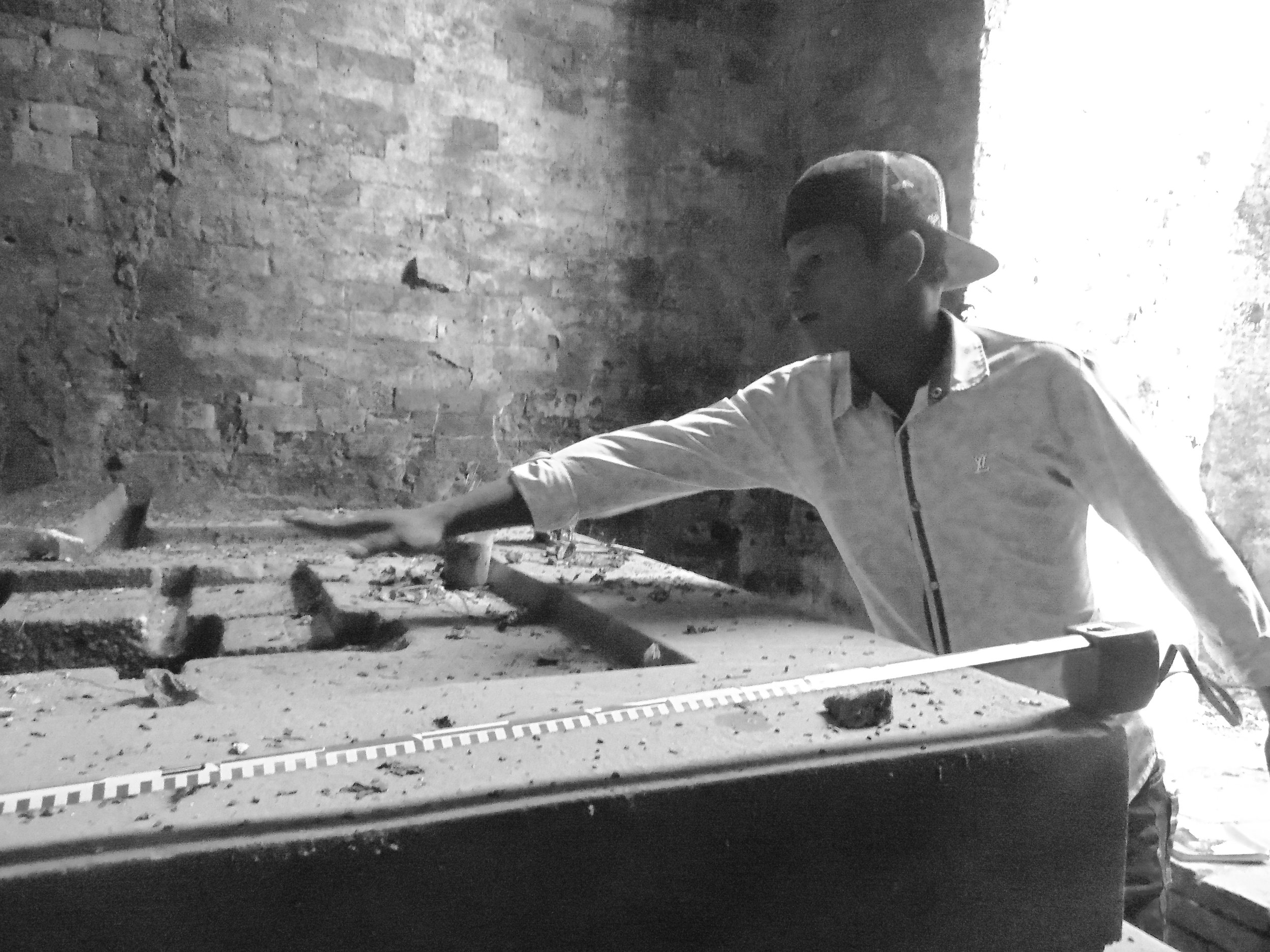
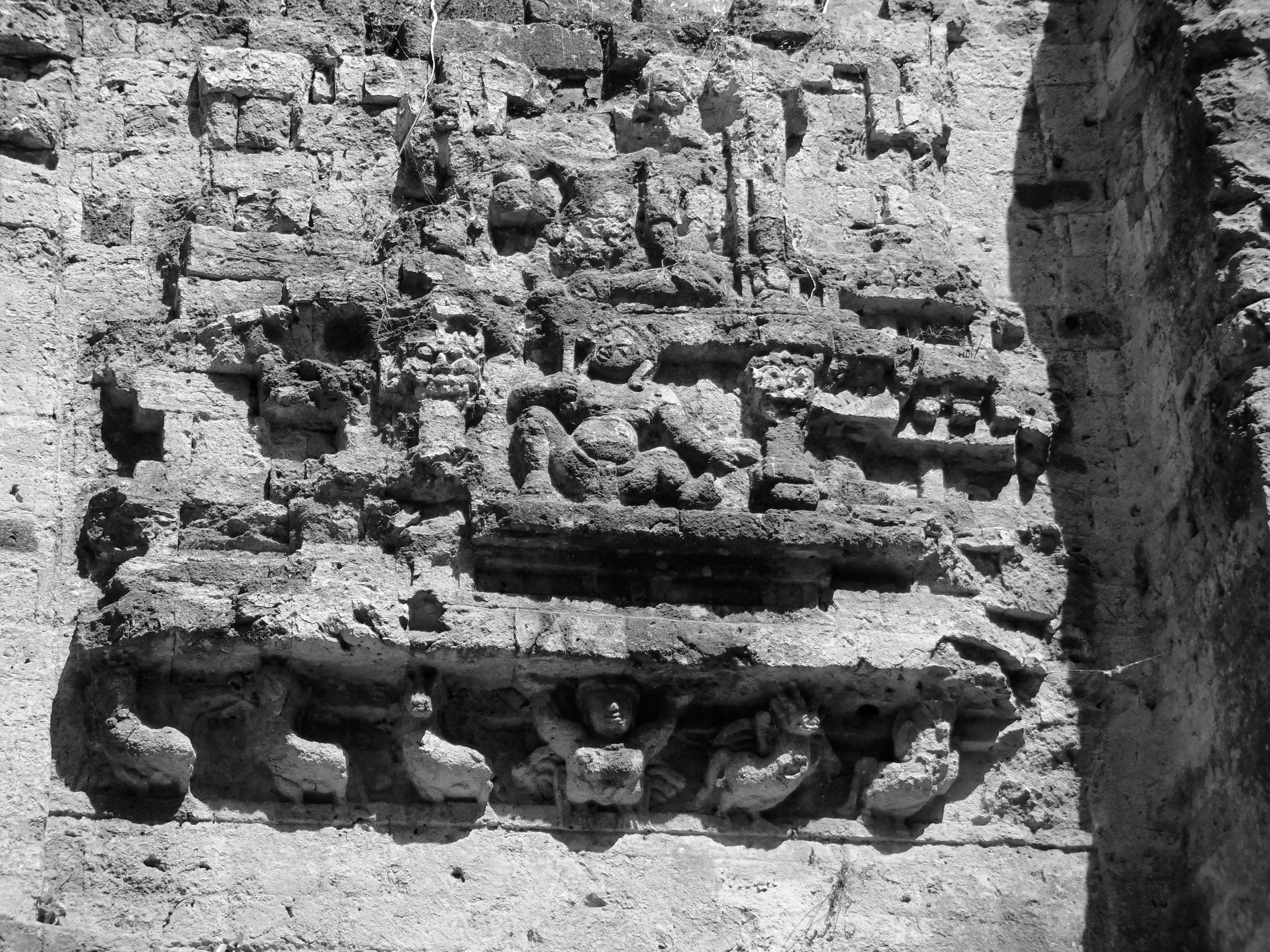
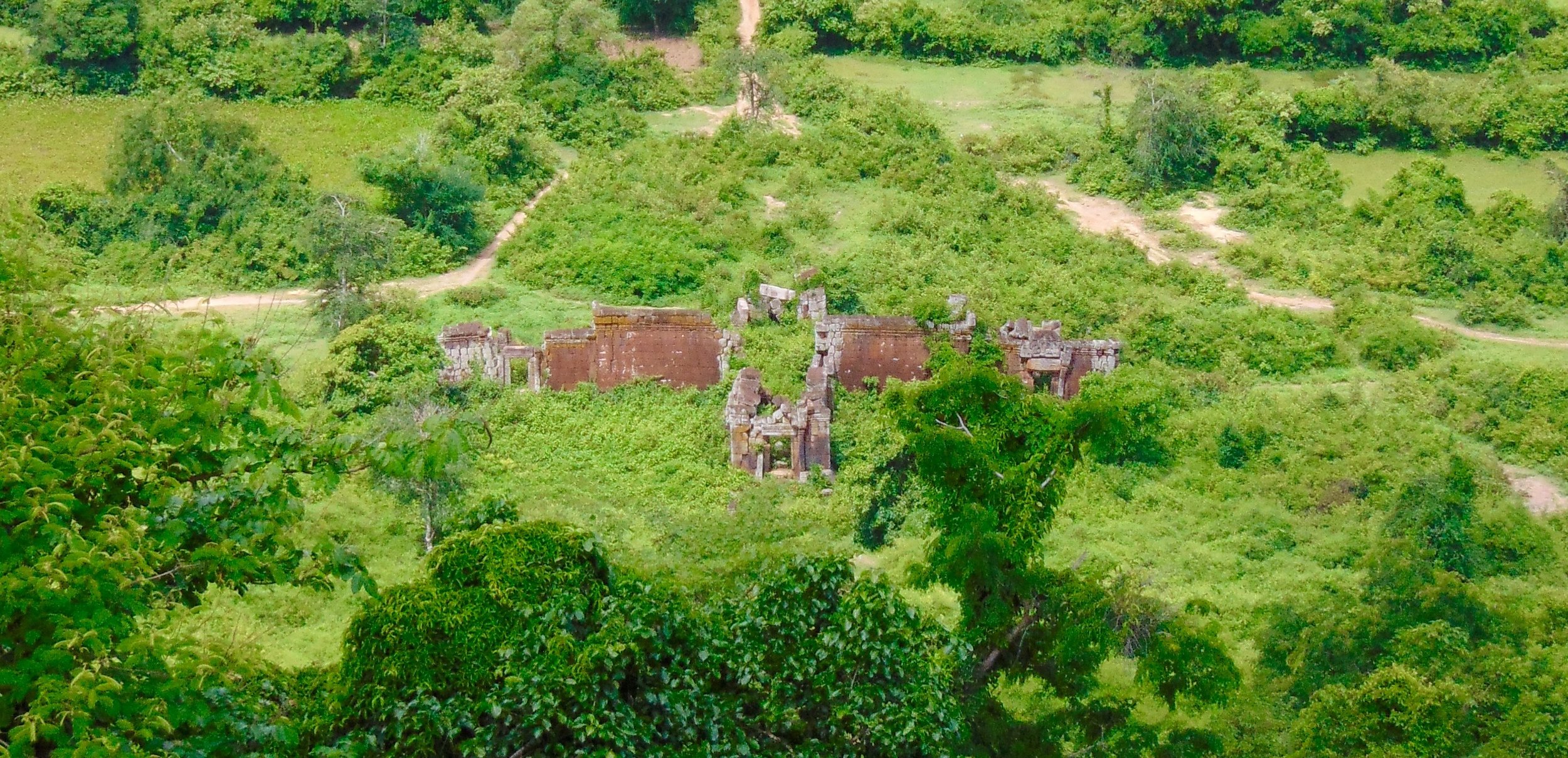
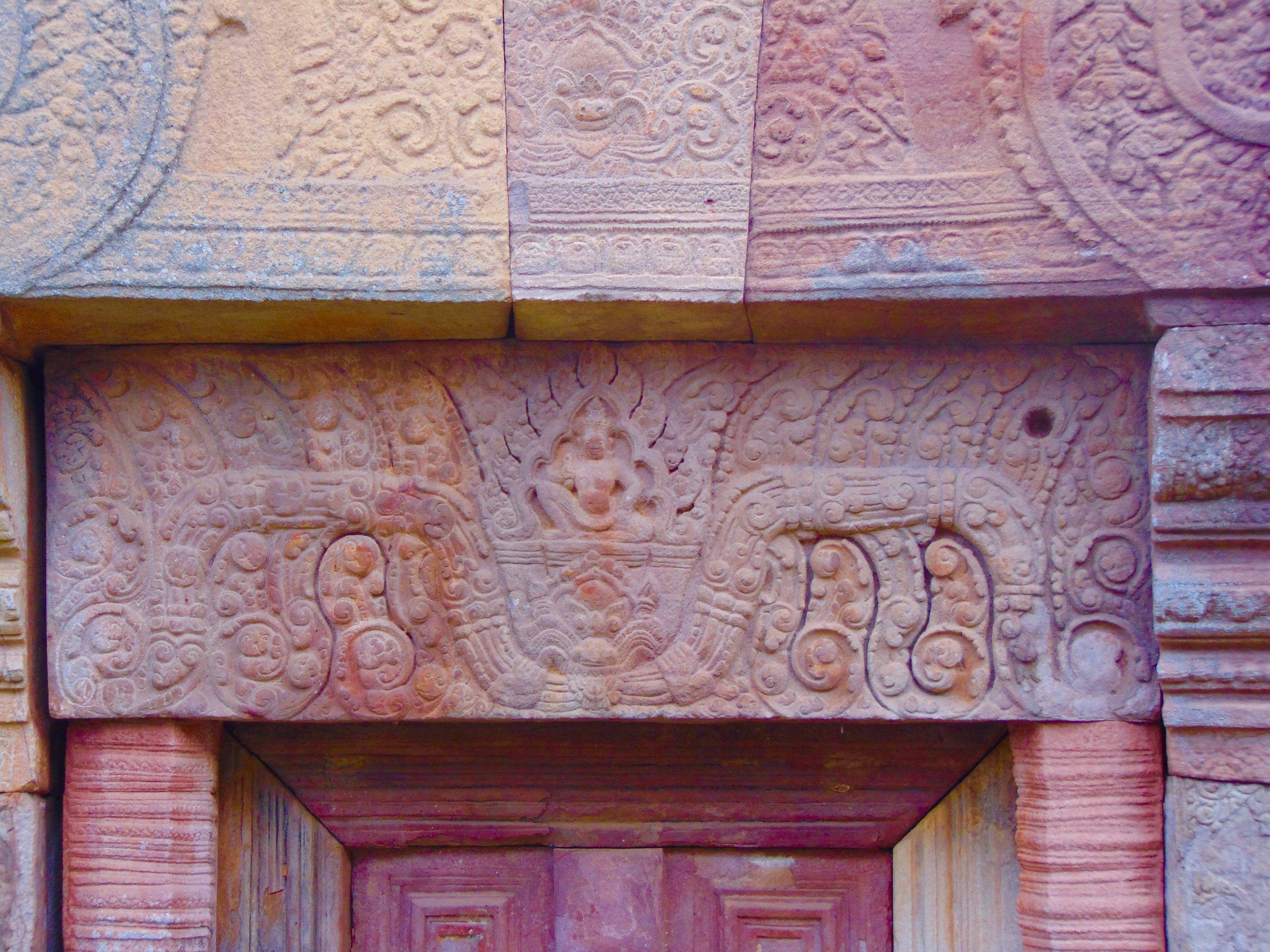
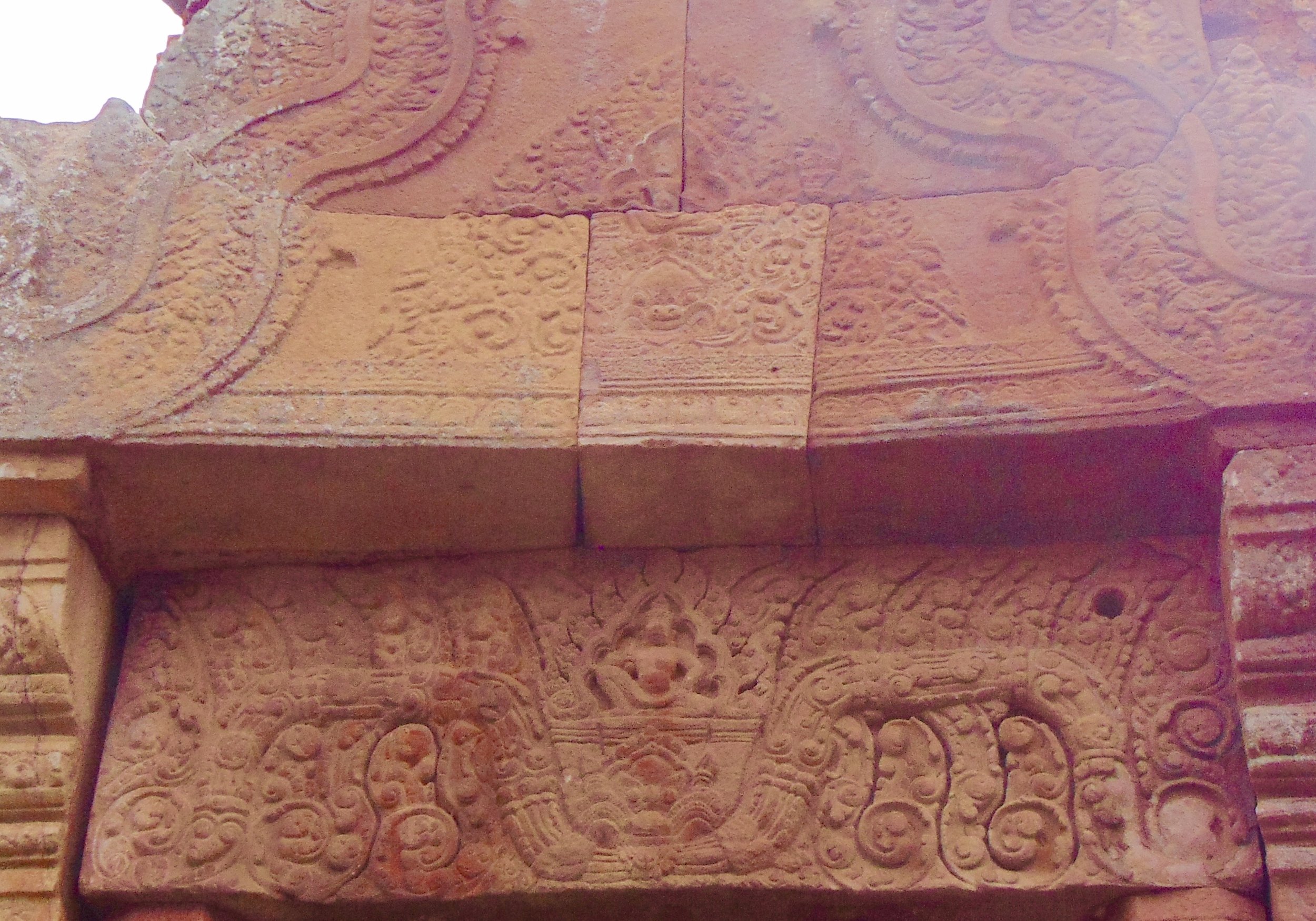
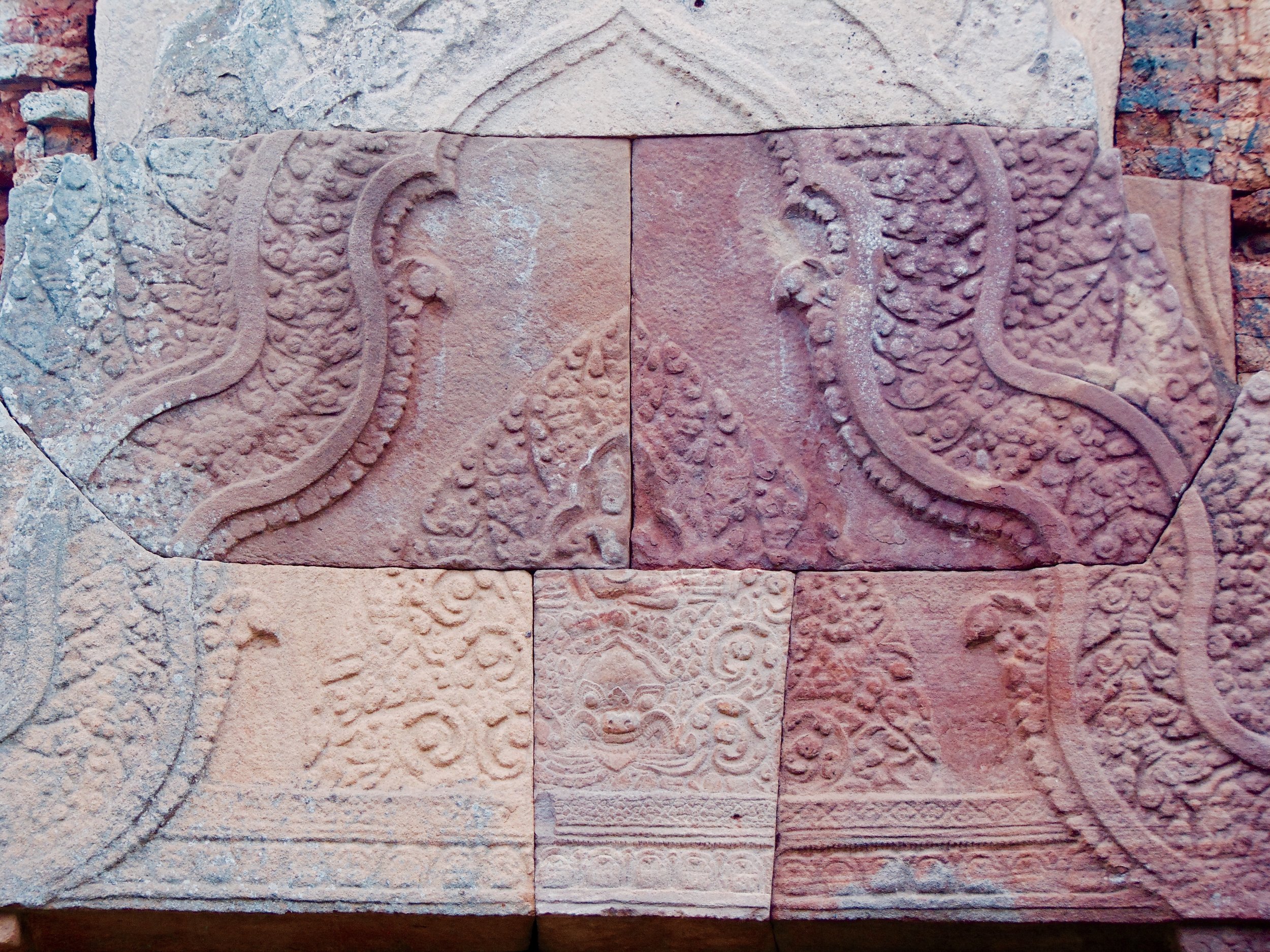
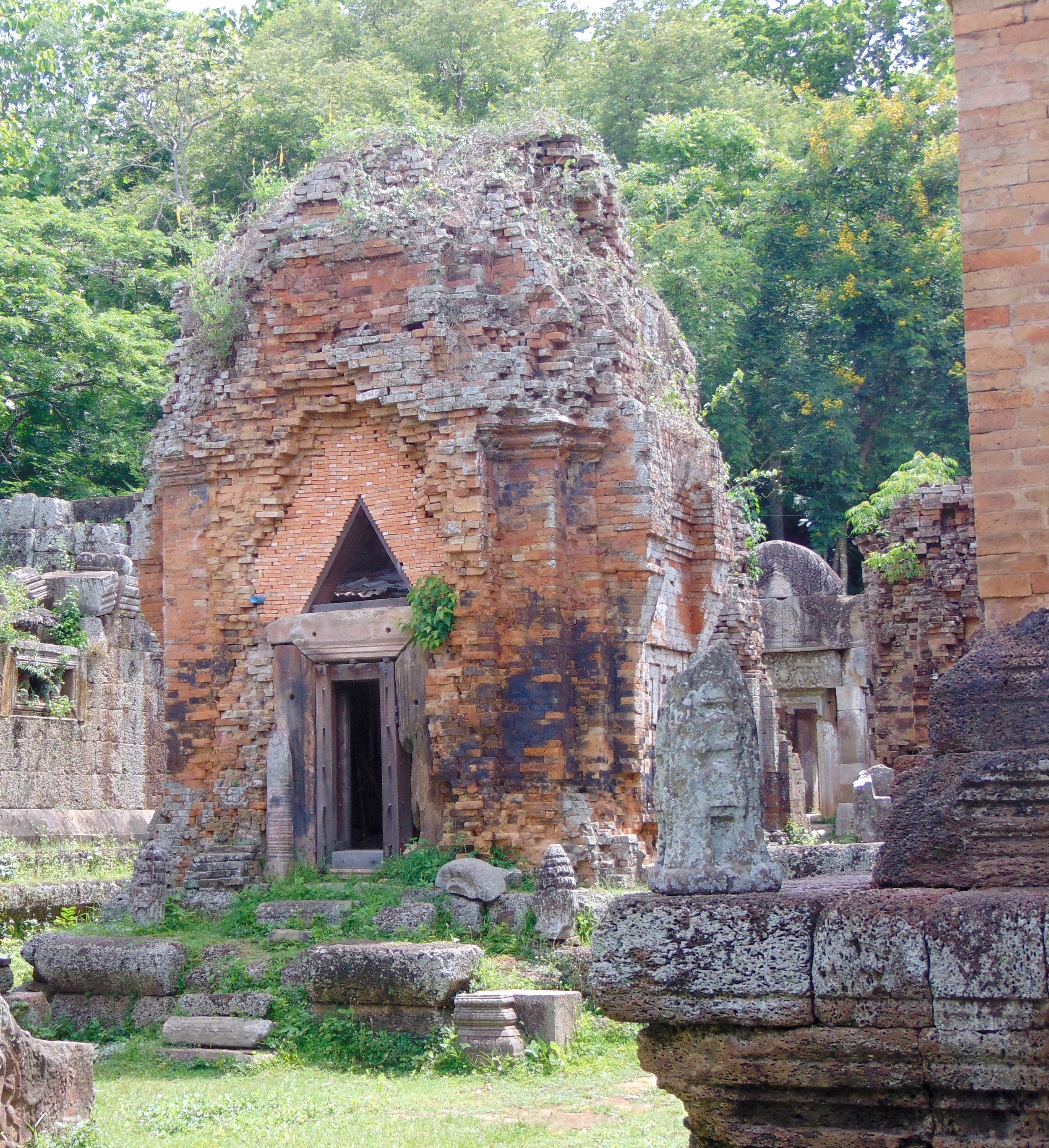
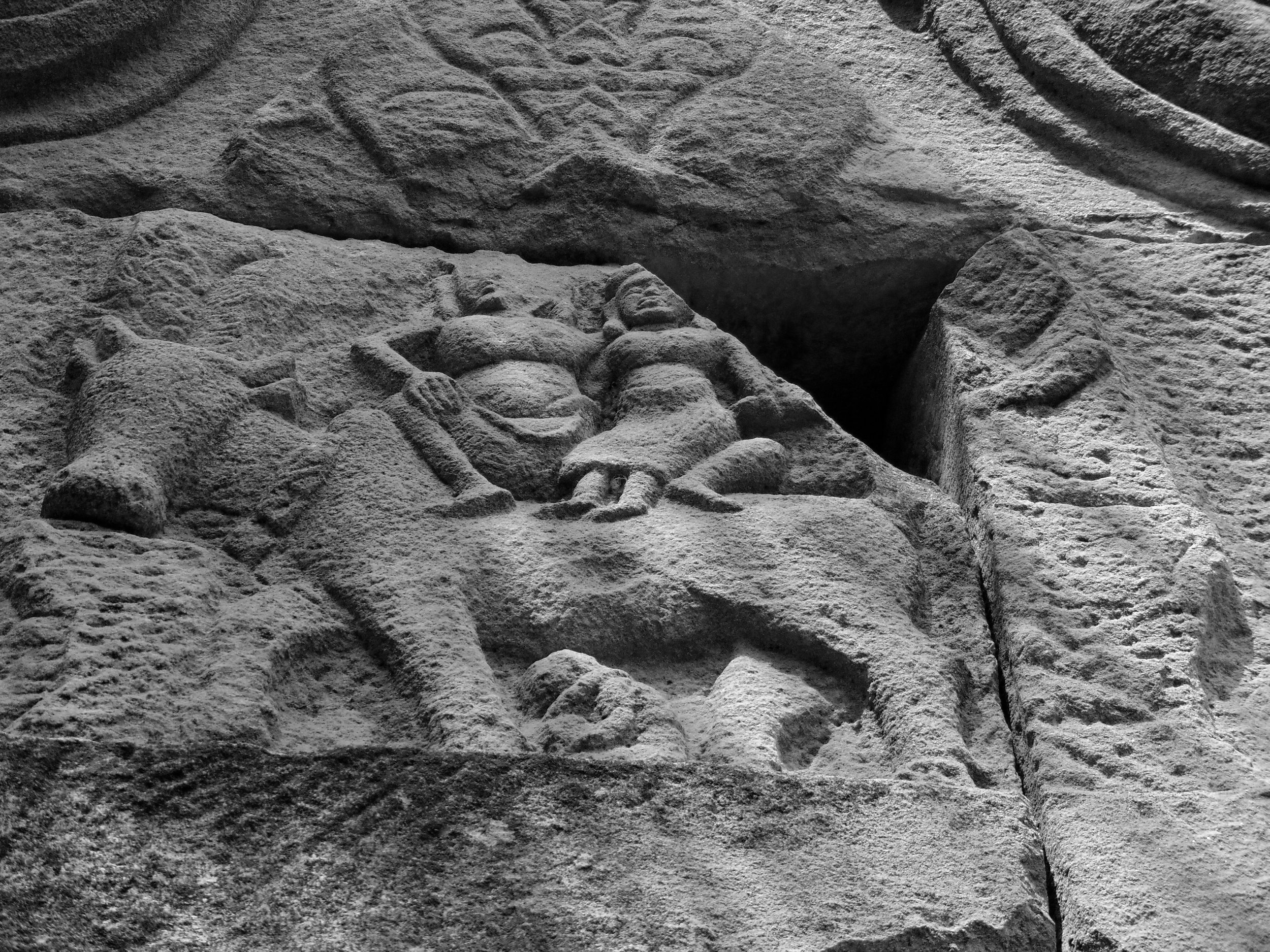
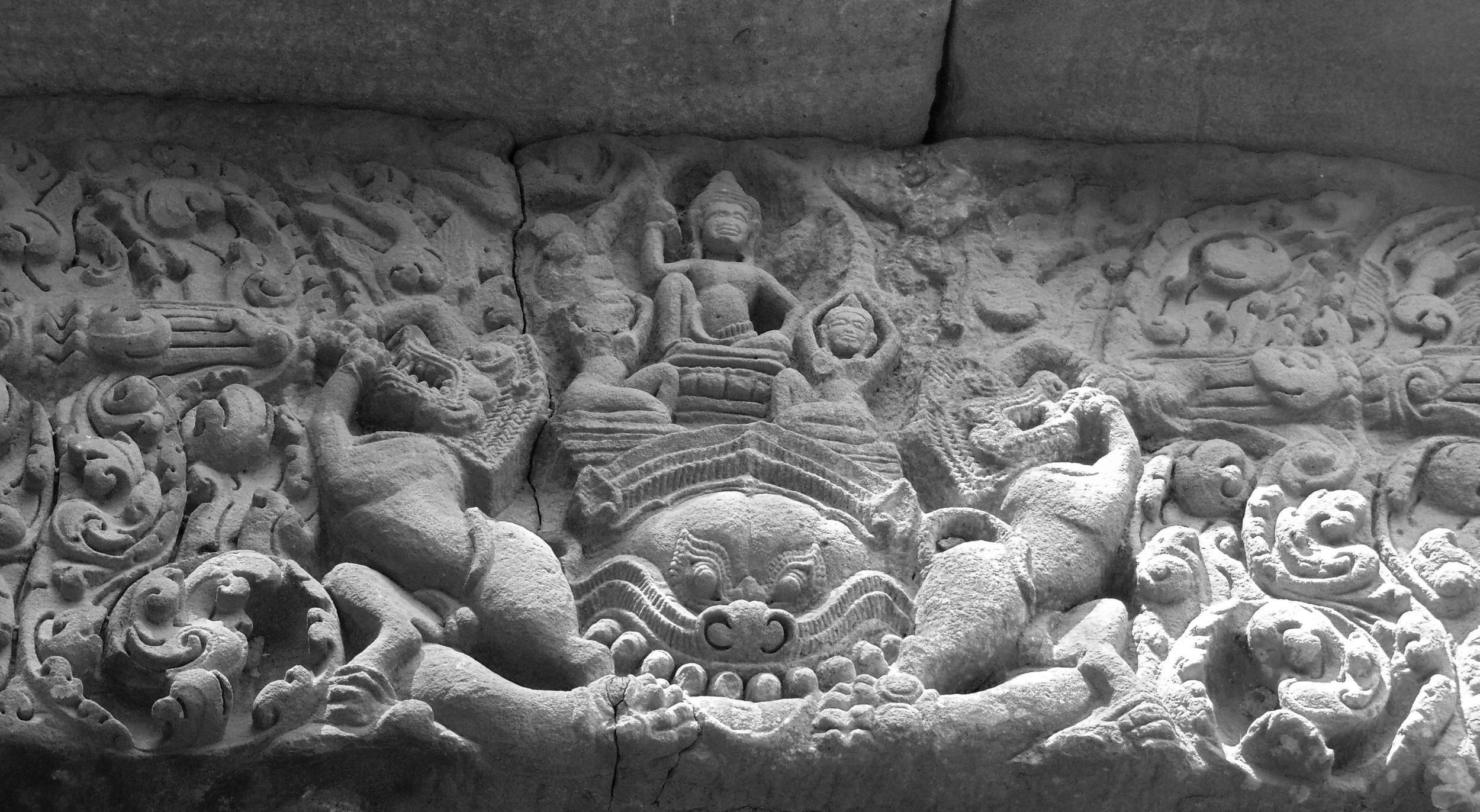
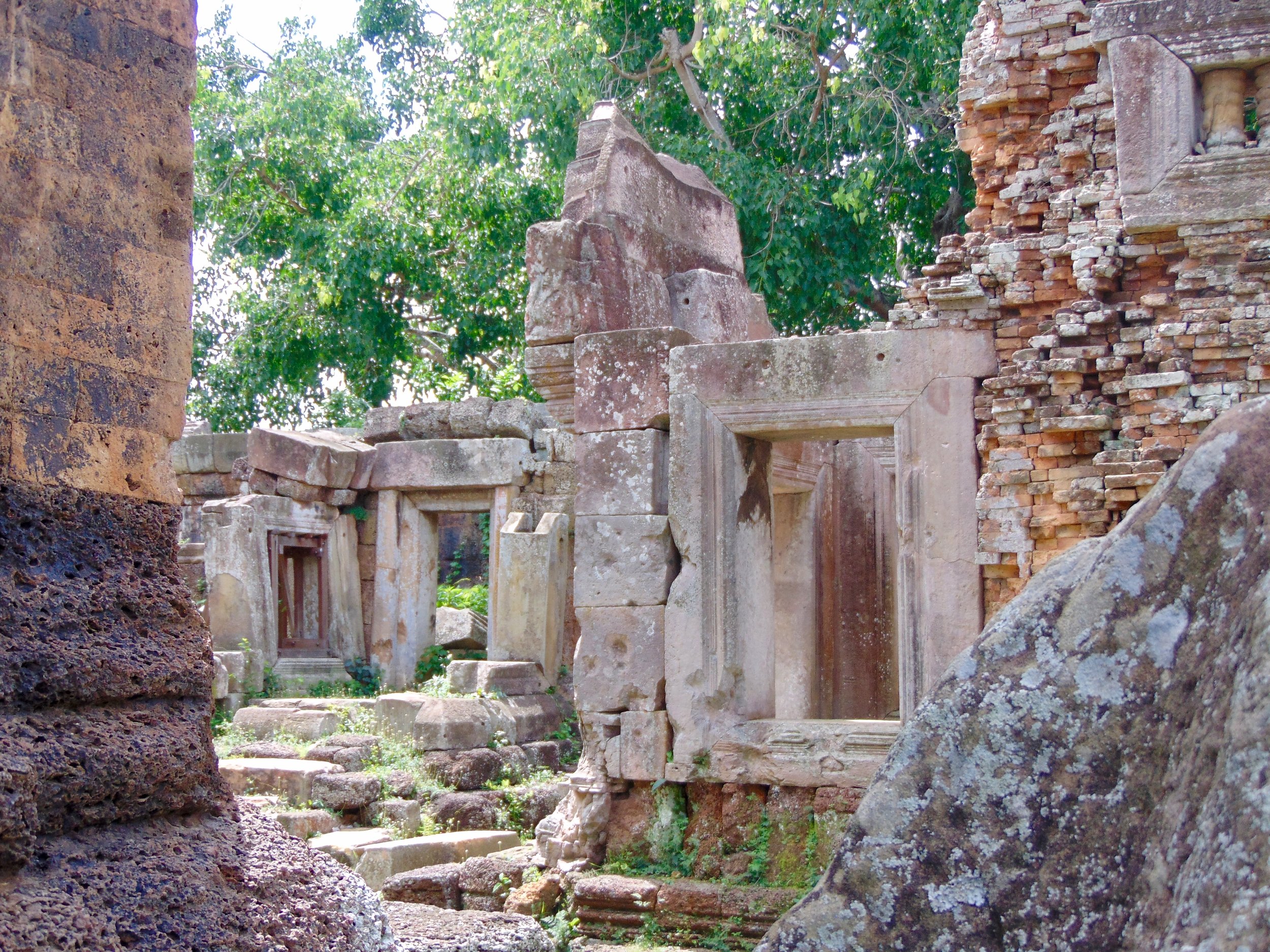
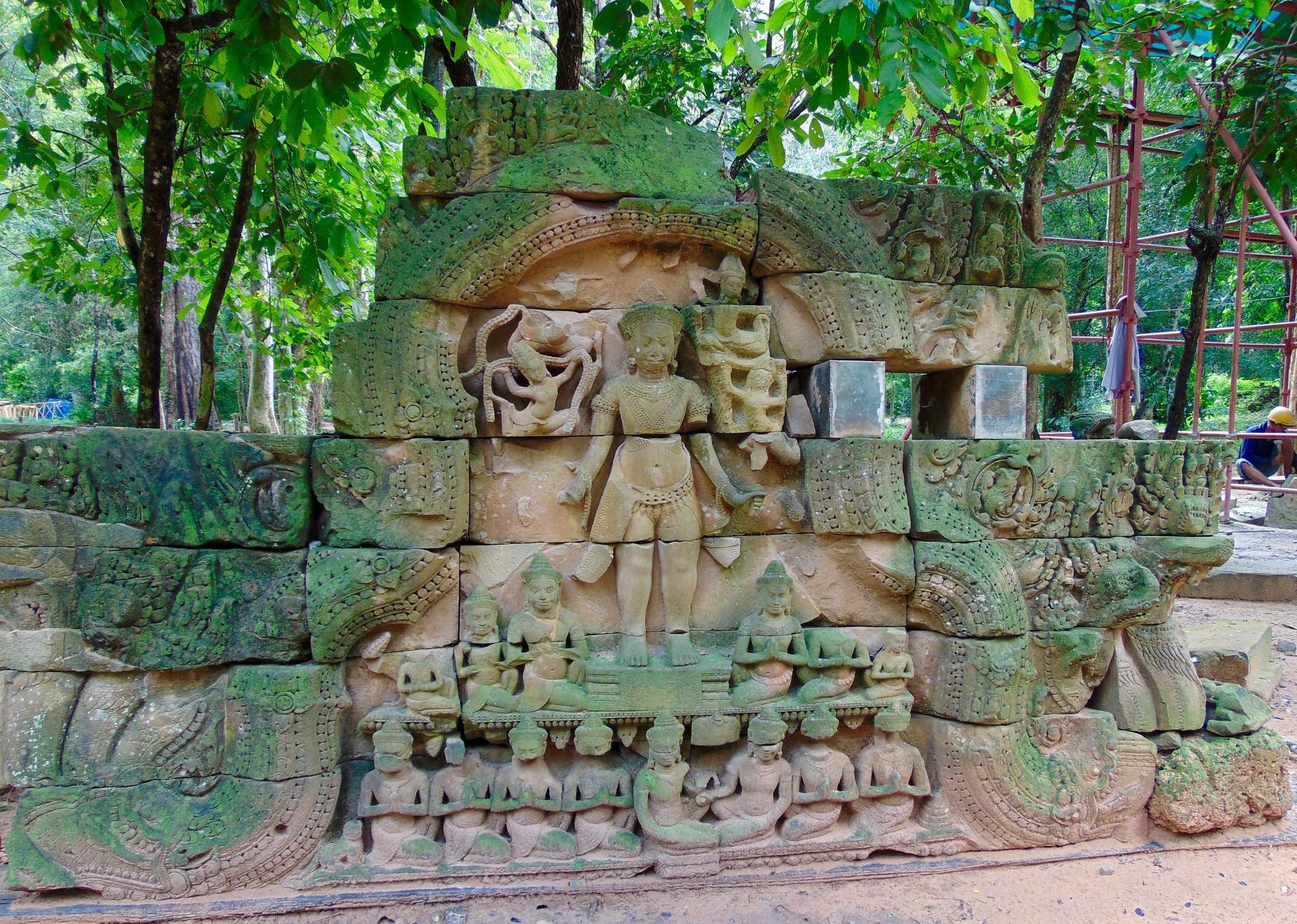
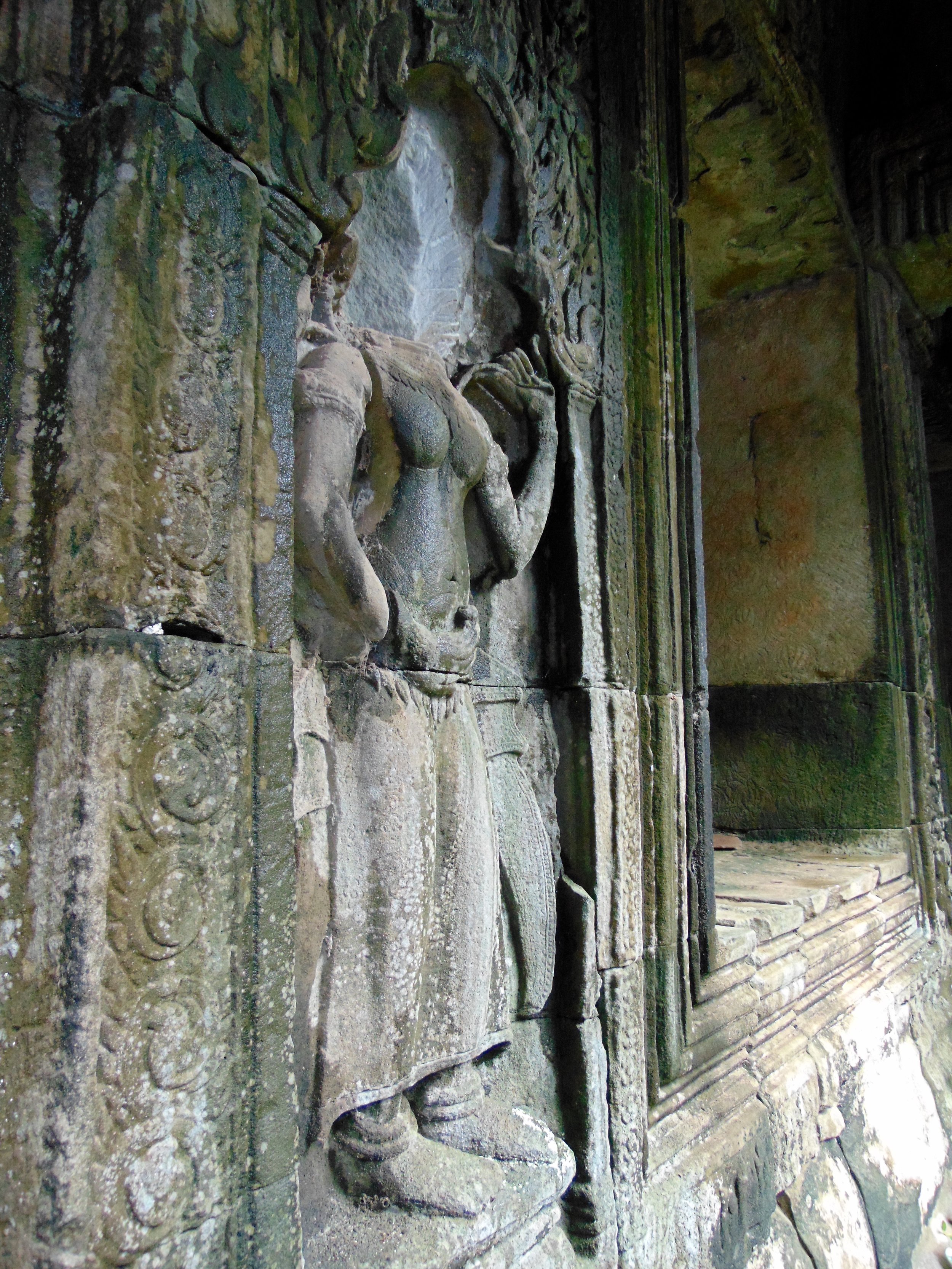
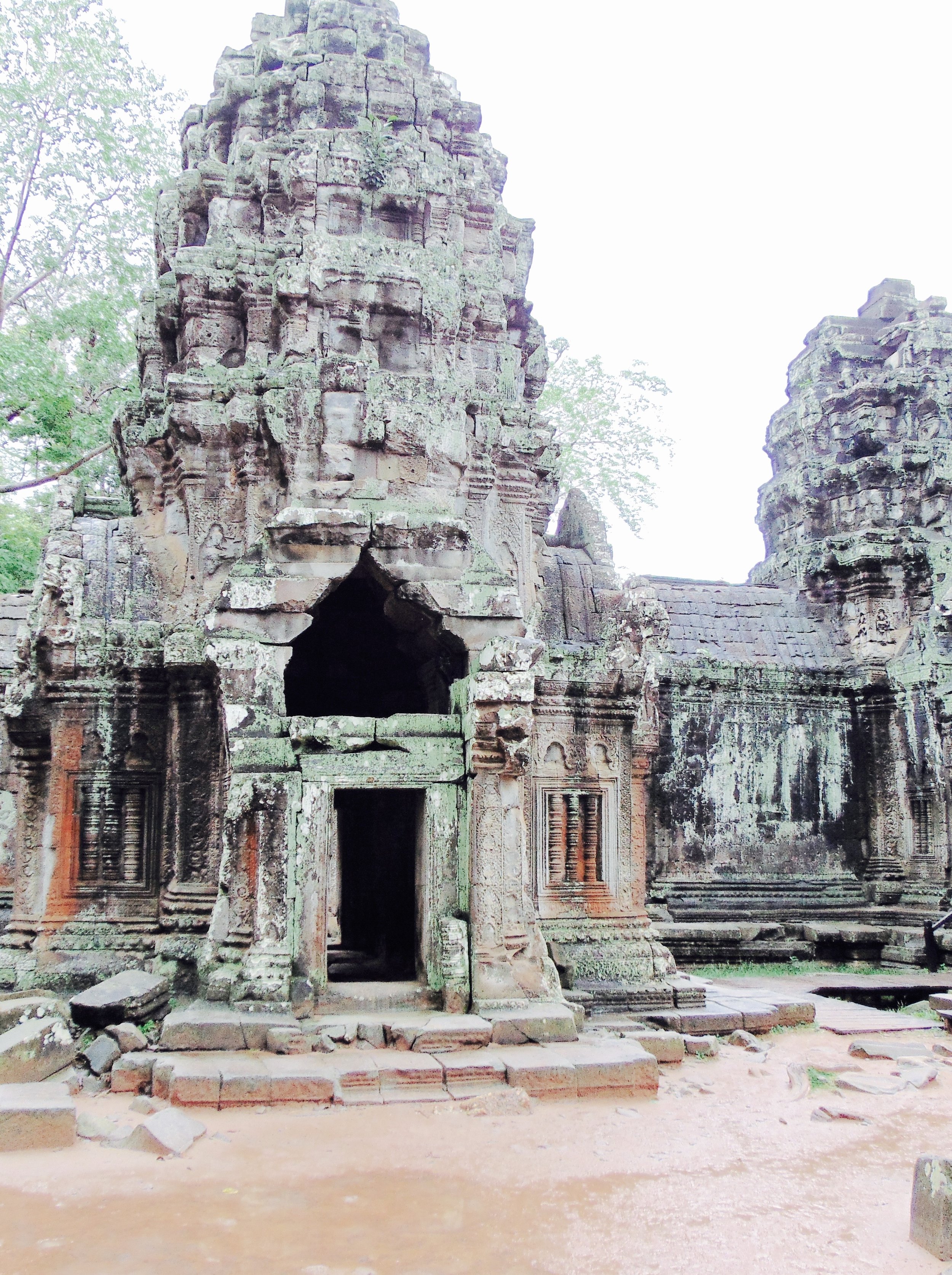
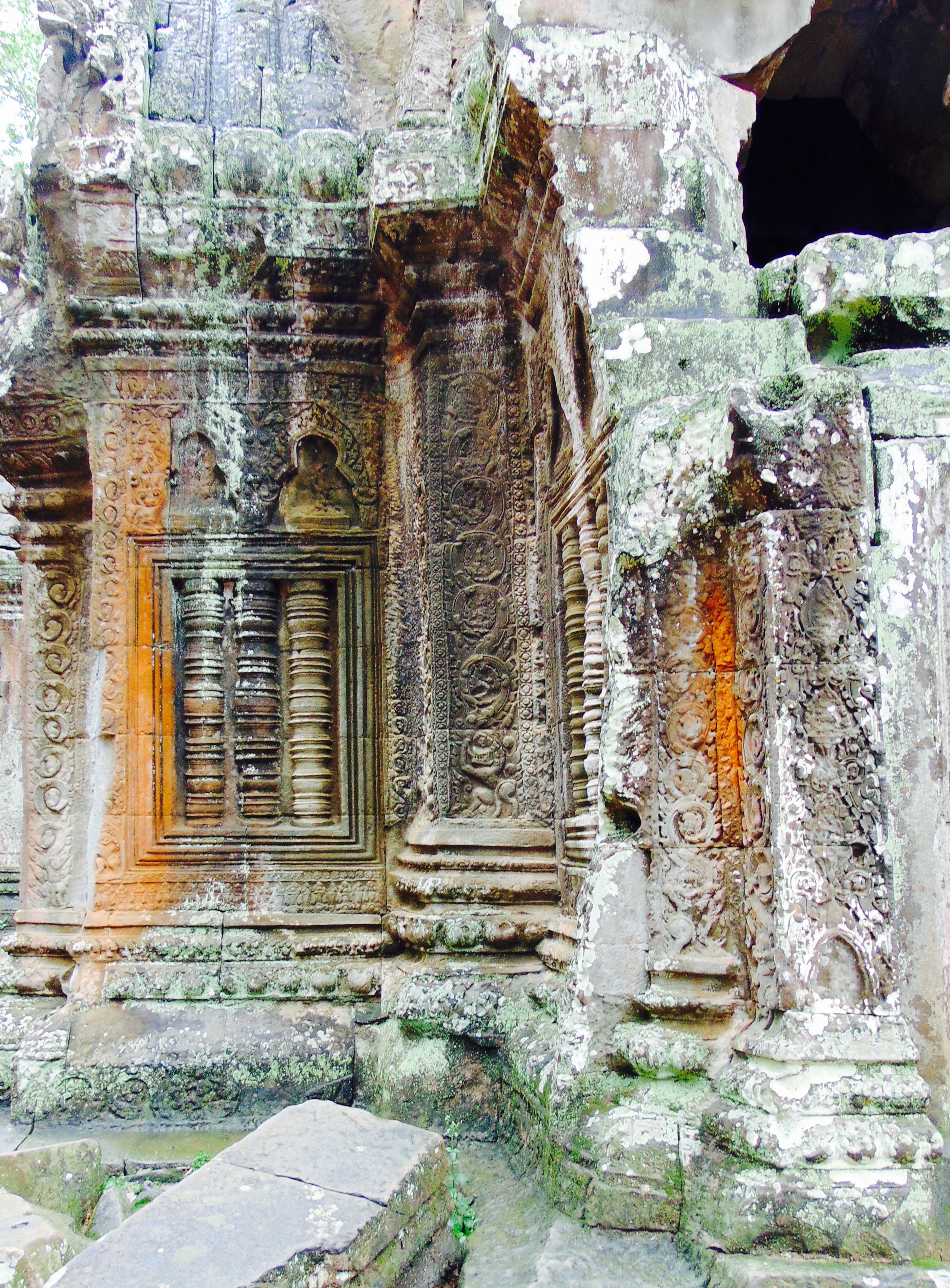
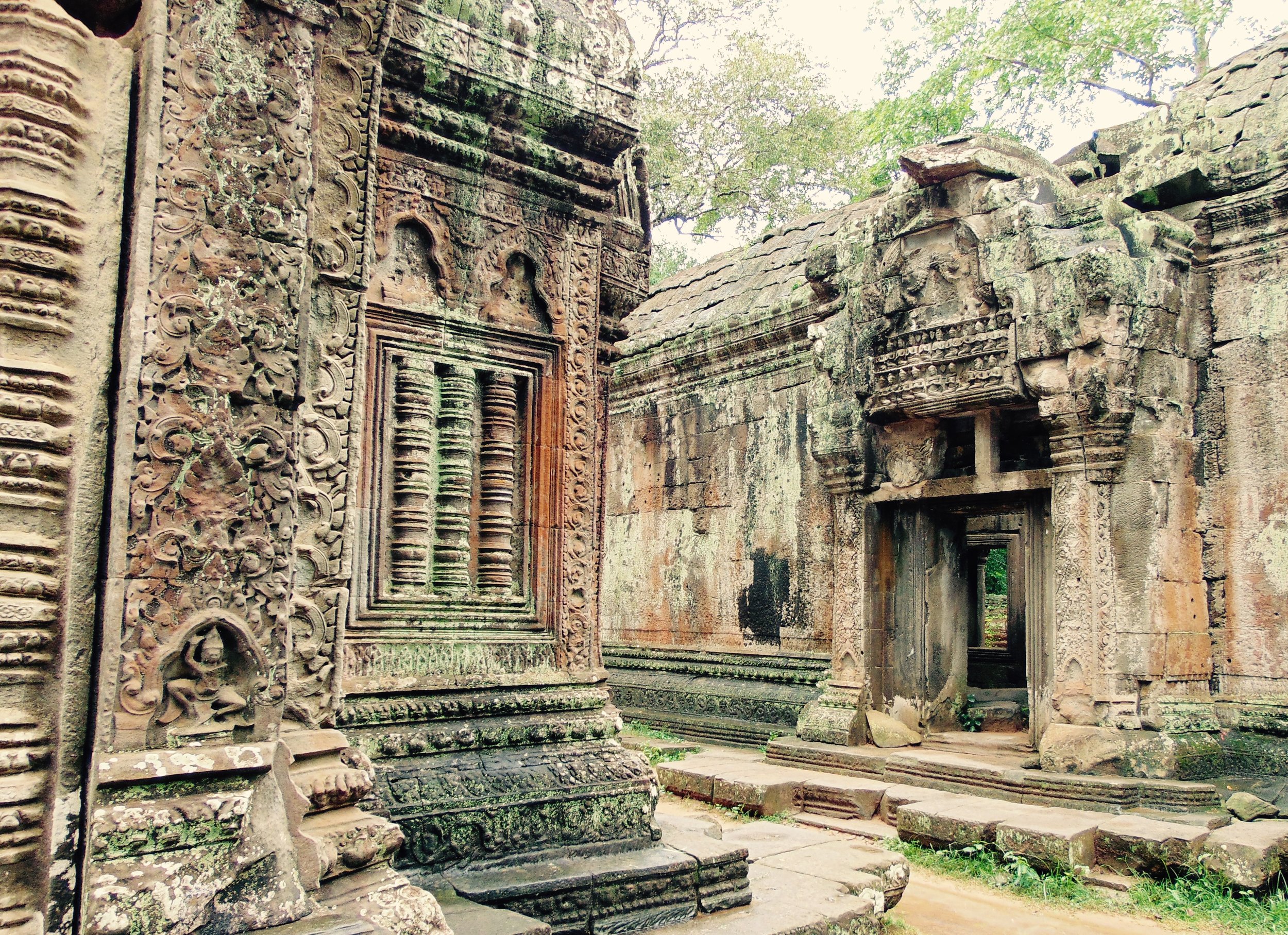
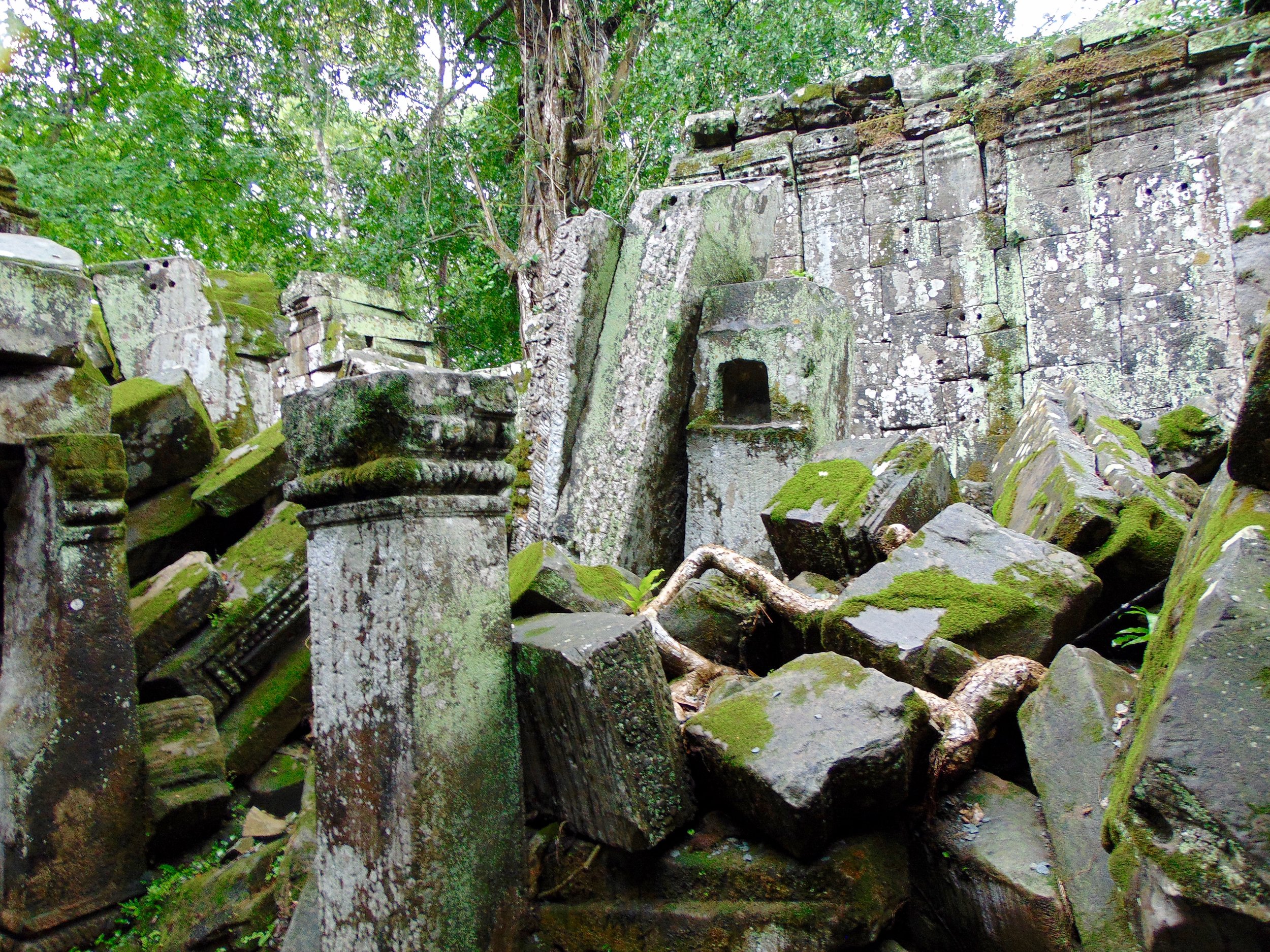
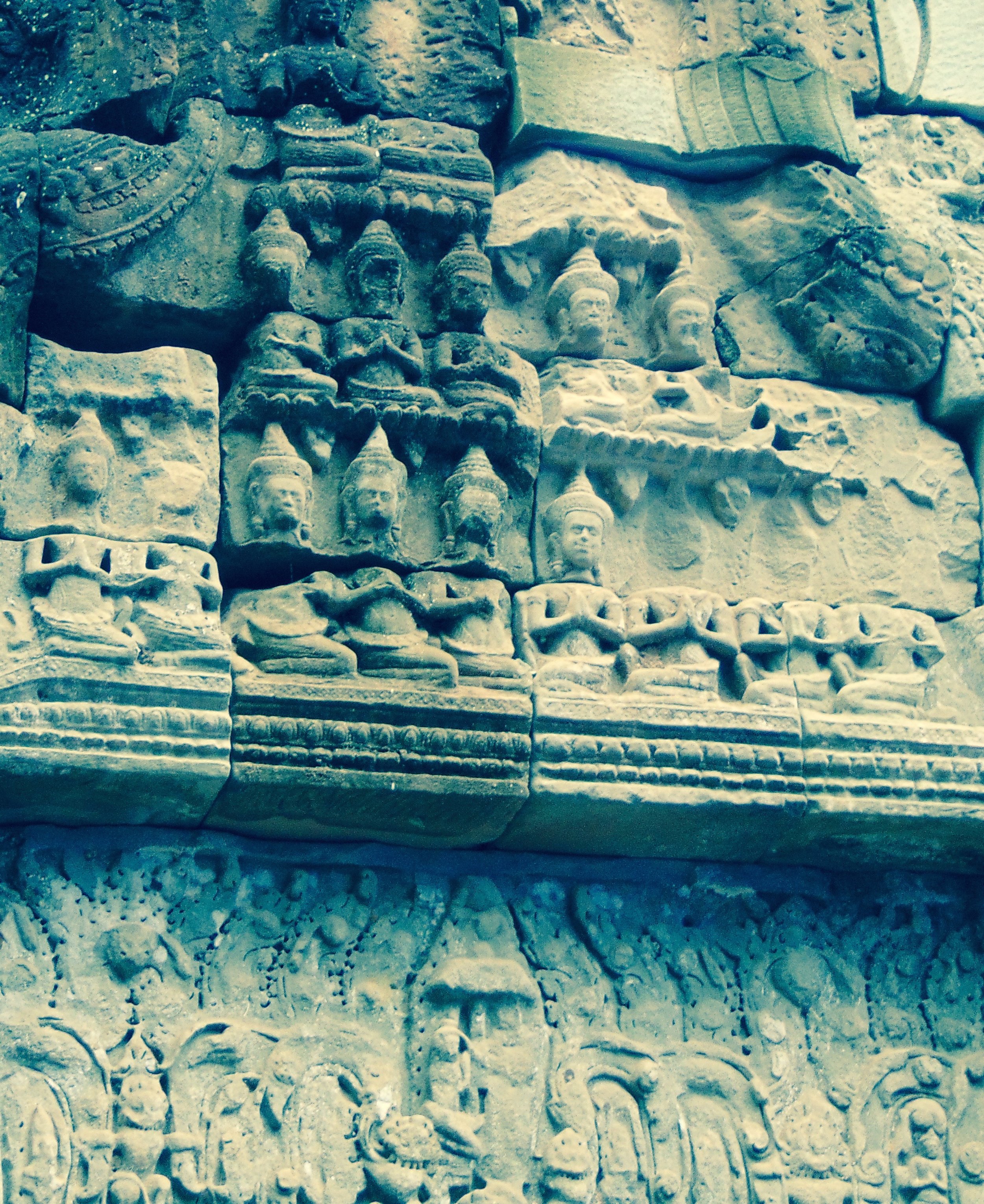
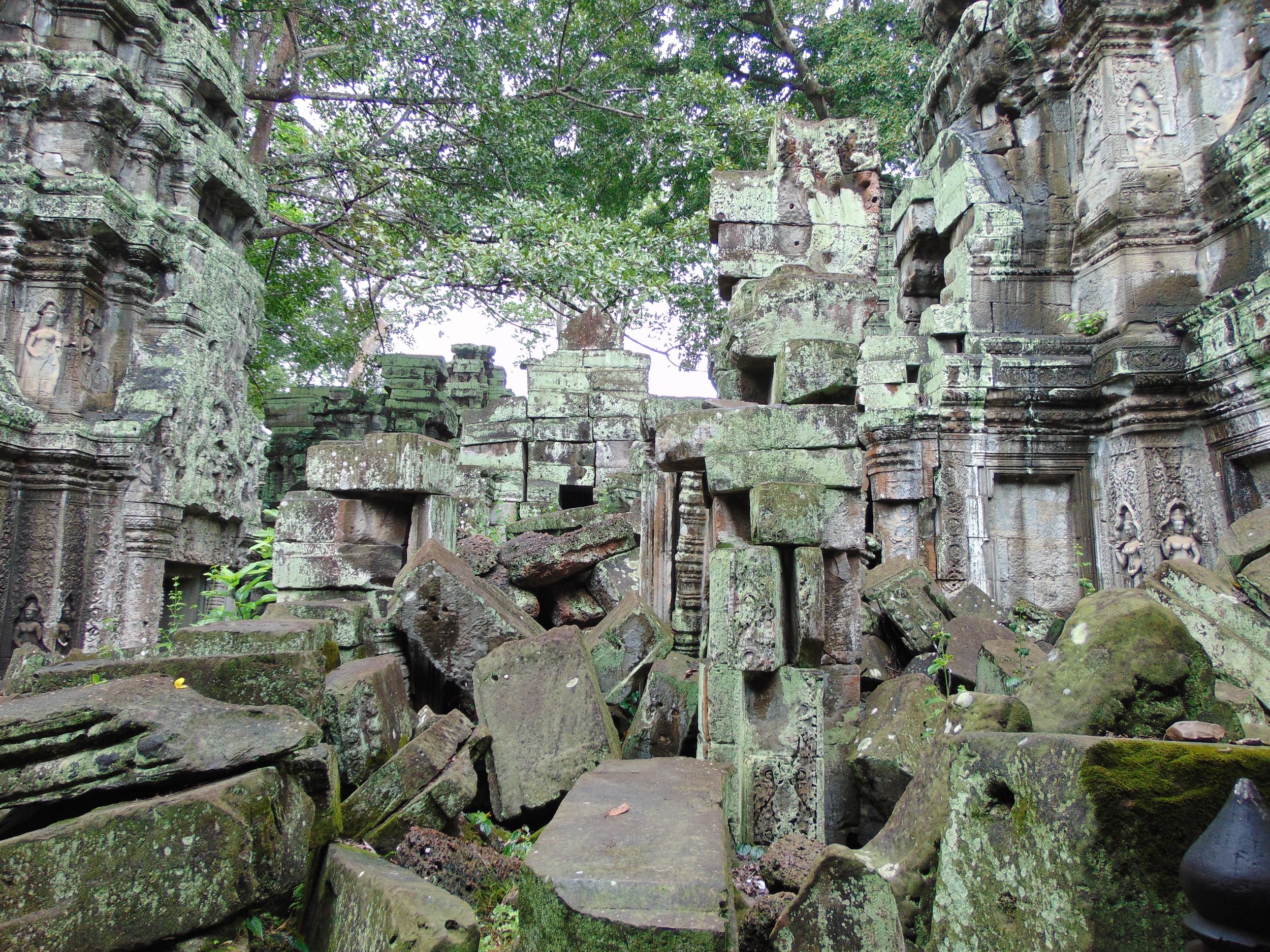
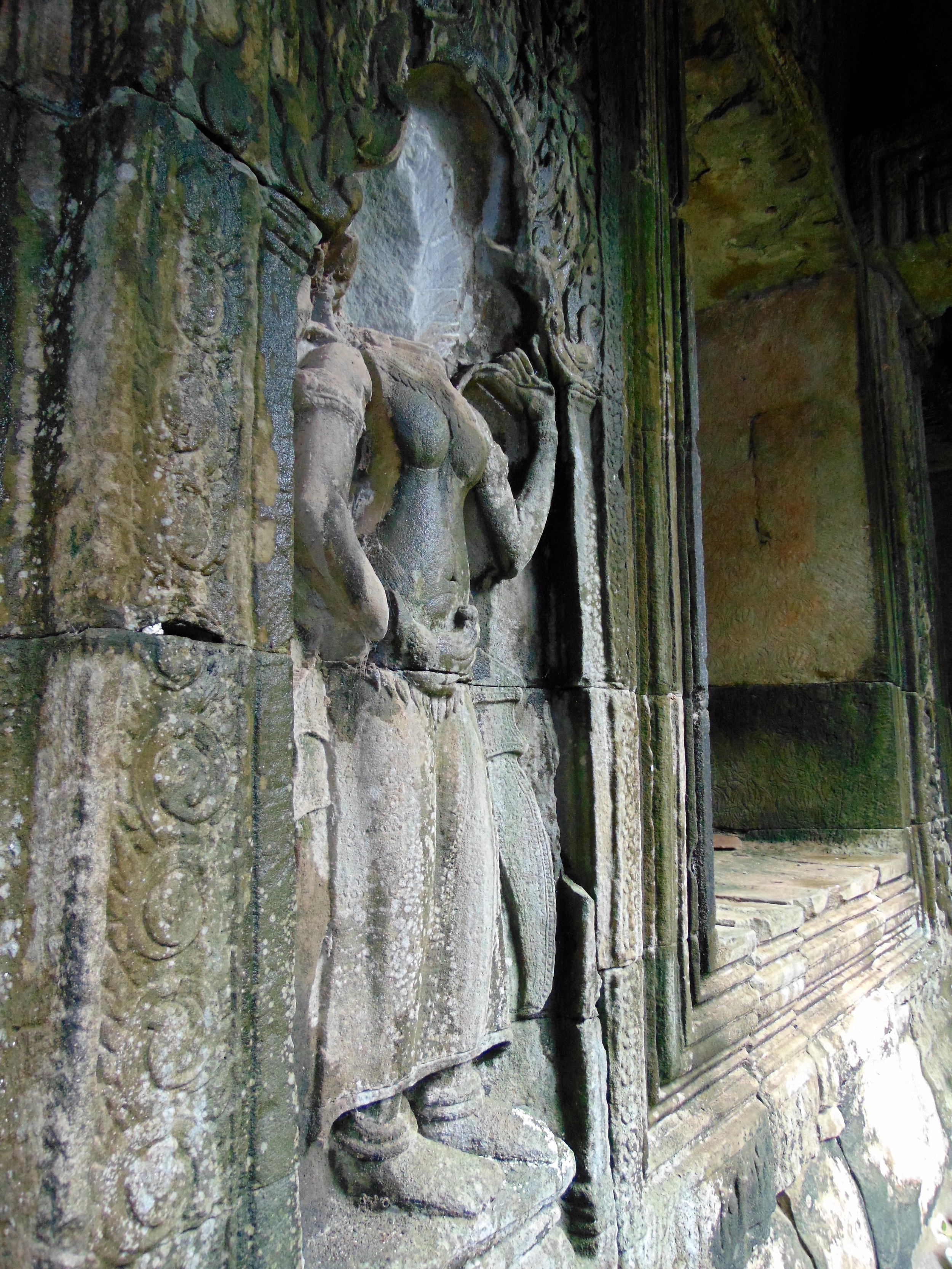
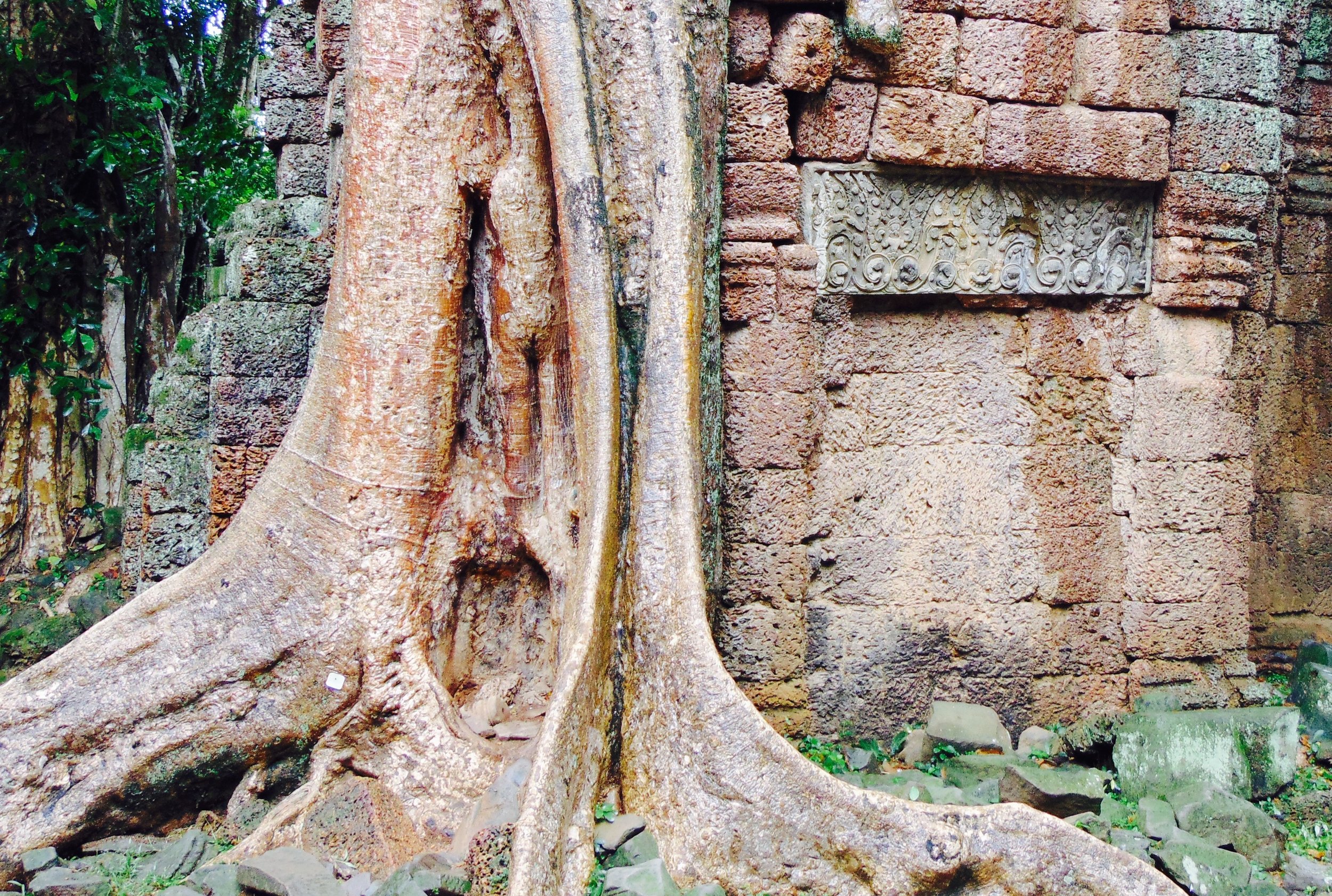
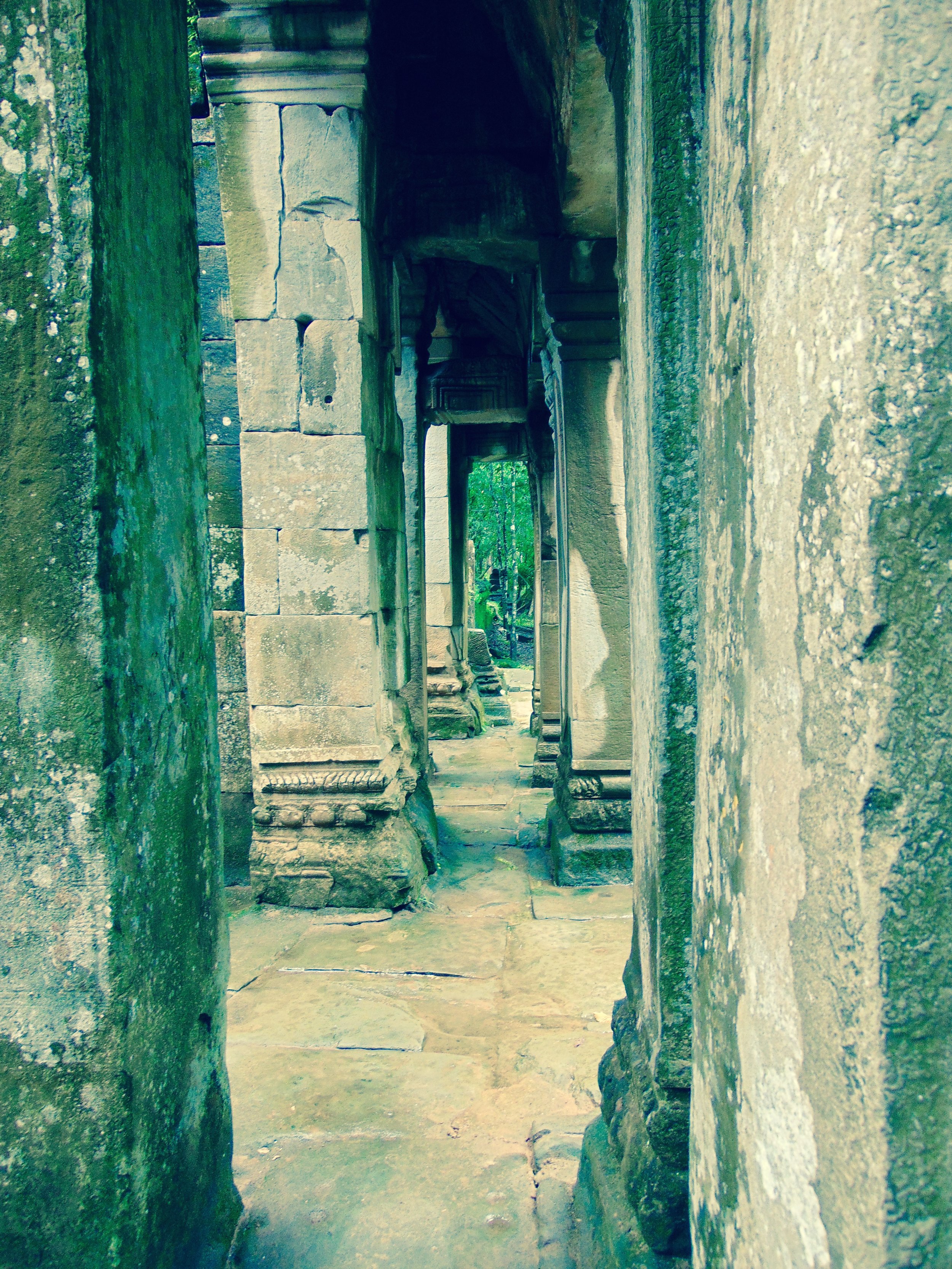
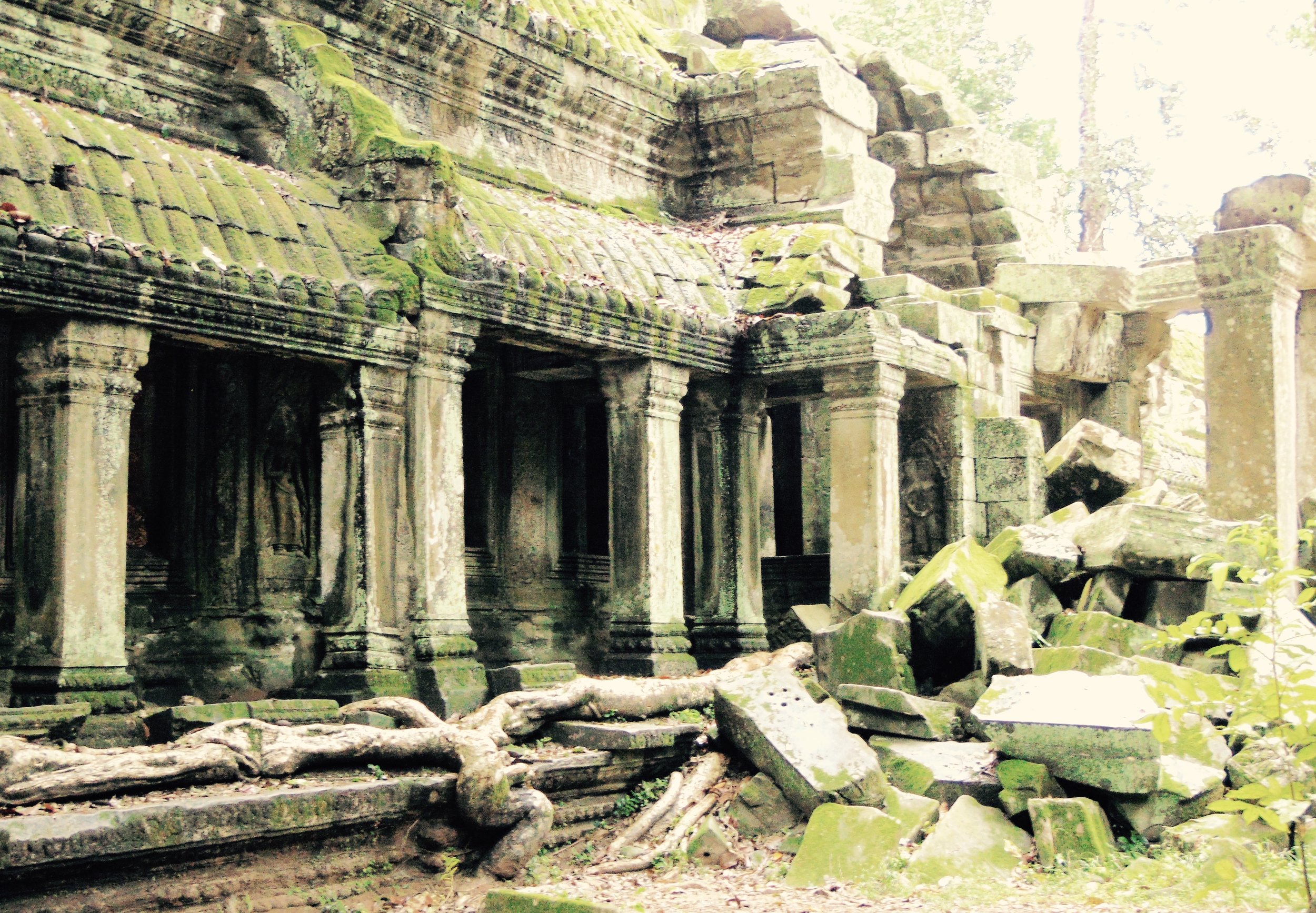
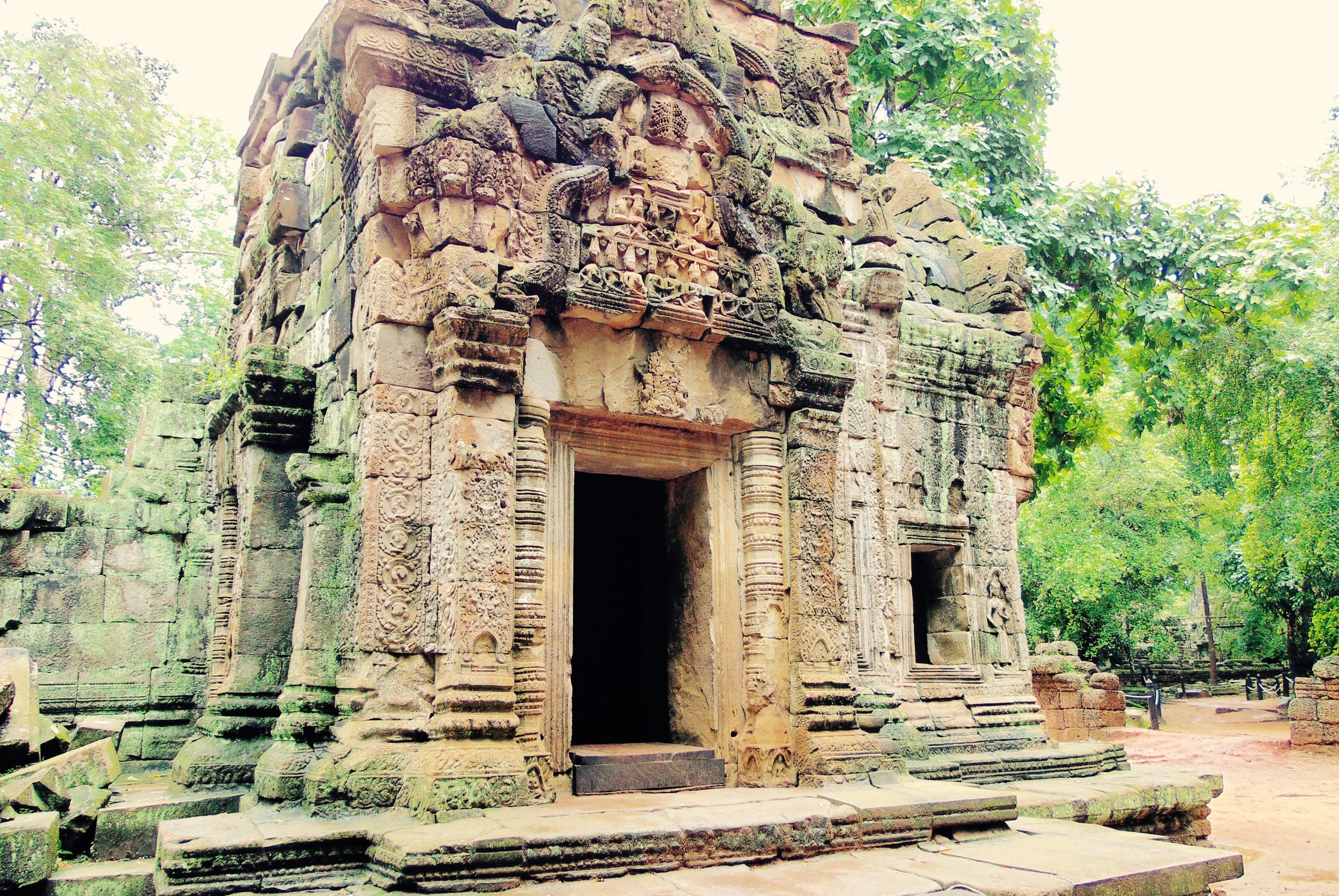
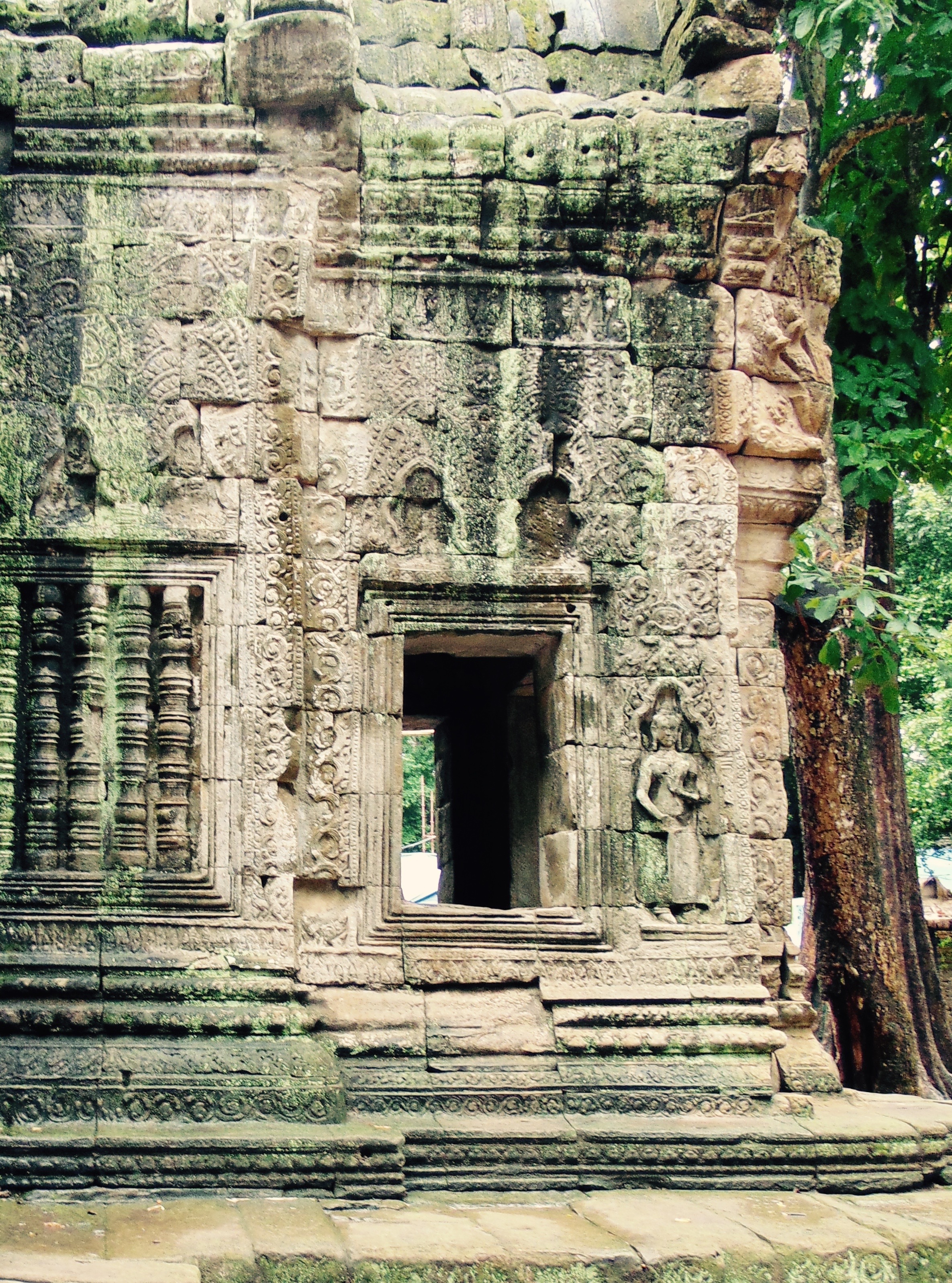
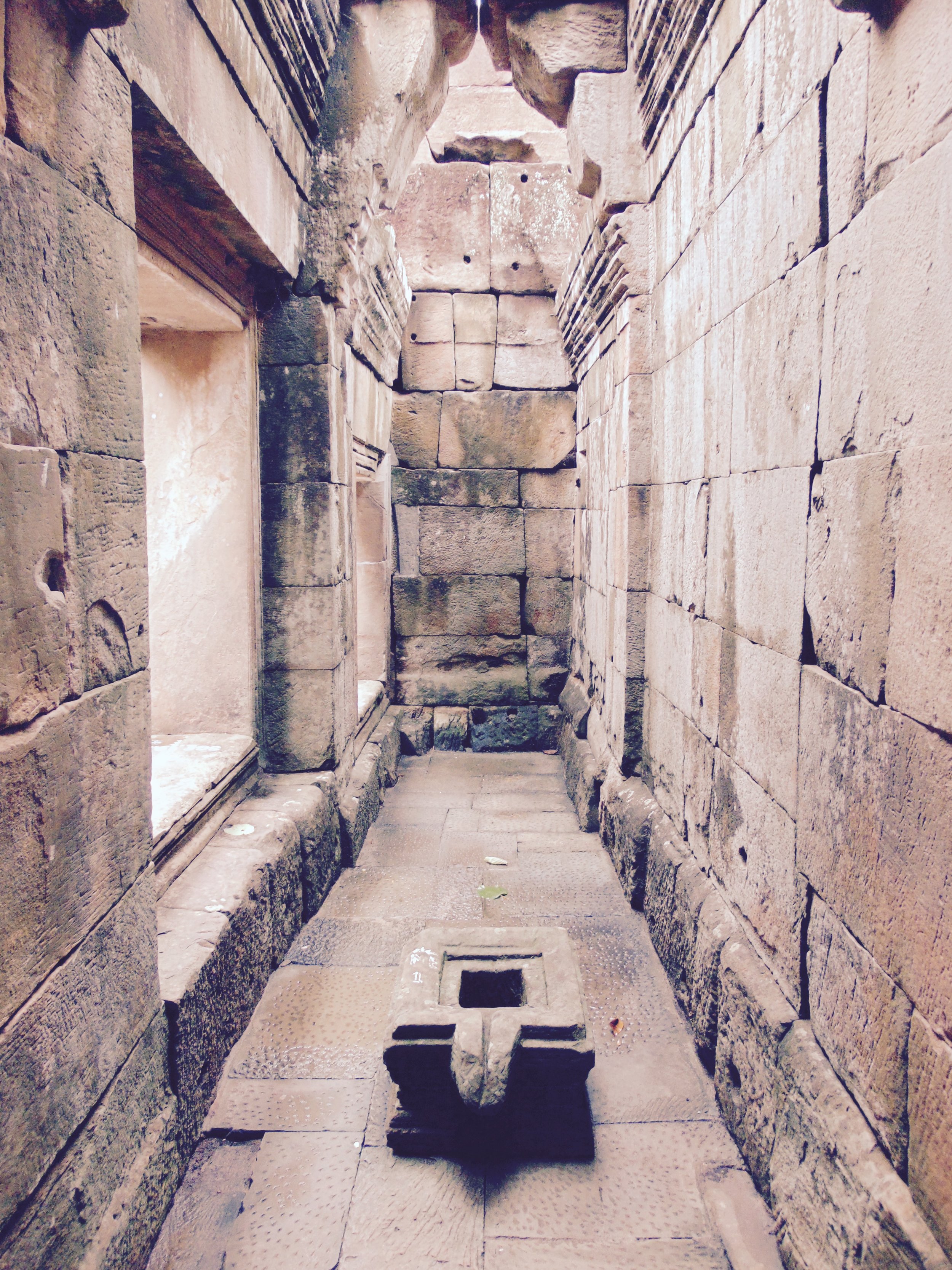
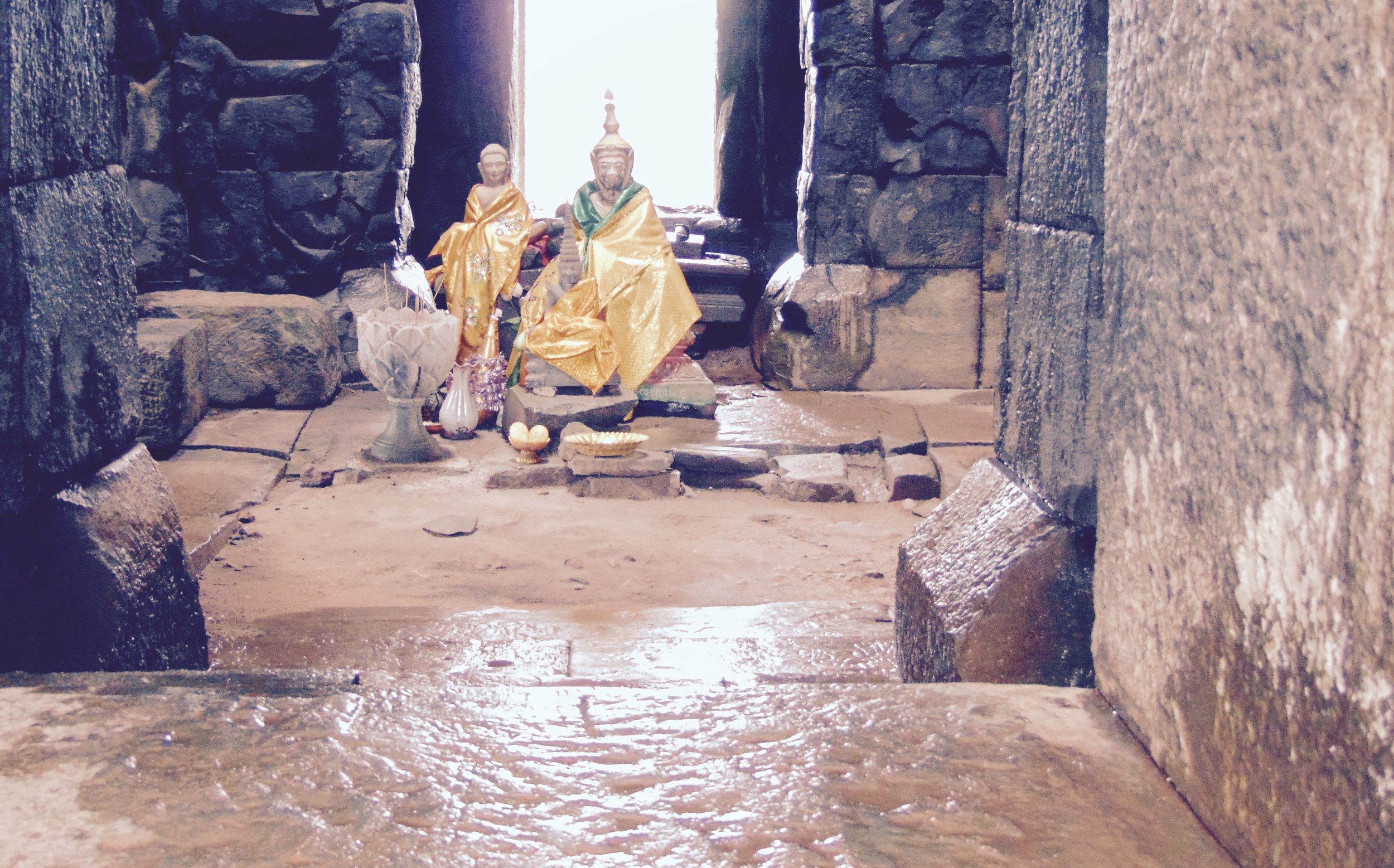
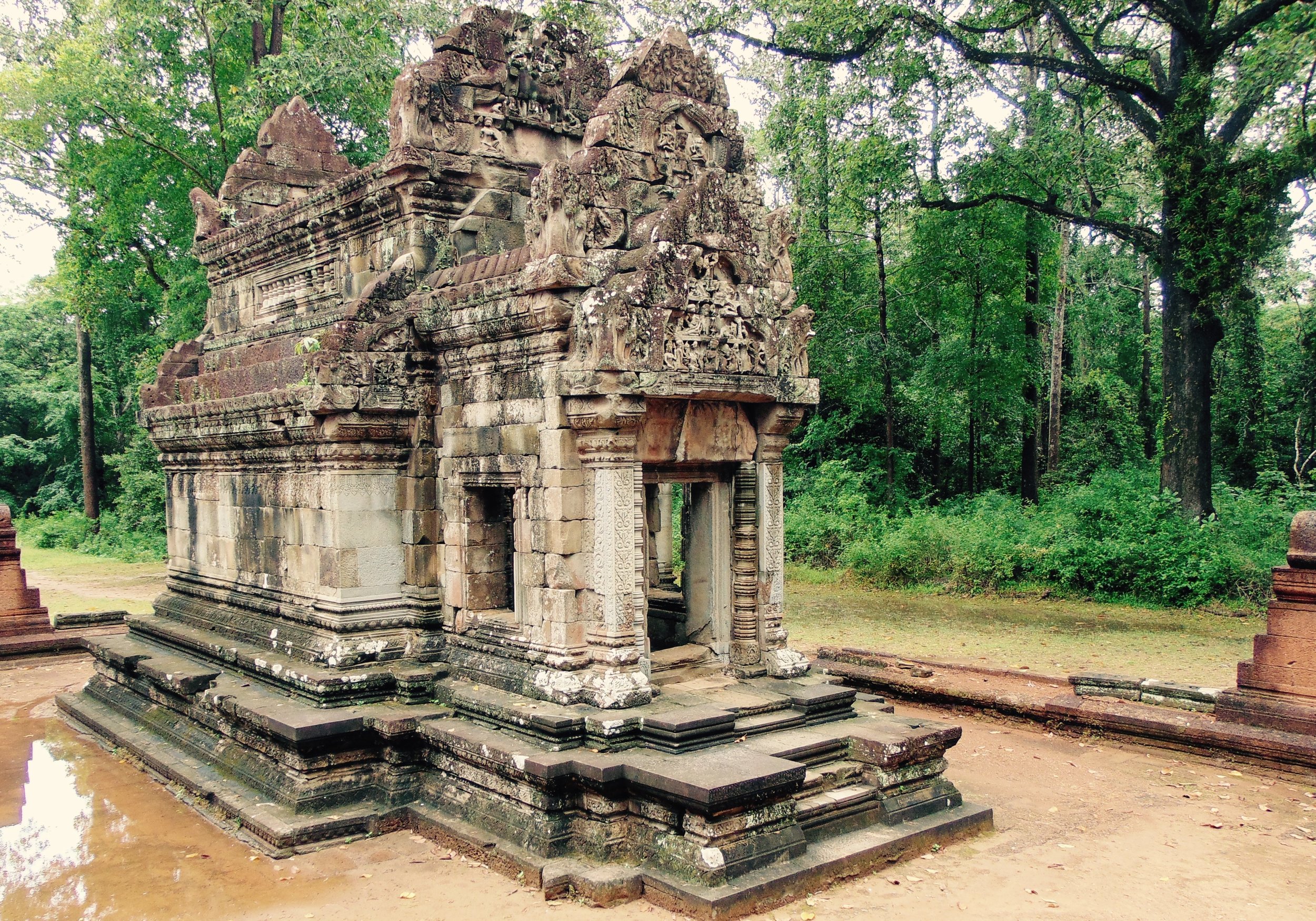
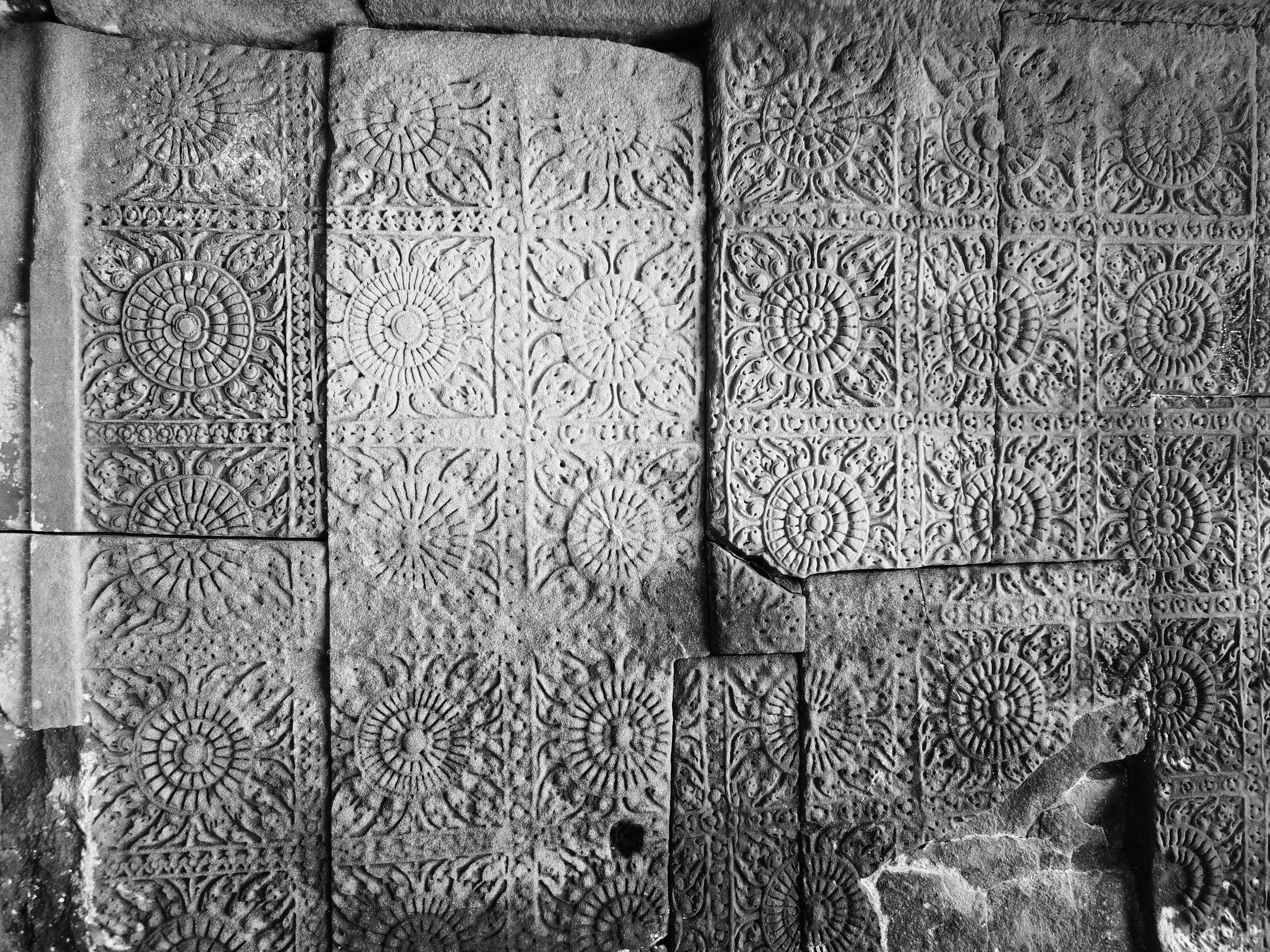
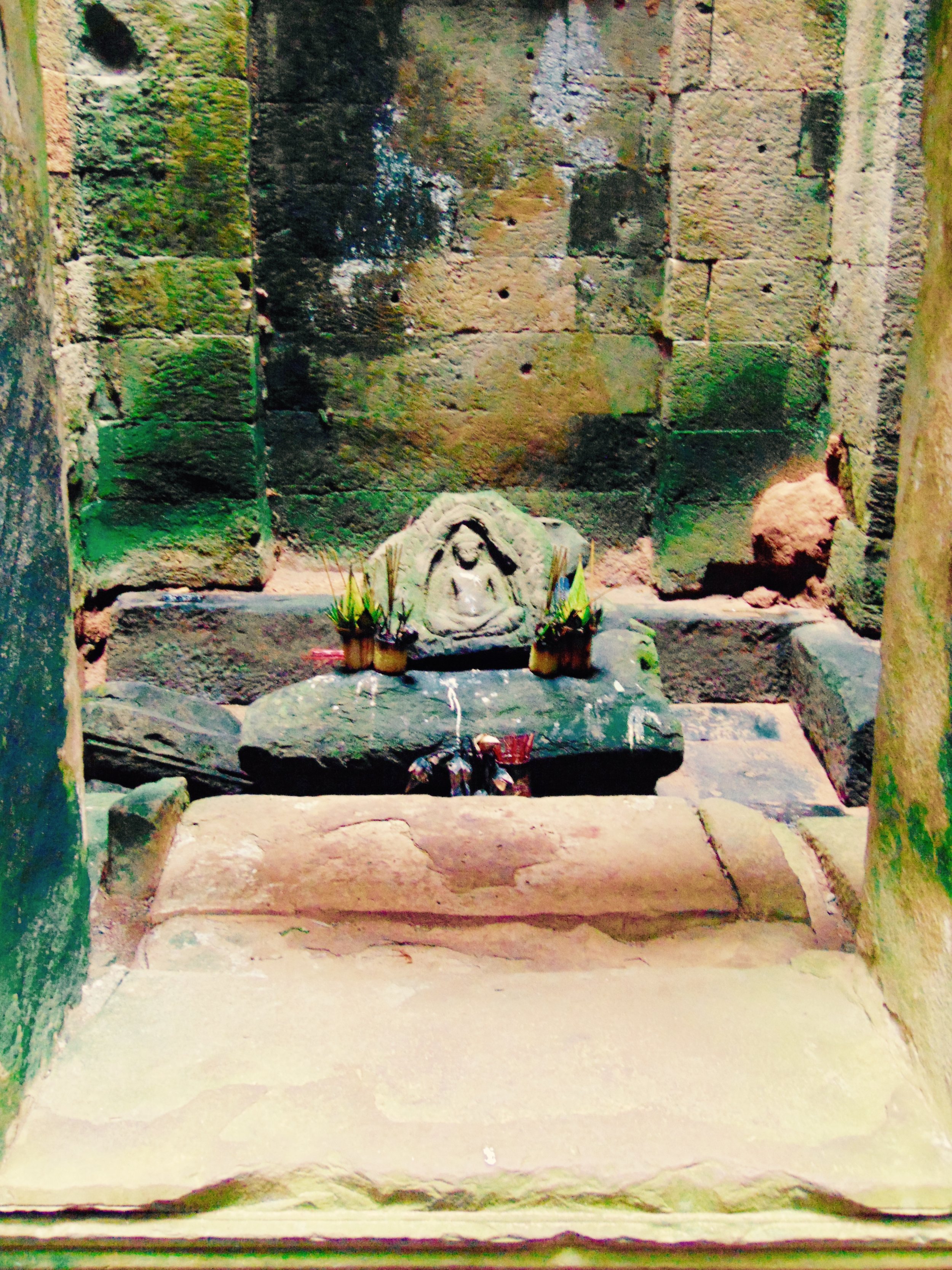
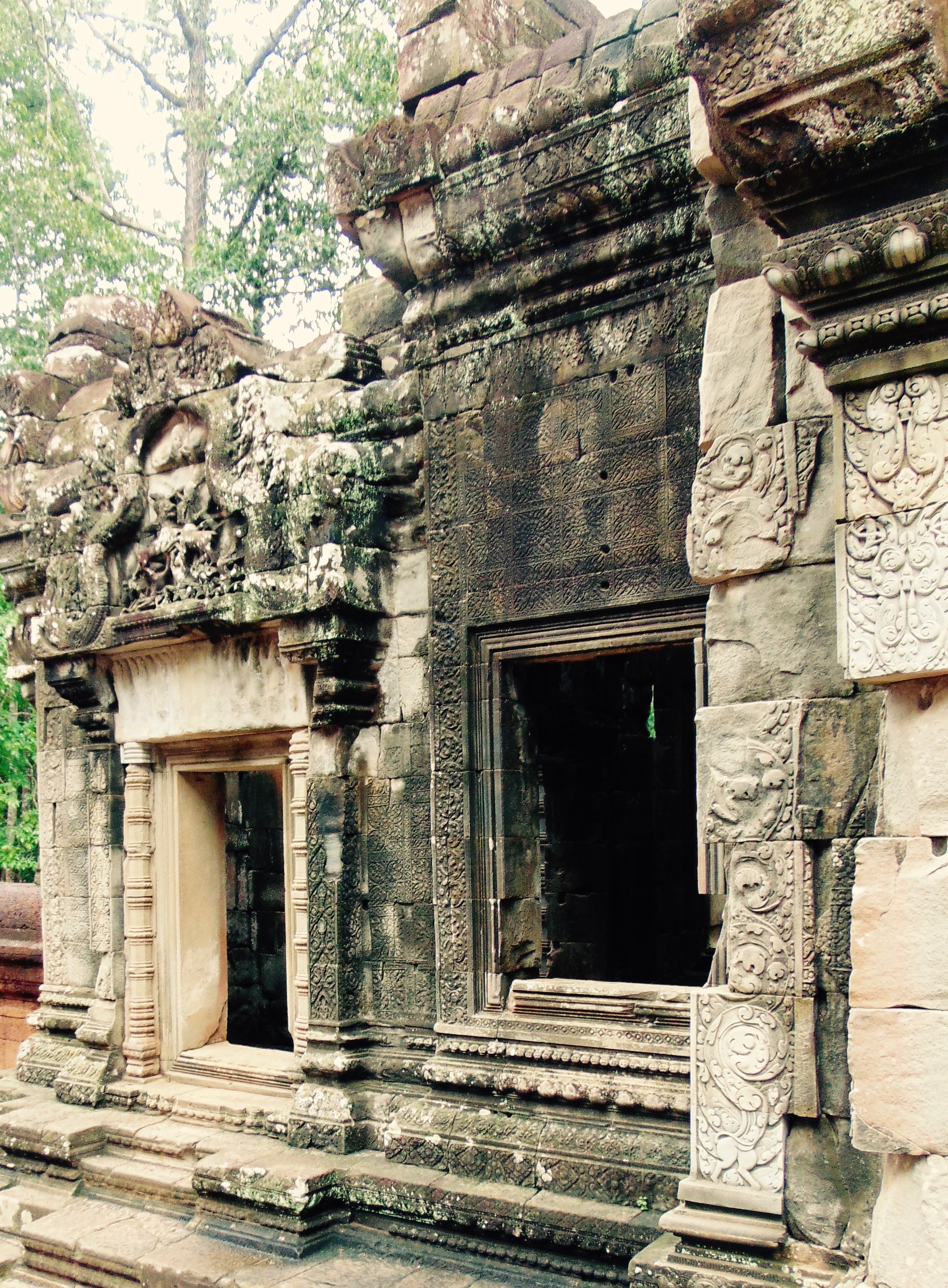
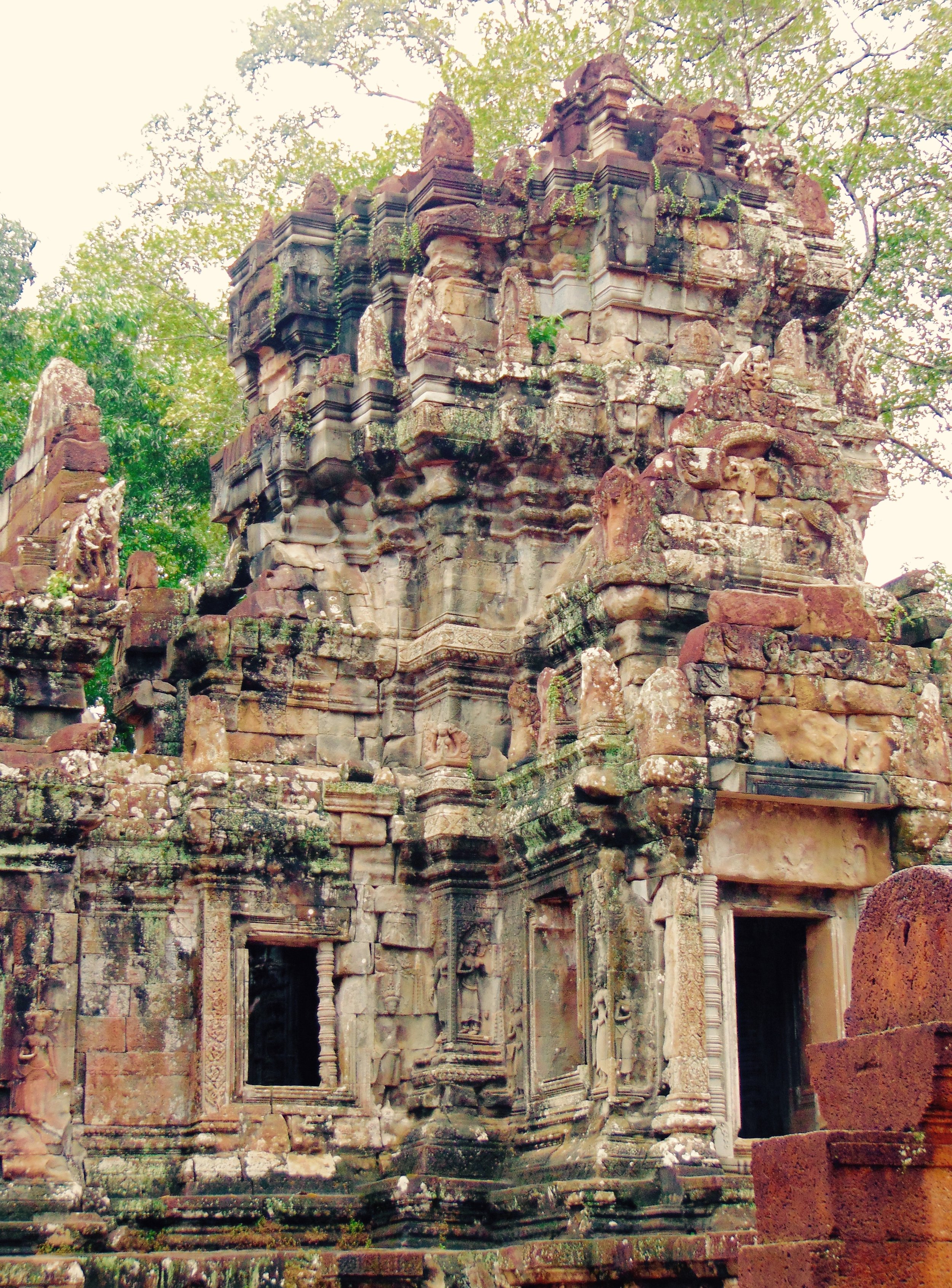
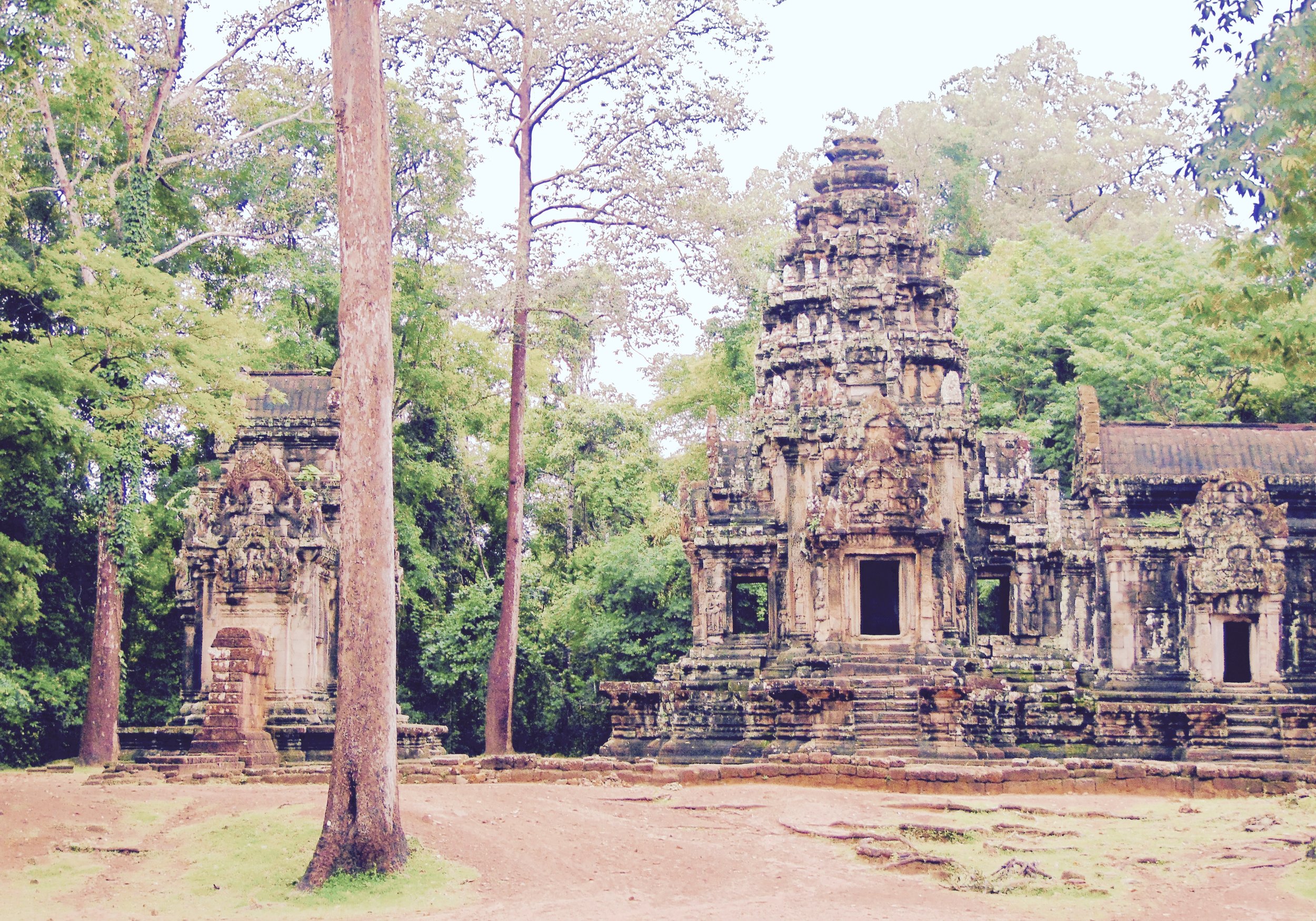
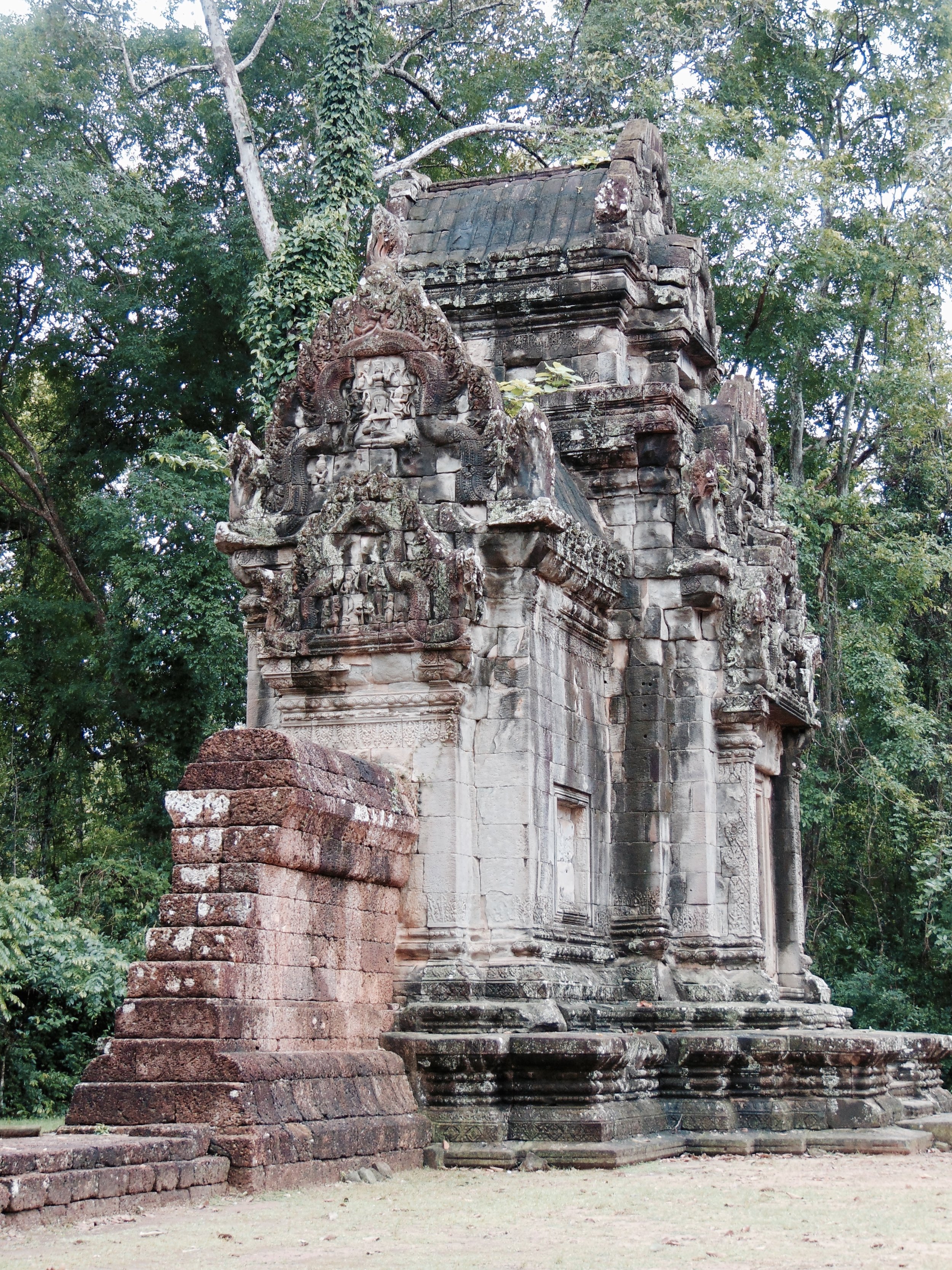
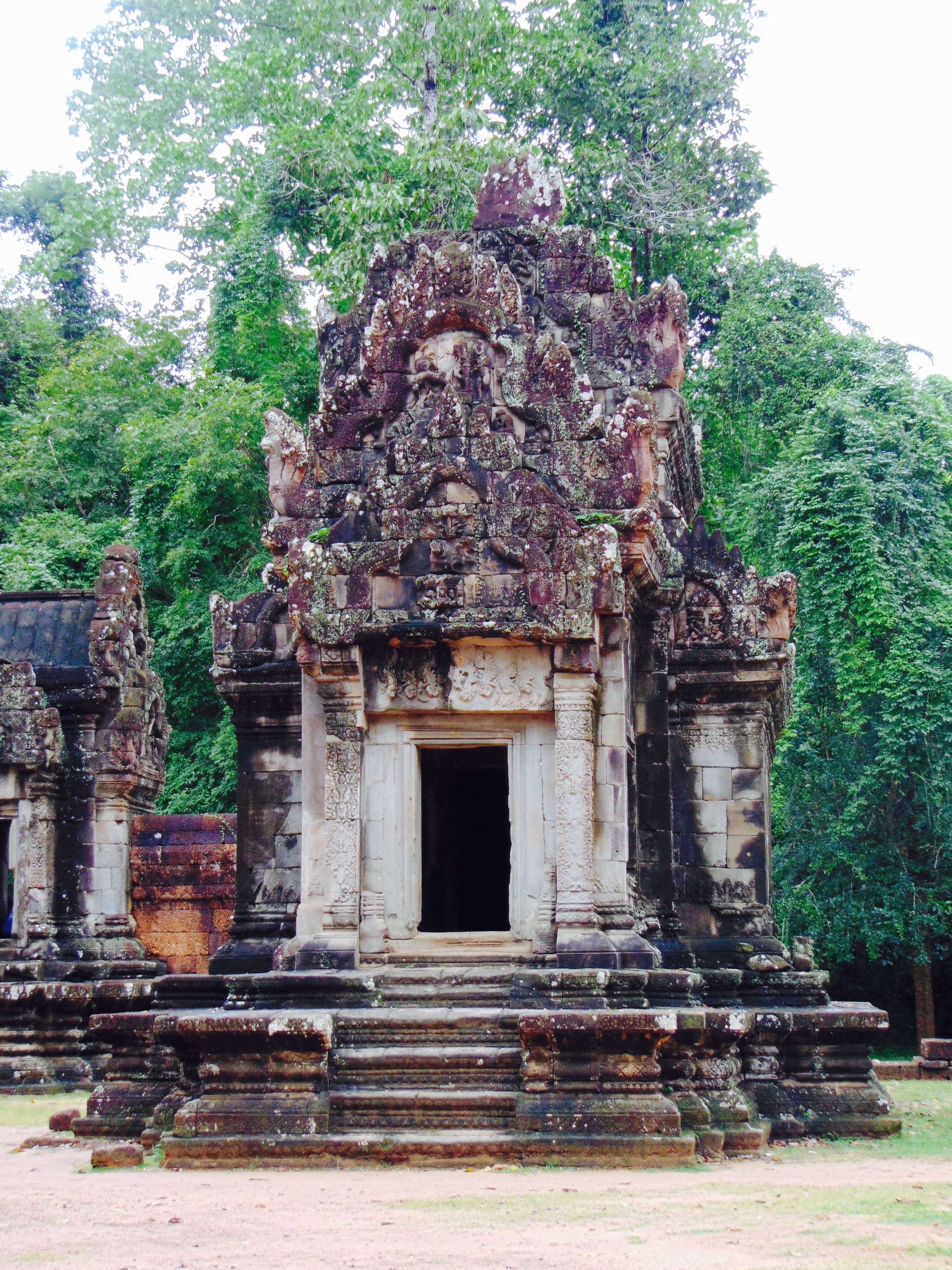
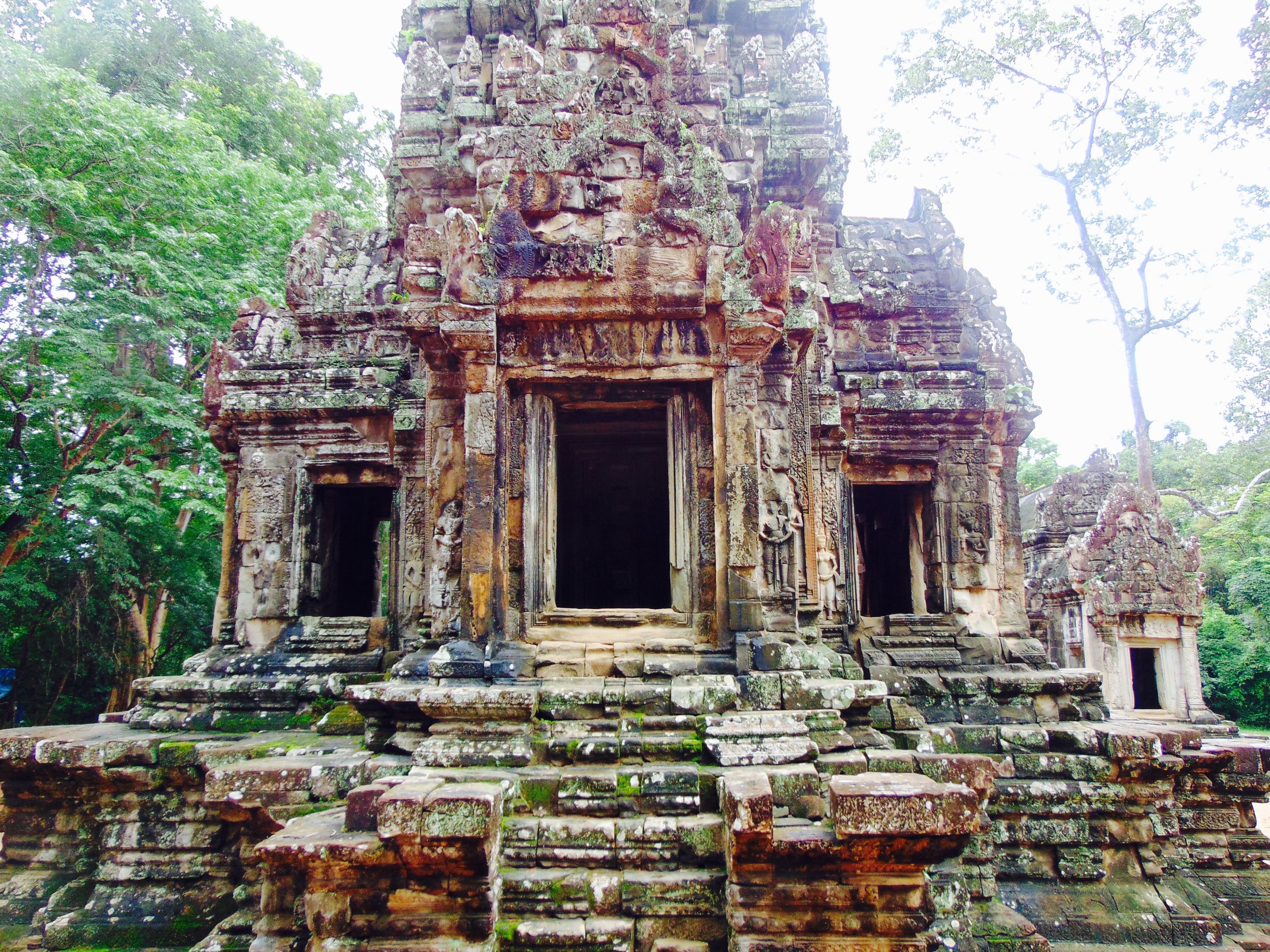
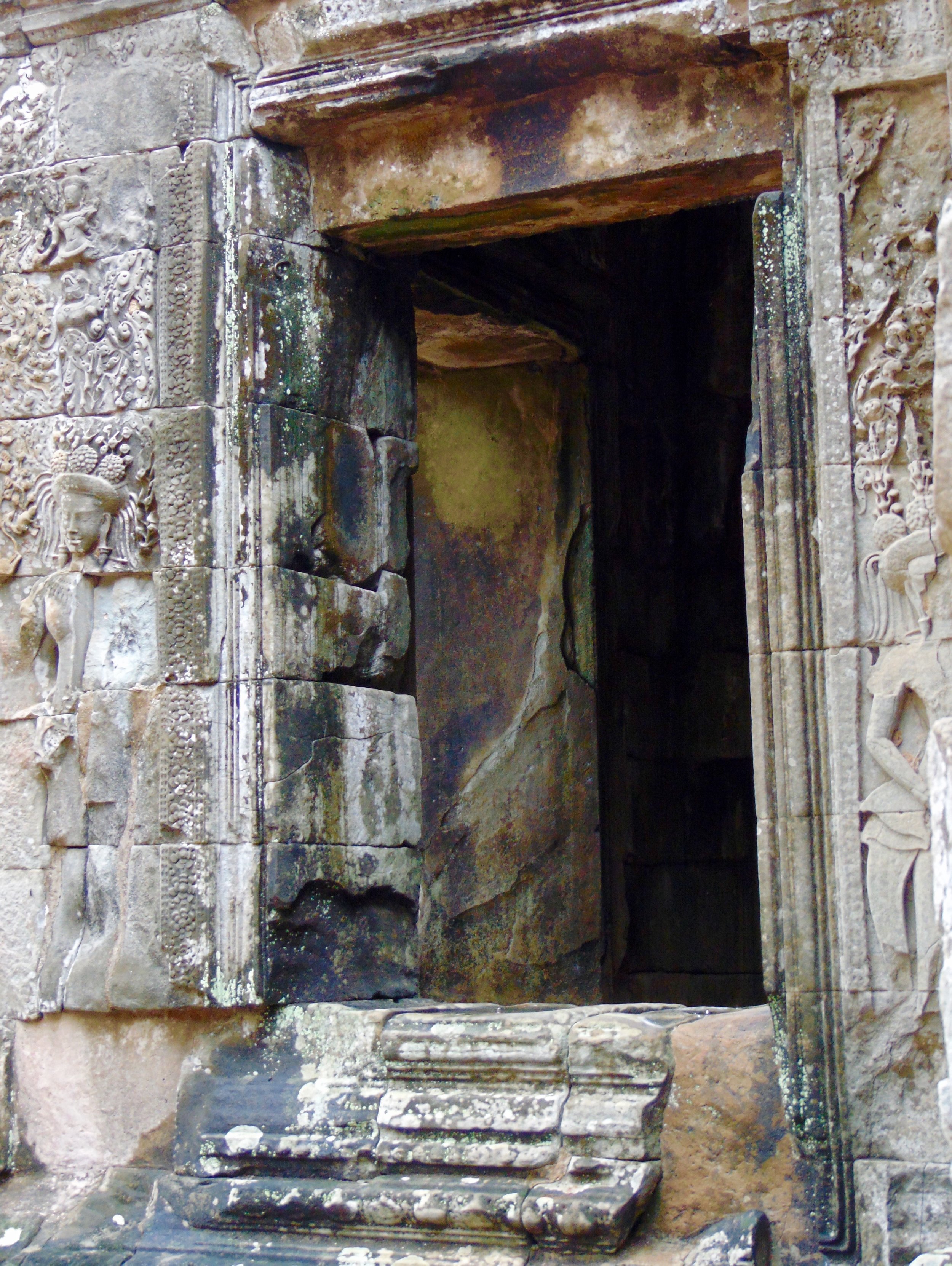
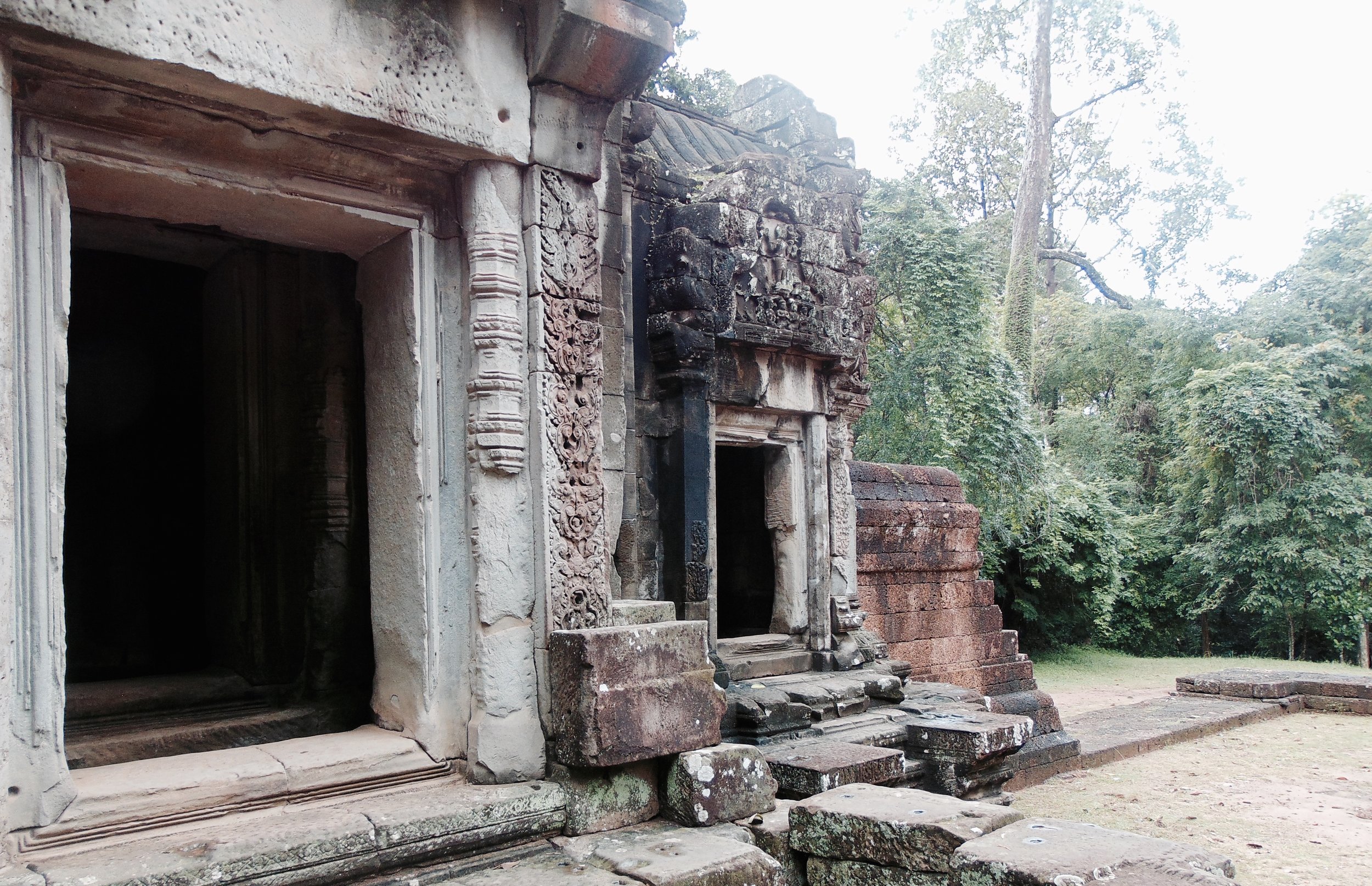
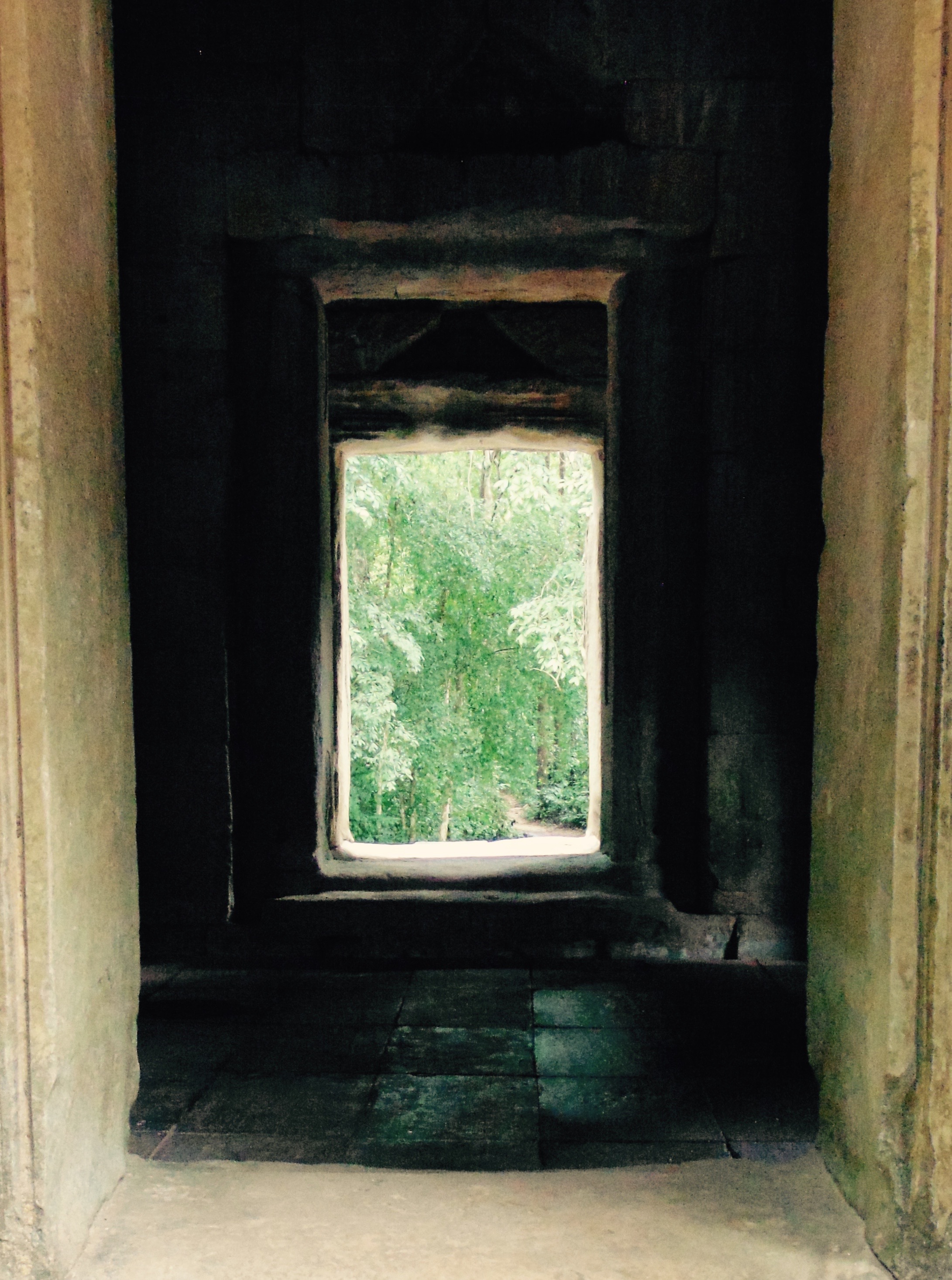
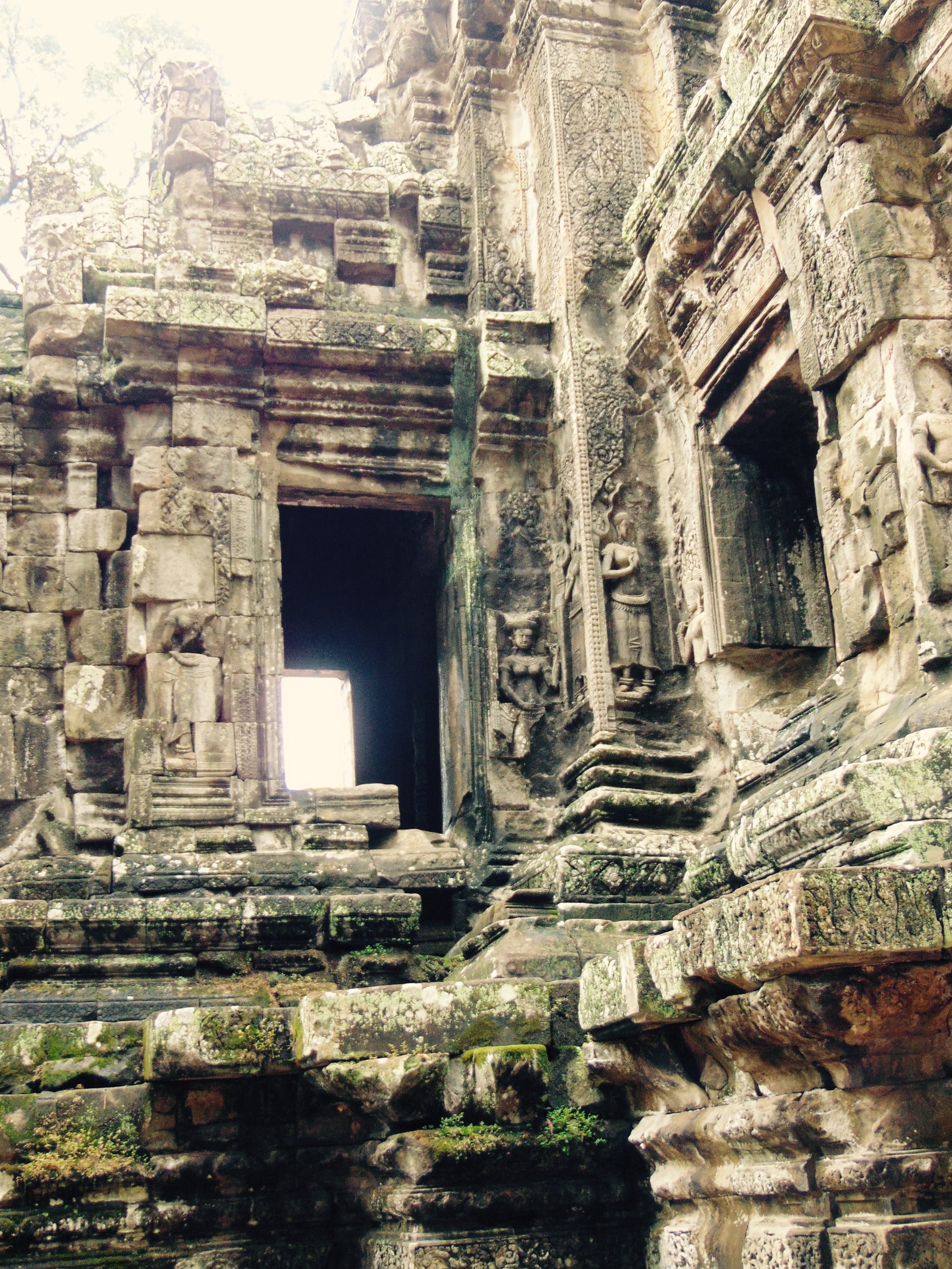
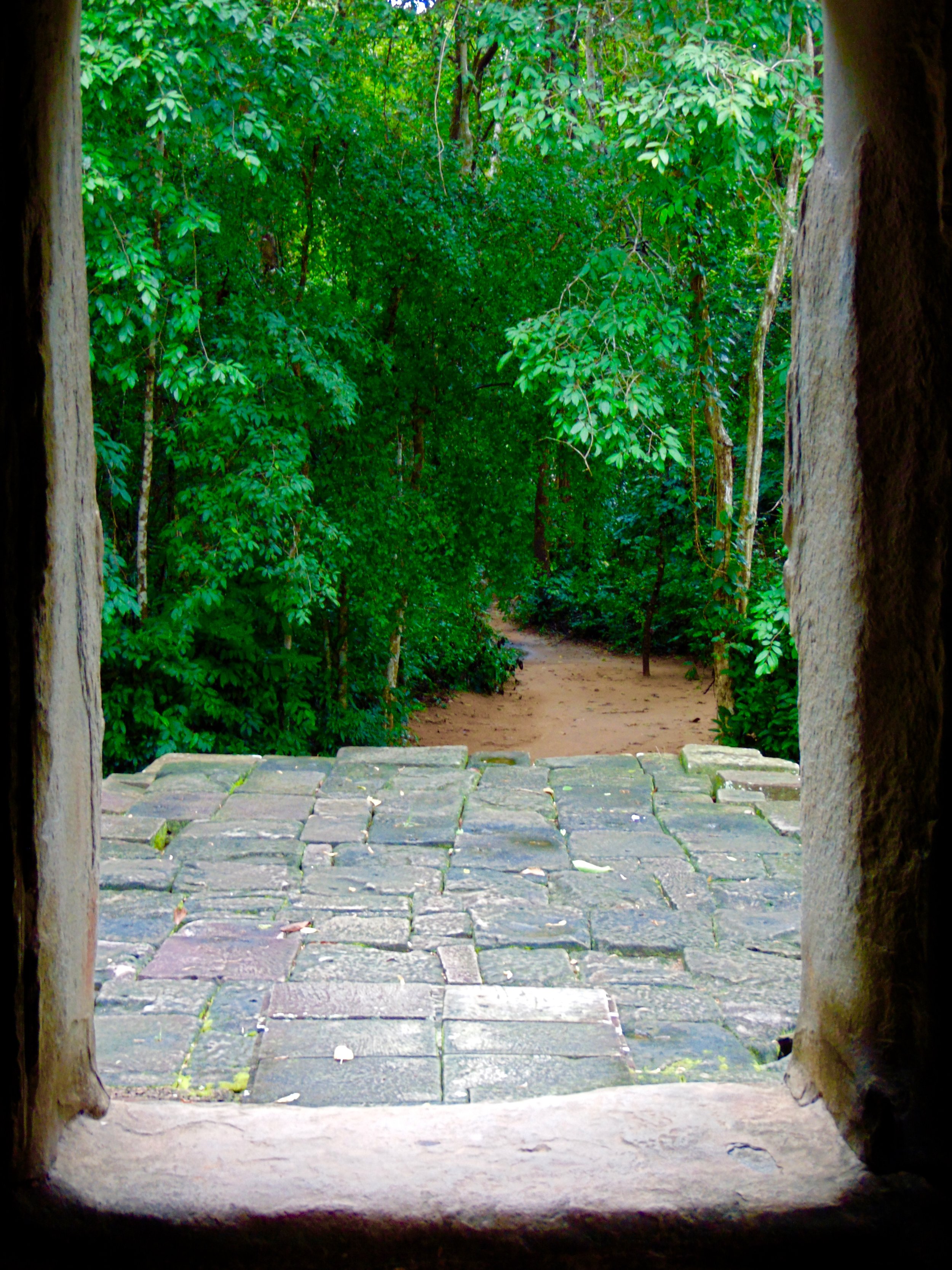
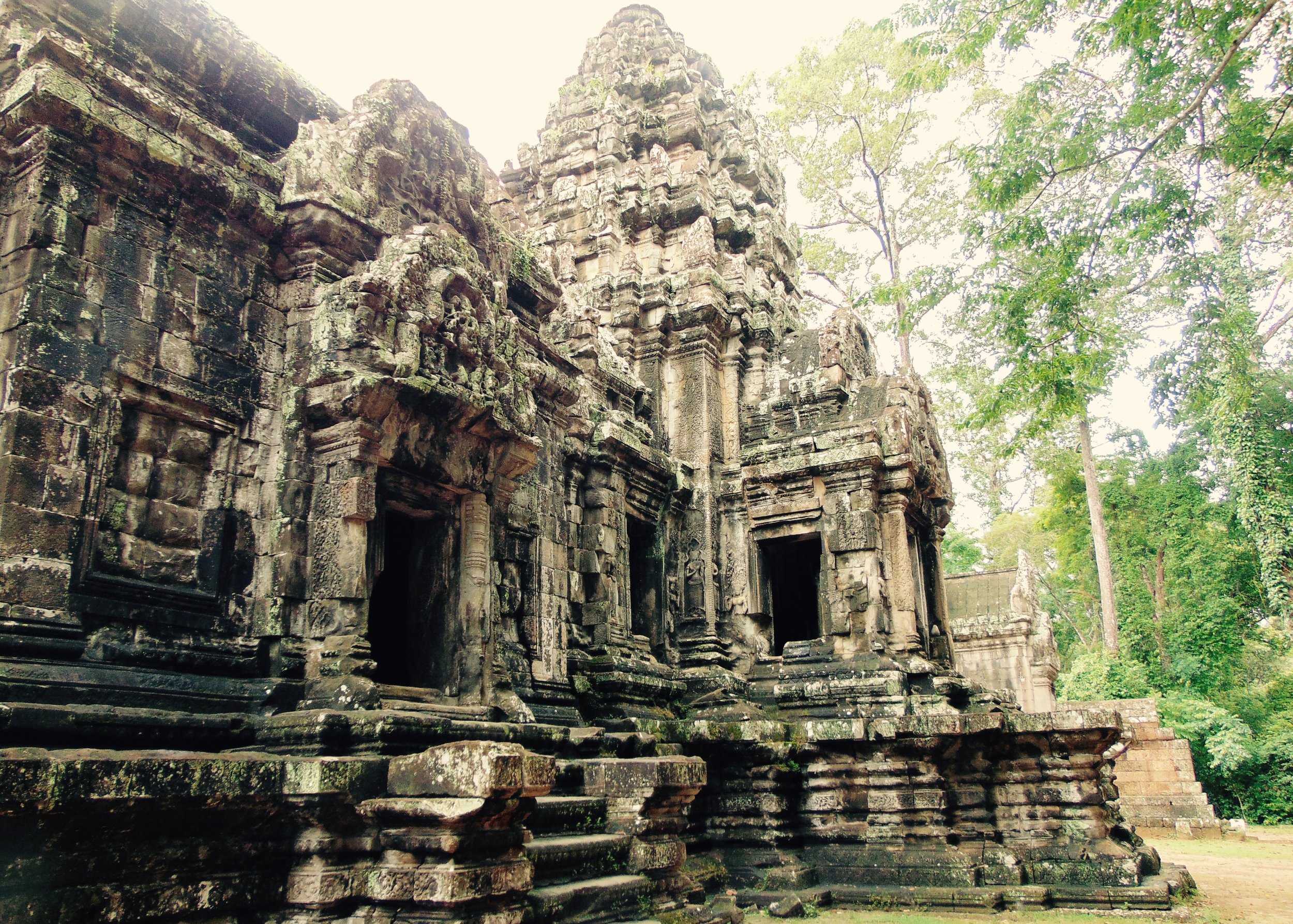
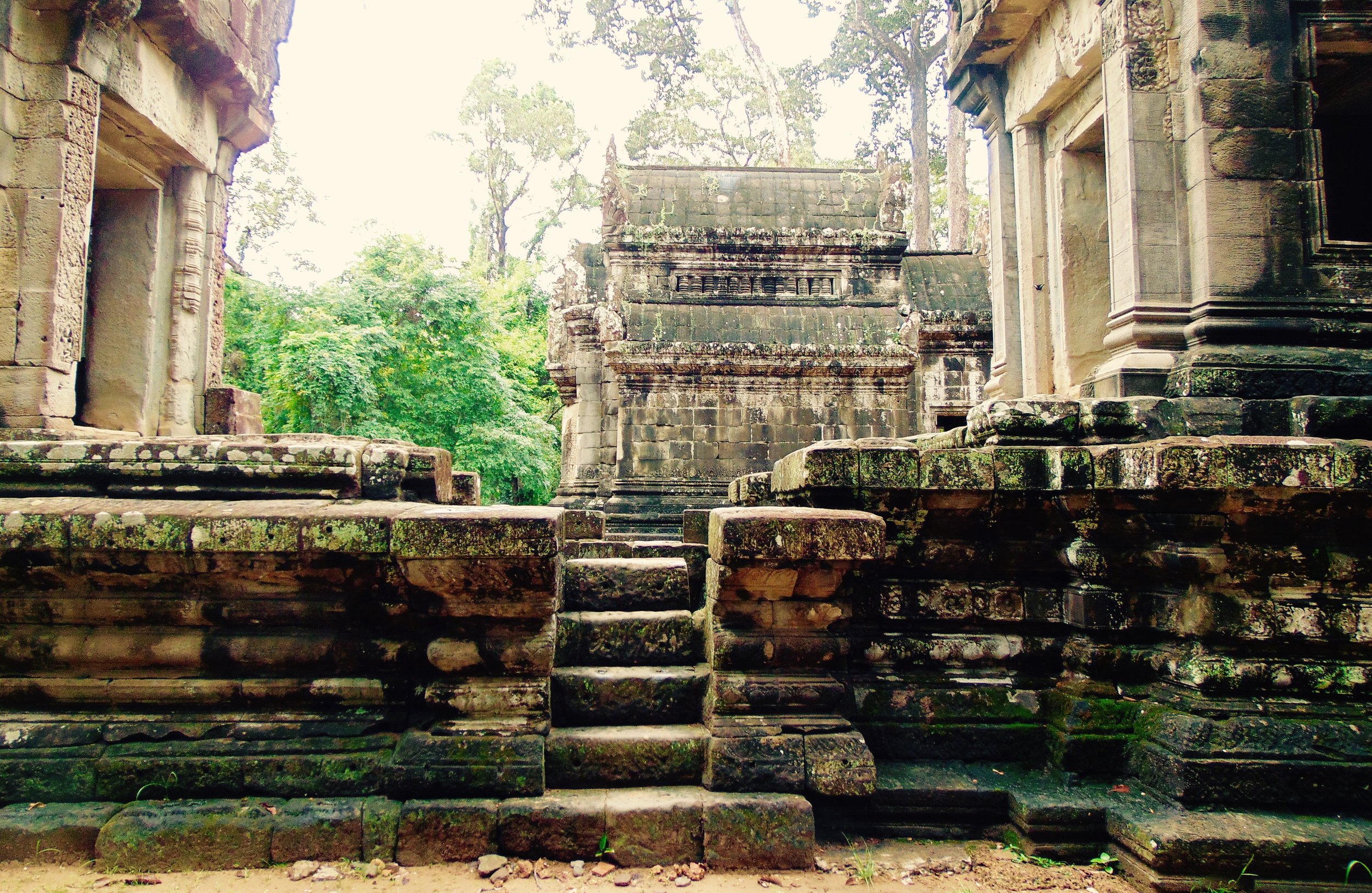
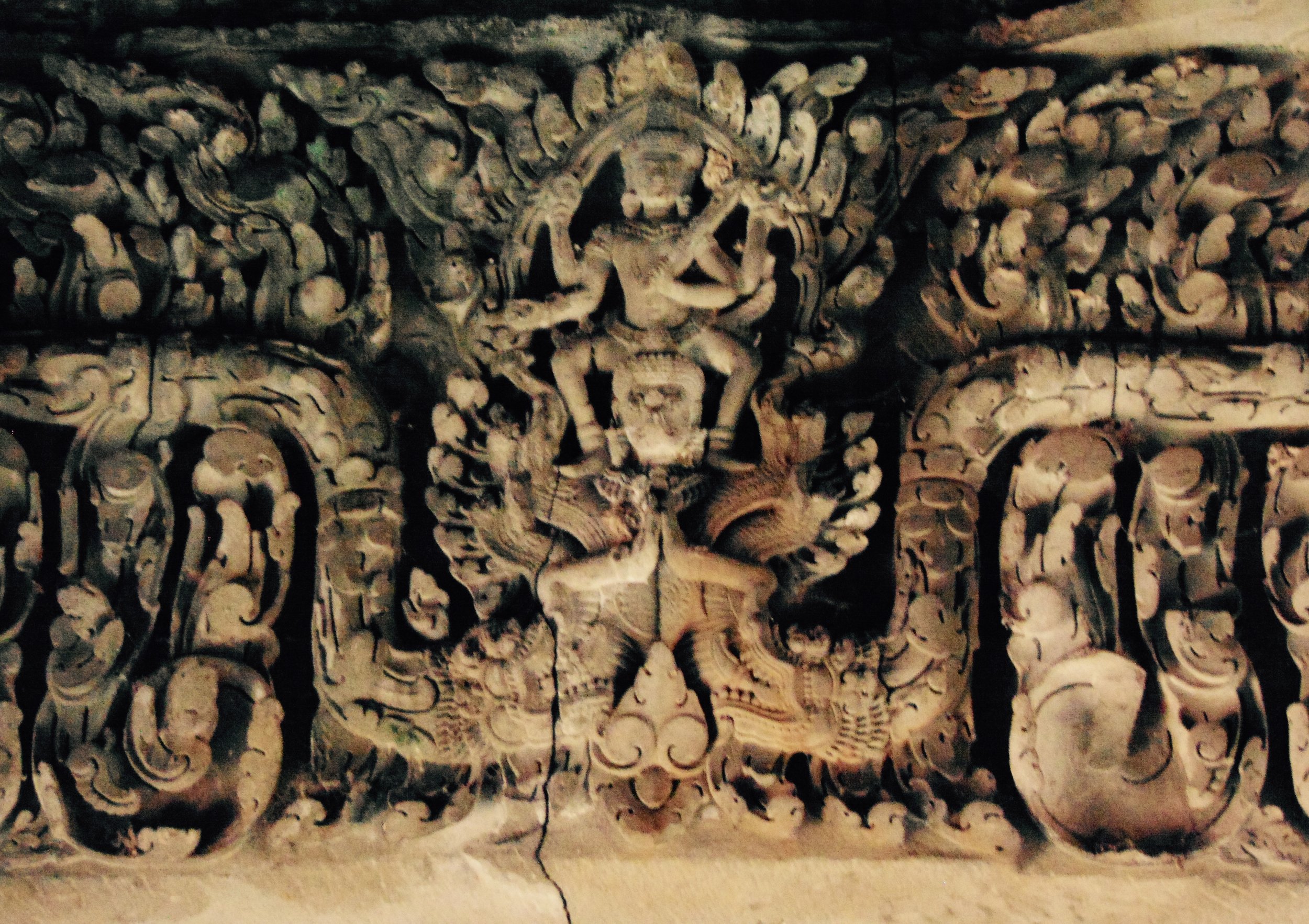
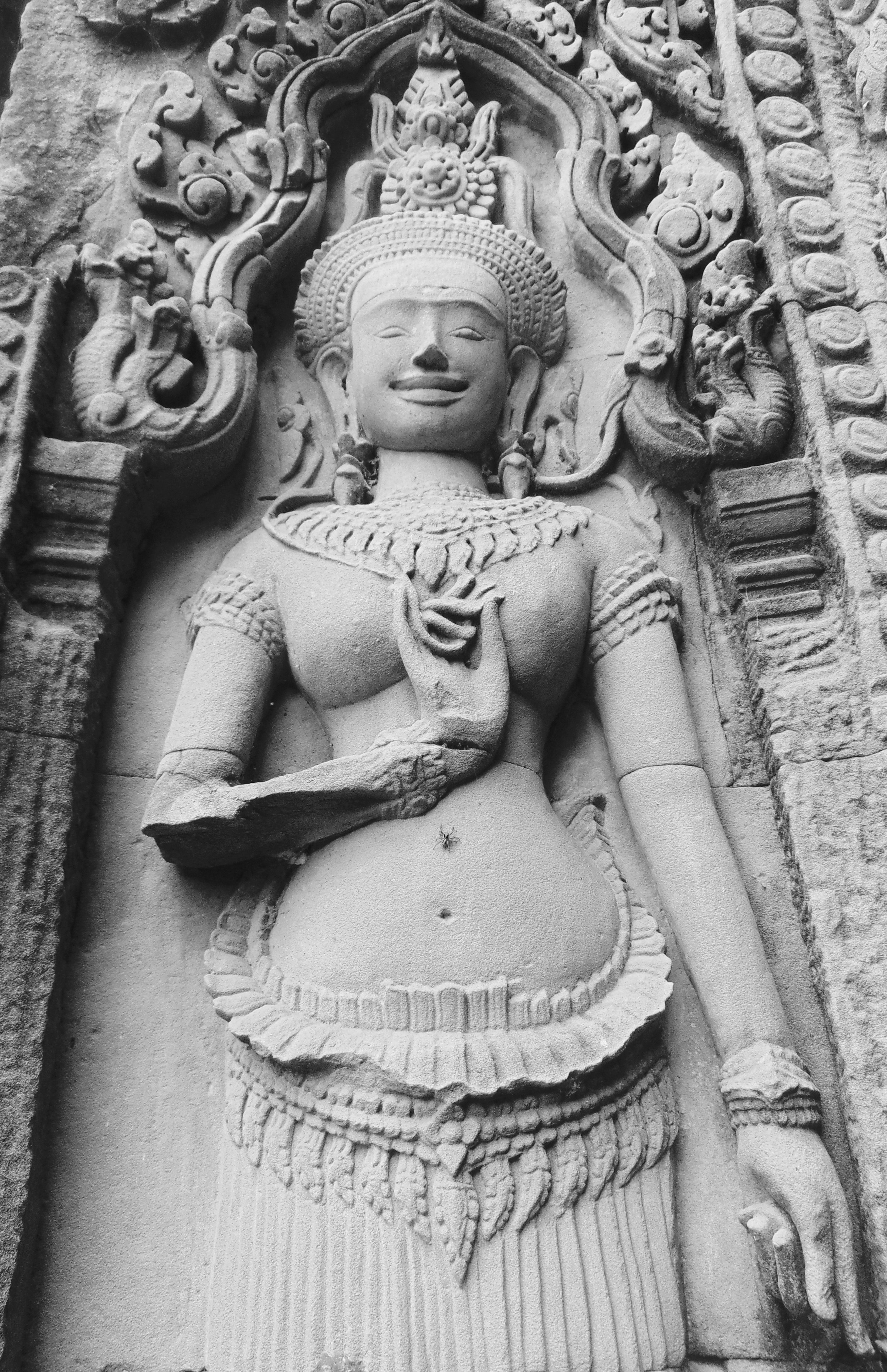
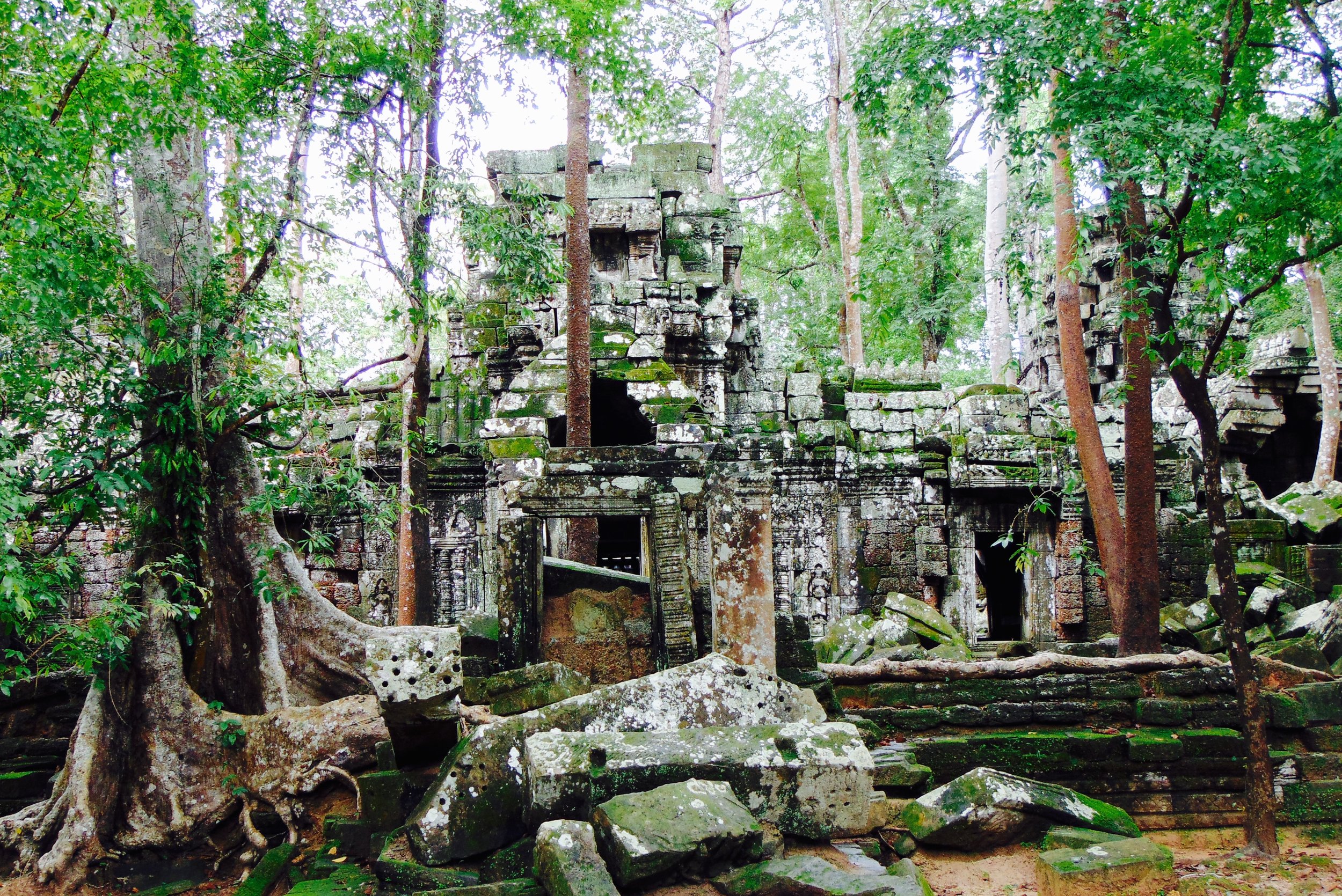
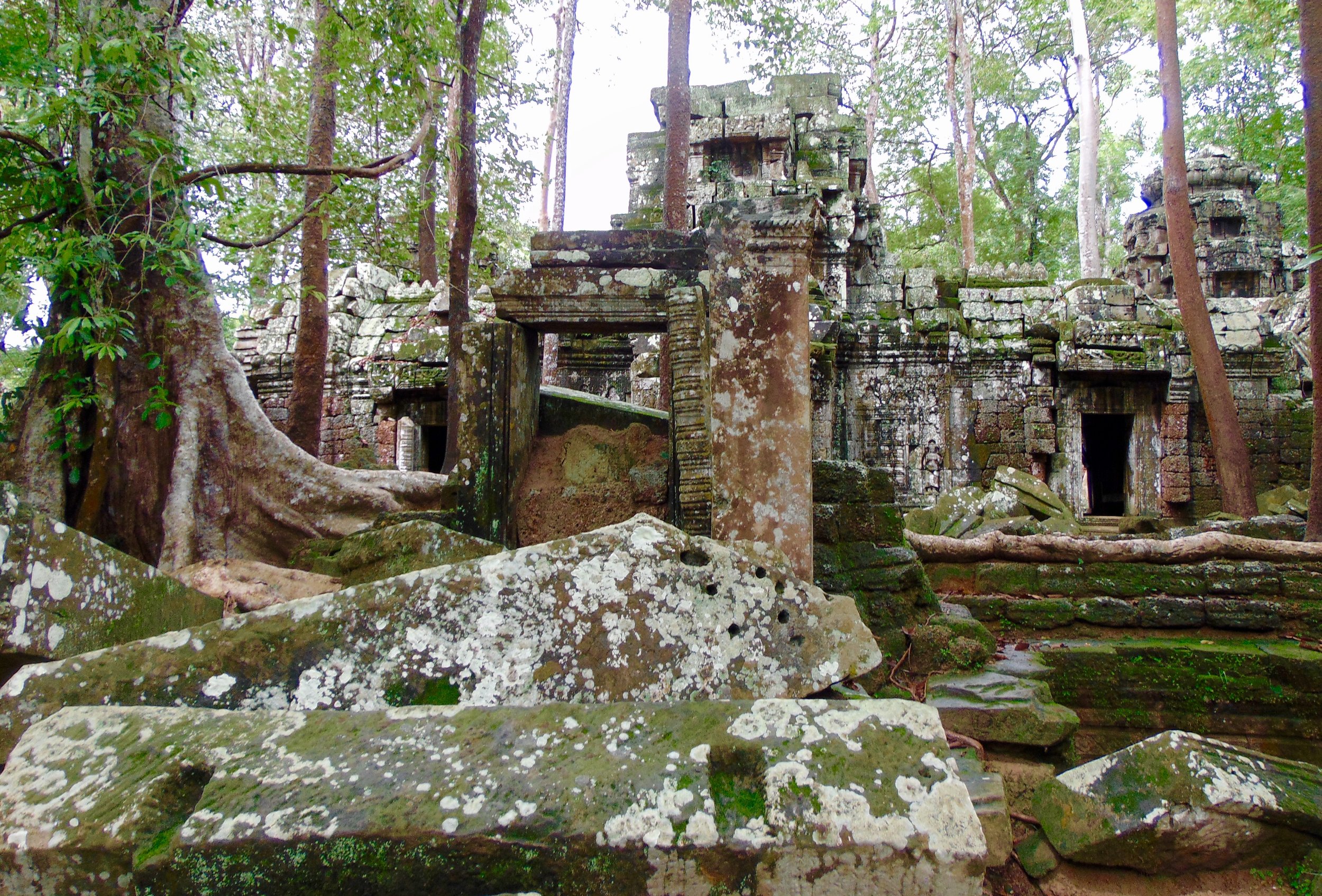
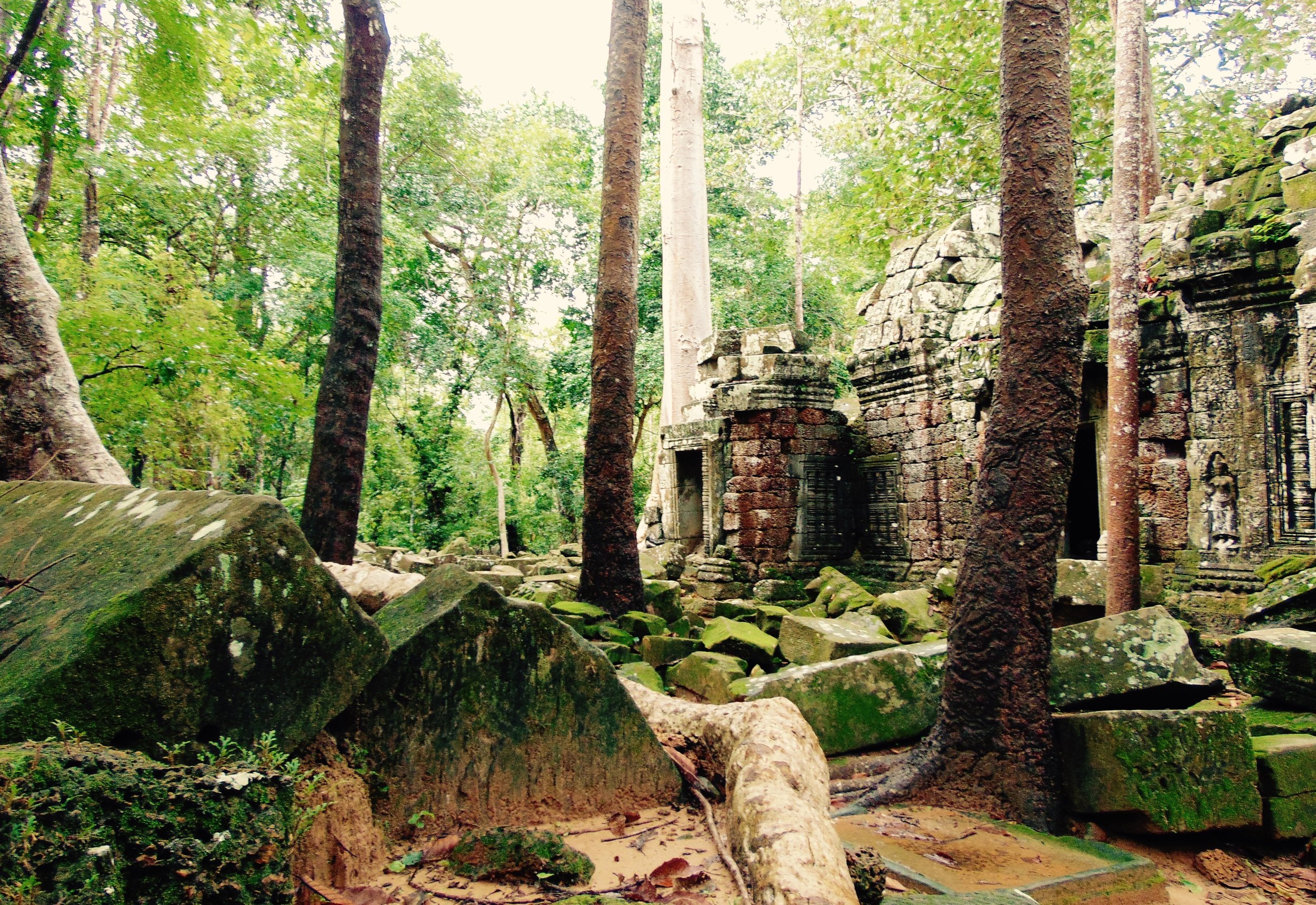
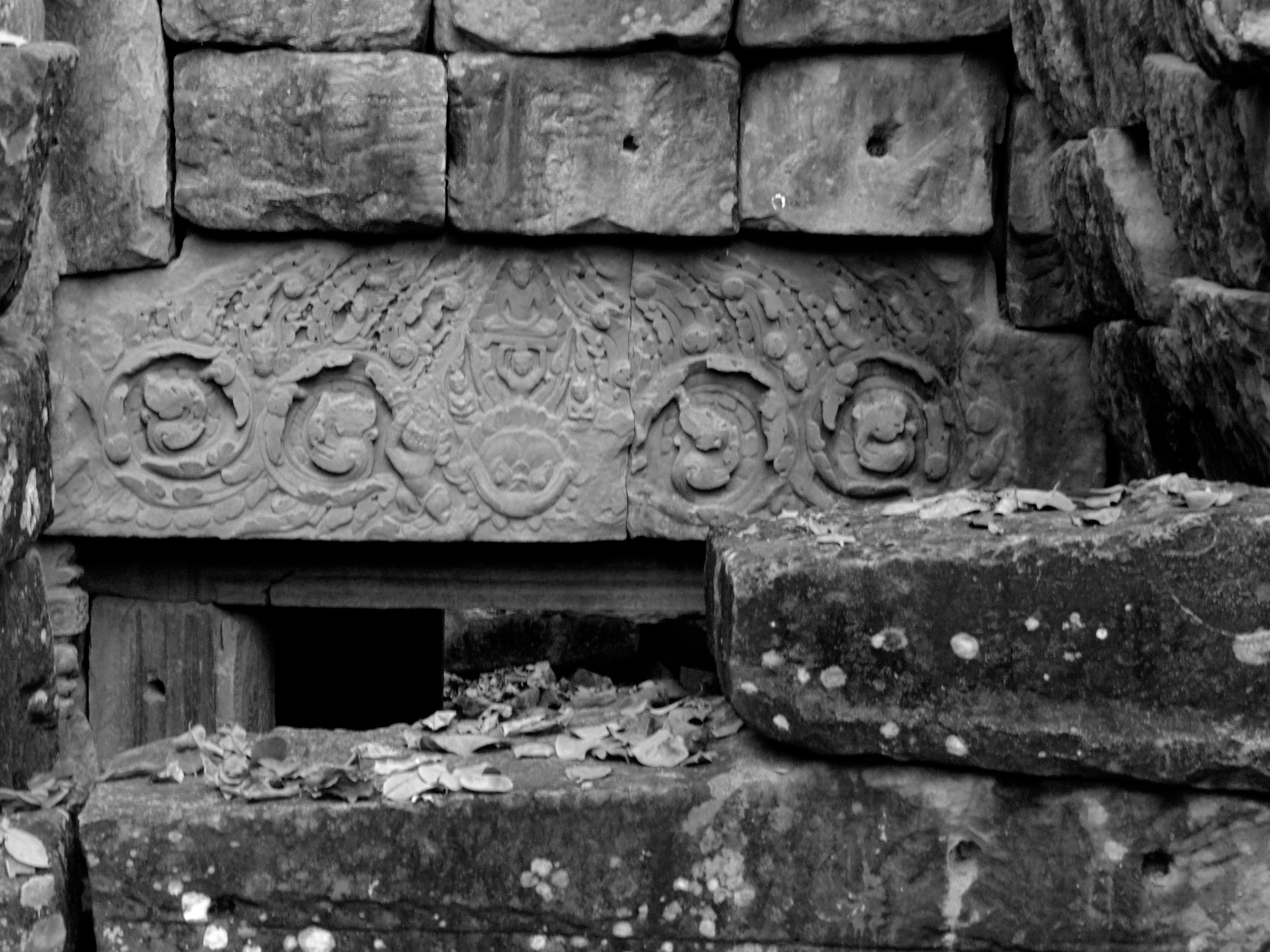
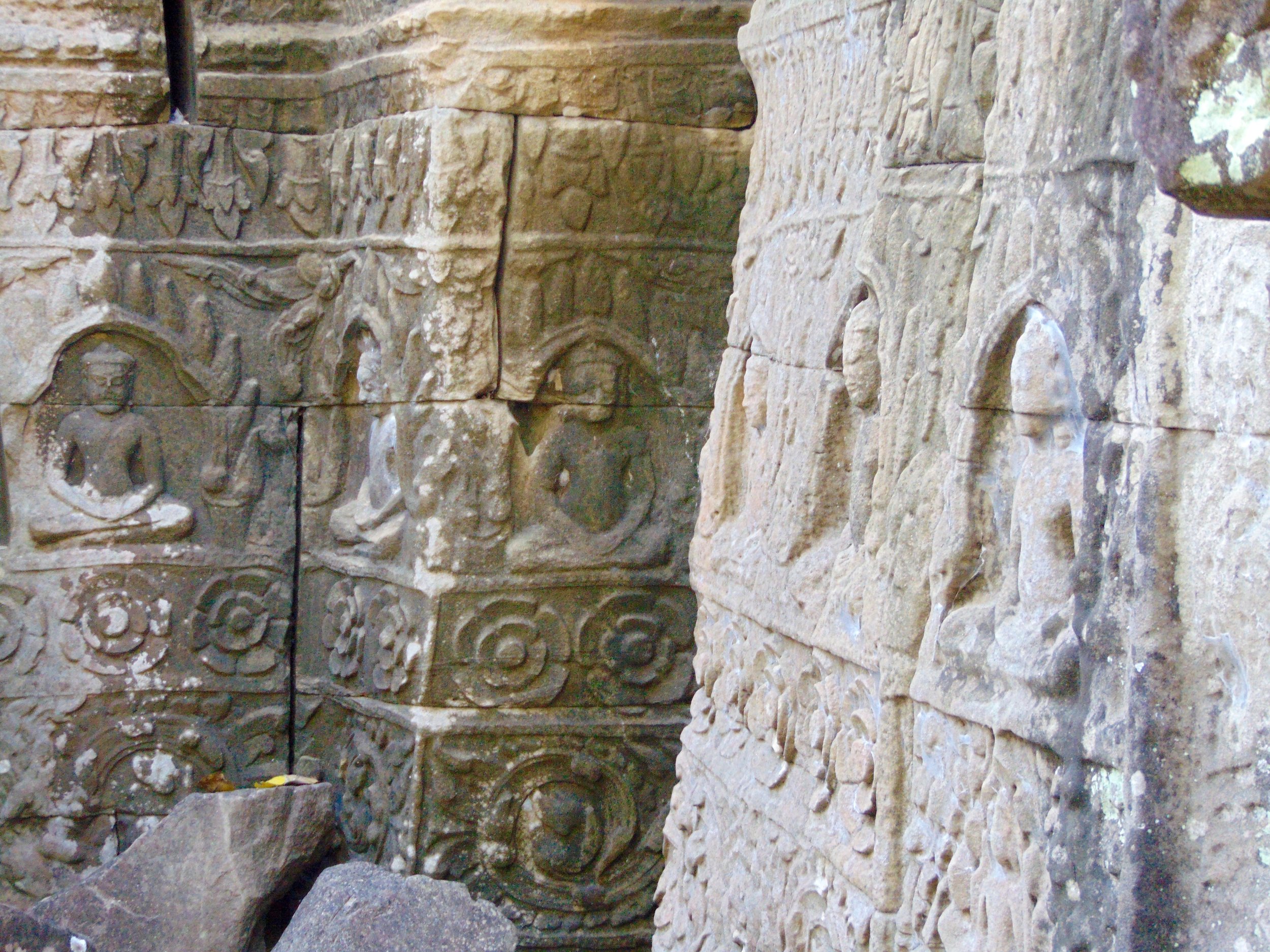
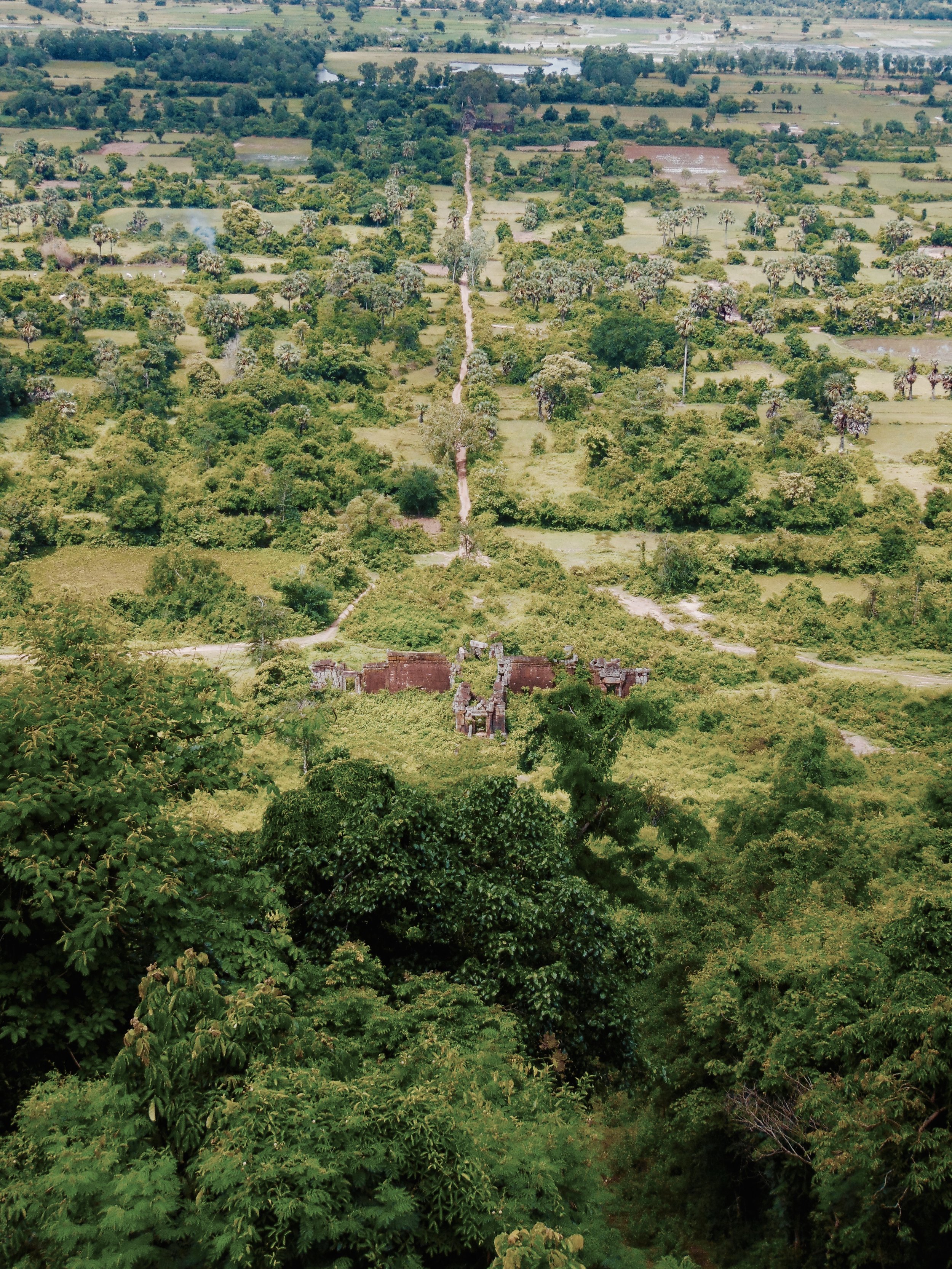Angkor Wat is one of the most important archaeological sites in South-East Asia. Stretching over some 400 km2, including forested area, Angkor Archaeological Park contains the magnificent remains of the different capitals of the Khmer Empire, from the 9th to the 15th century. These include the famous Temple of Angkor Wat and, at Angkor Thom, the Bayon Temple with its countless sculptural decorations. The ICC-ANGKOR 2015 report reveals that, since 1993, more than 36 countries, 12 intergovernmental groups and 38 international teams have contributed millions of dollars to conservation, restoration, research and sustainable development projects.
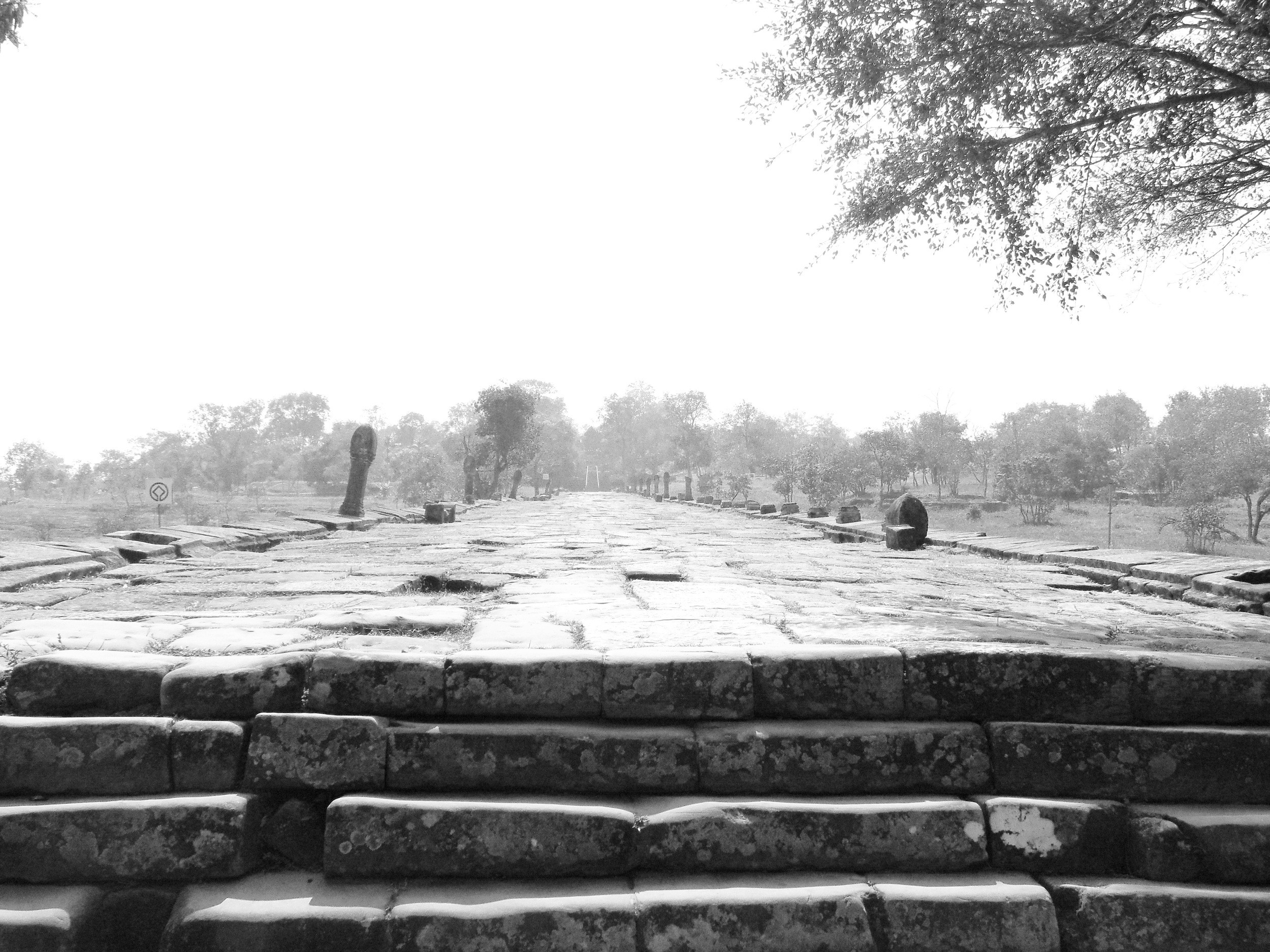
Image of Angkor's processional entrance. Courtesy of Vincent Ko Hon Chui, UNESCO.
APSARA, the Authority for the Protection and Management of Angkor and the Region of Siem Reap, is in charge of research, protection and conservation of the site, as well as urban and tourist development in surrounding areas. This site and it's research teams are located in Siem Reap, Cambodia.
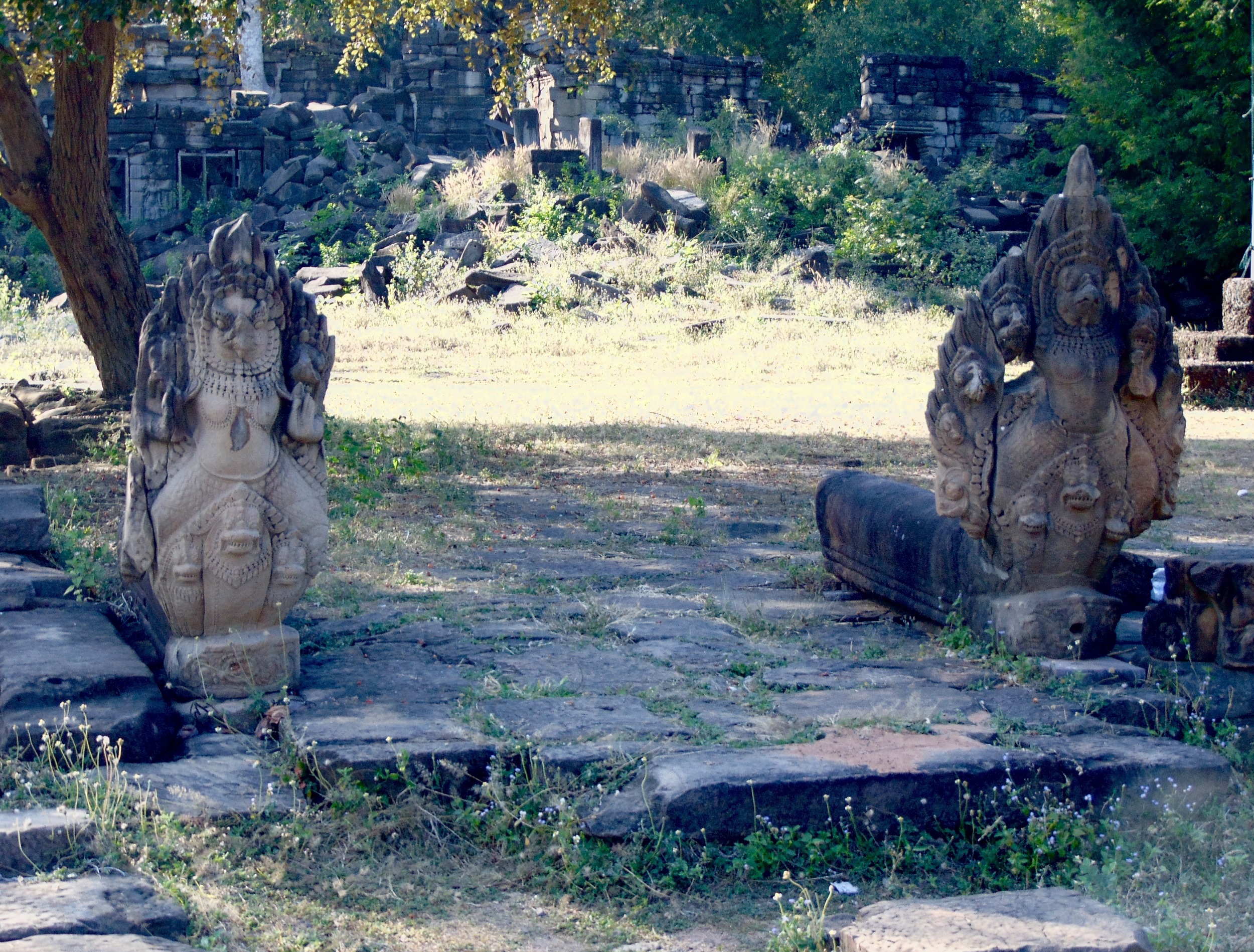
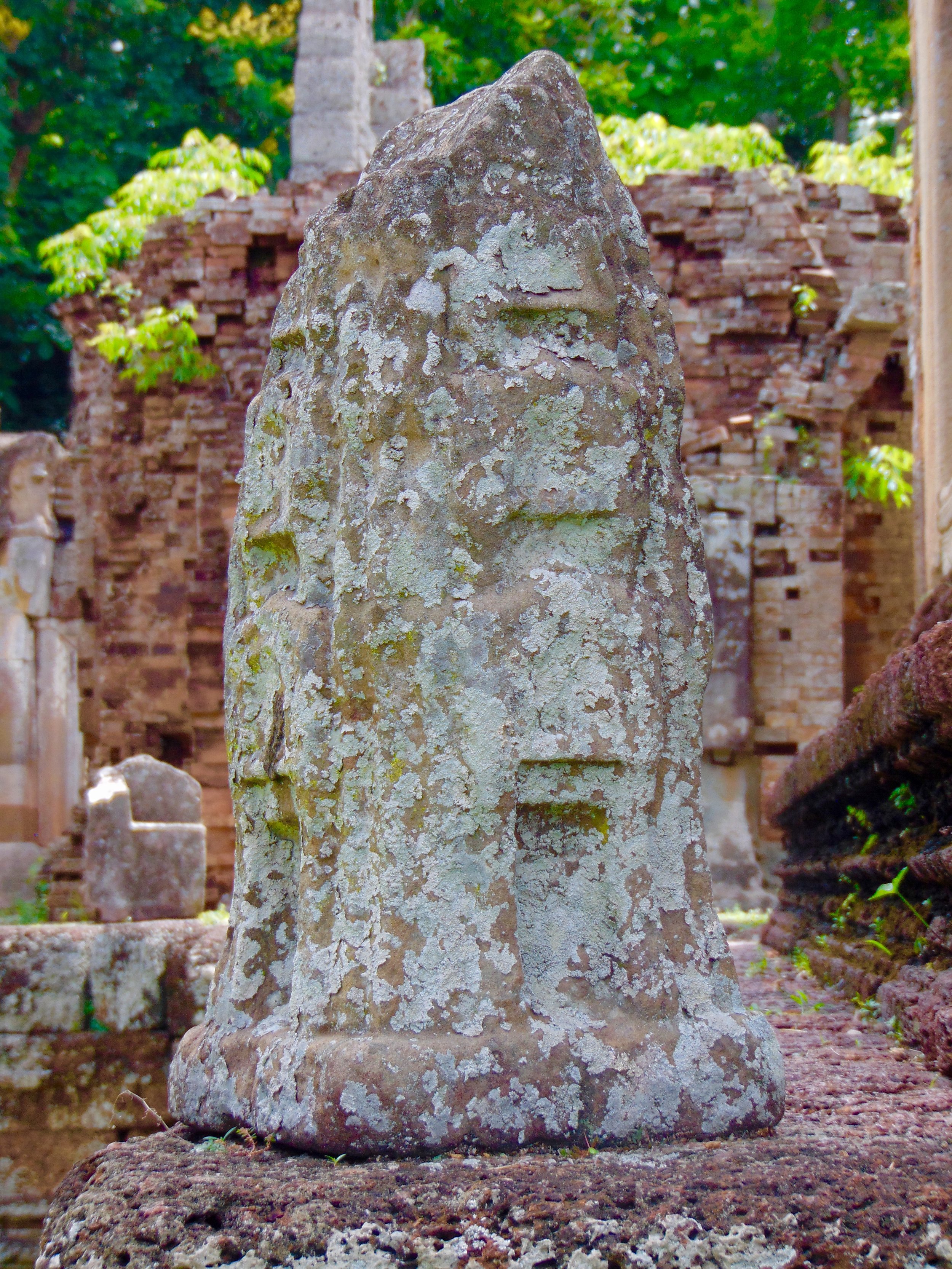
Guardians of Angkor Wat. Courtesy of SKH, 2001.
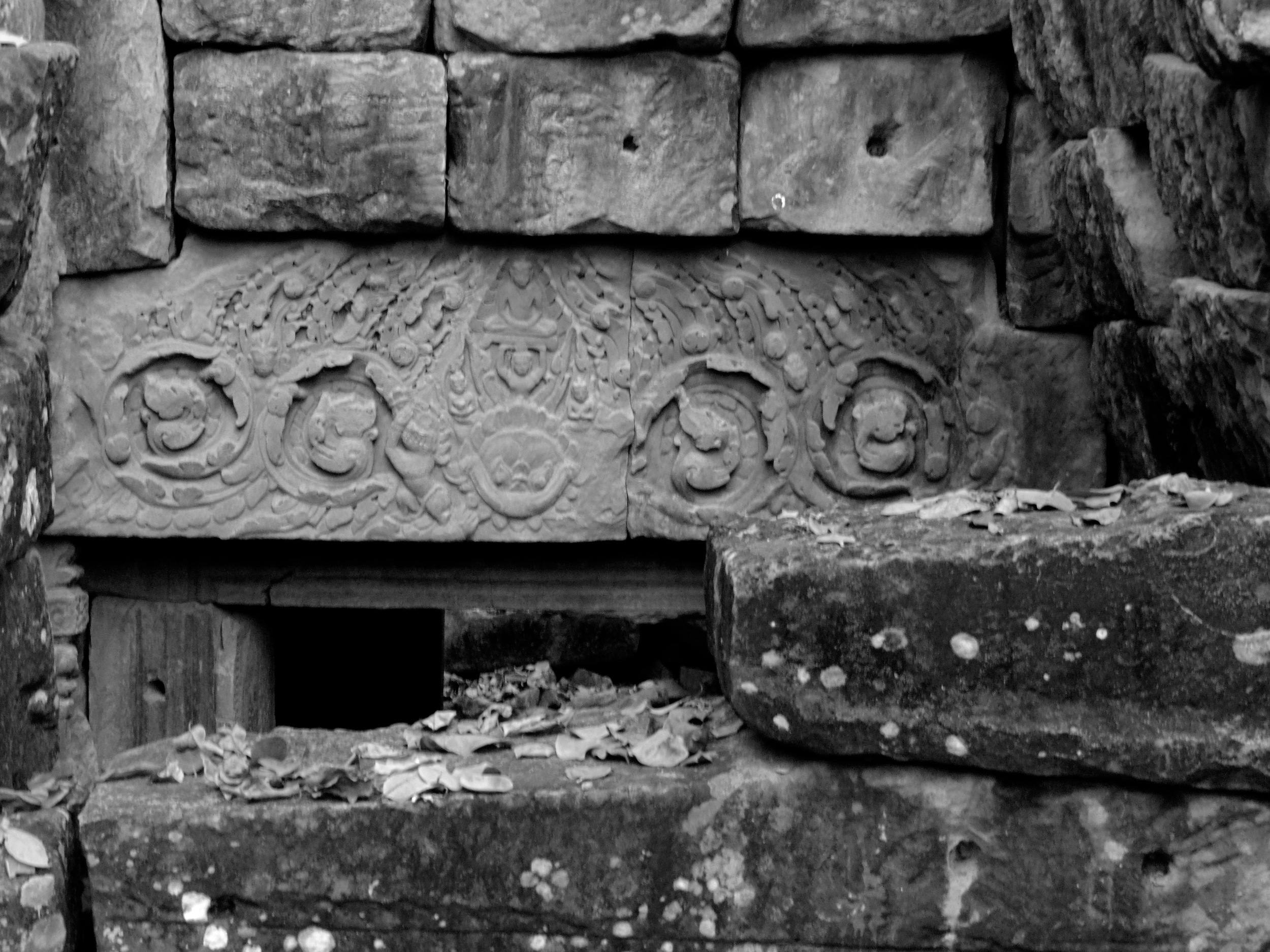
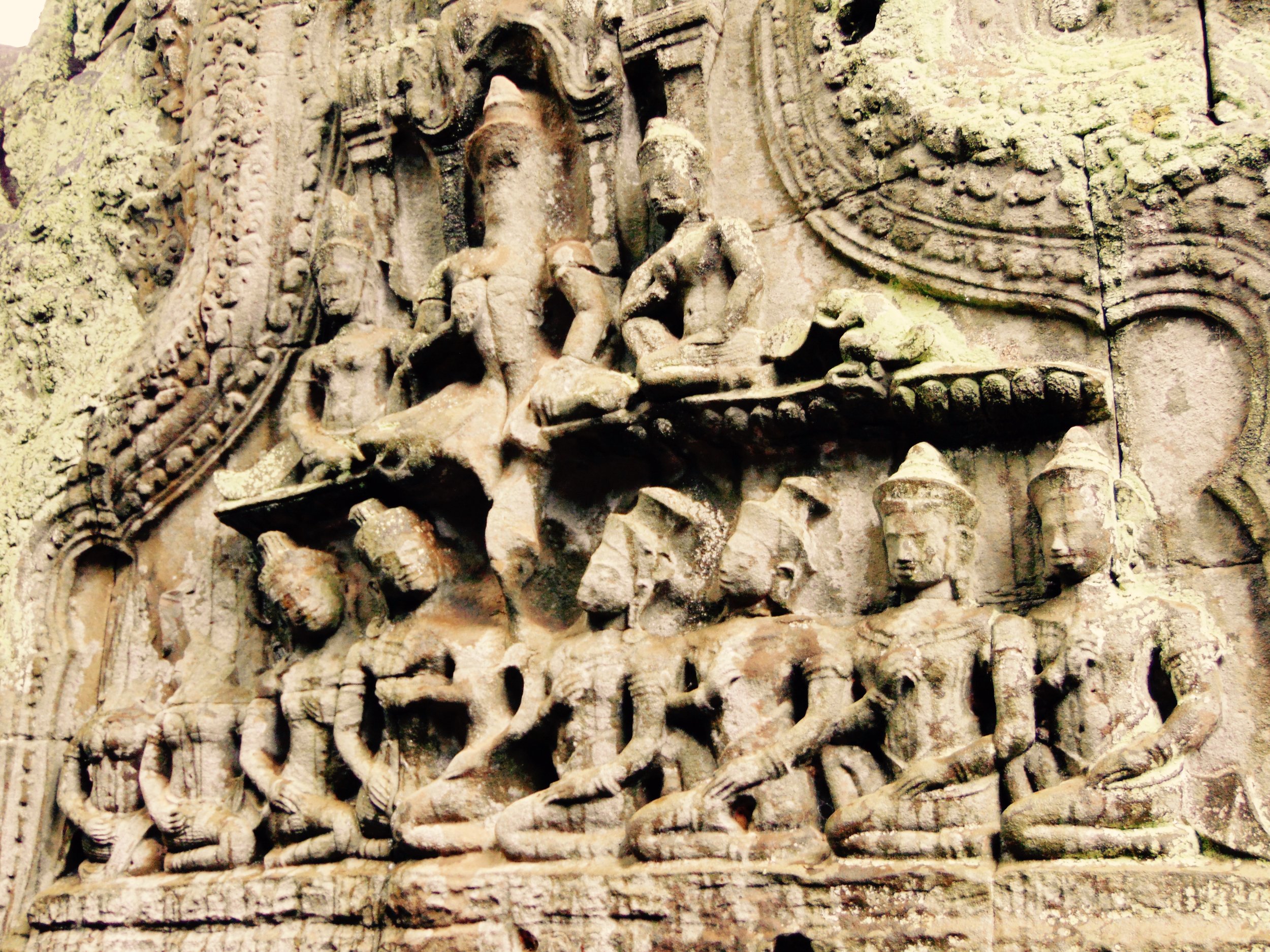
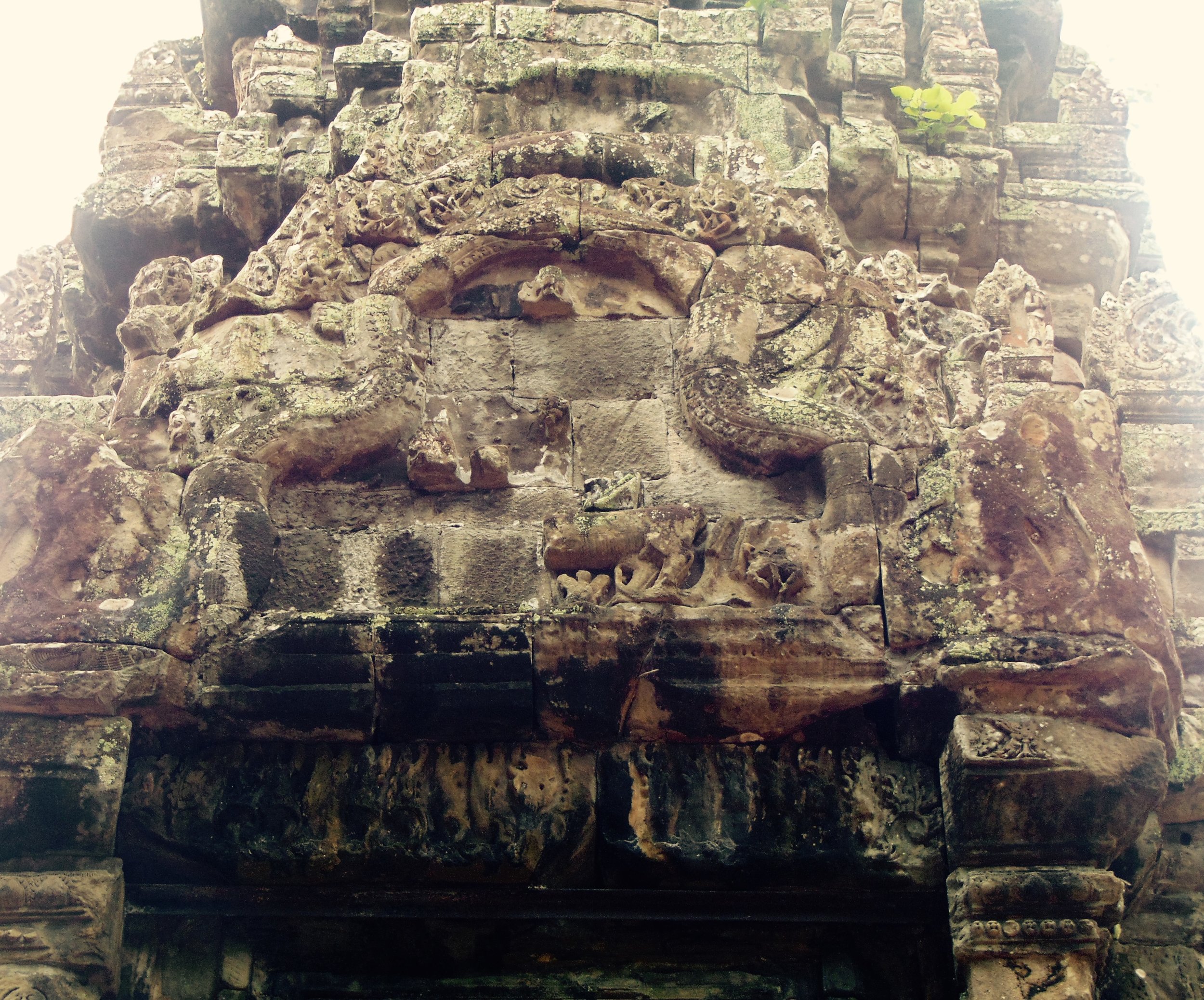
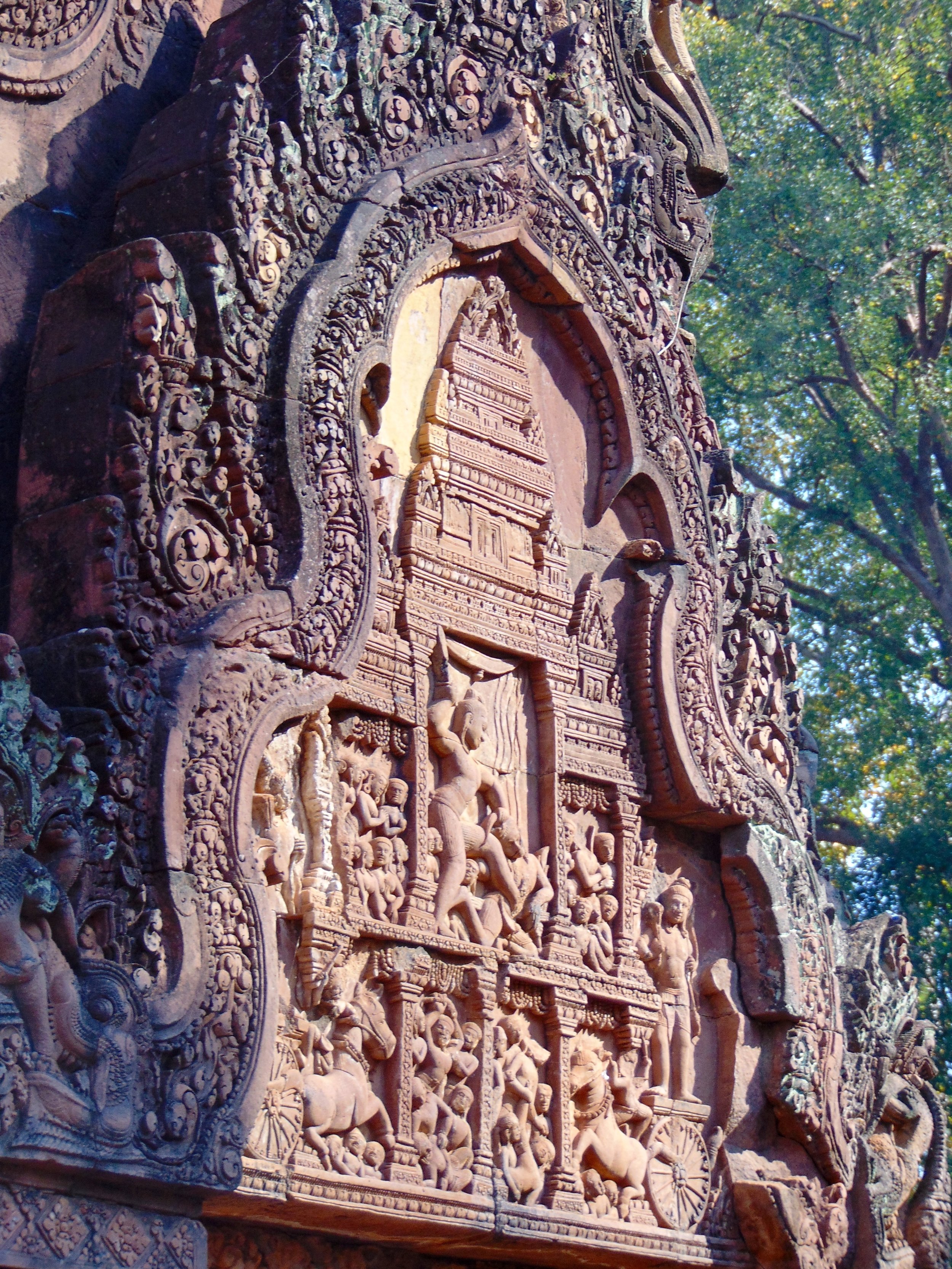
The Bayon, within the Angkor Wat. Courtesy of SKH, 2001
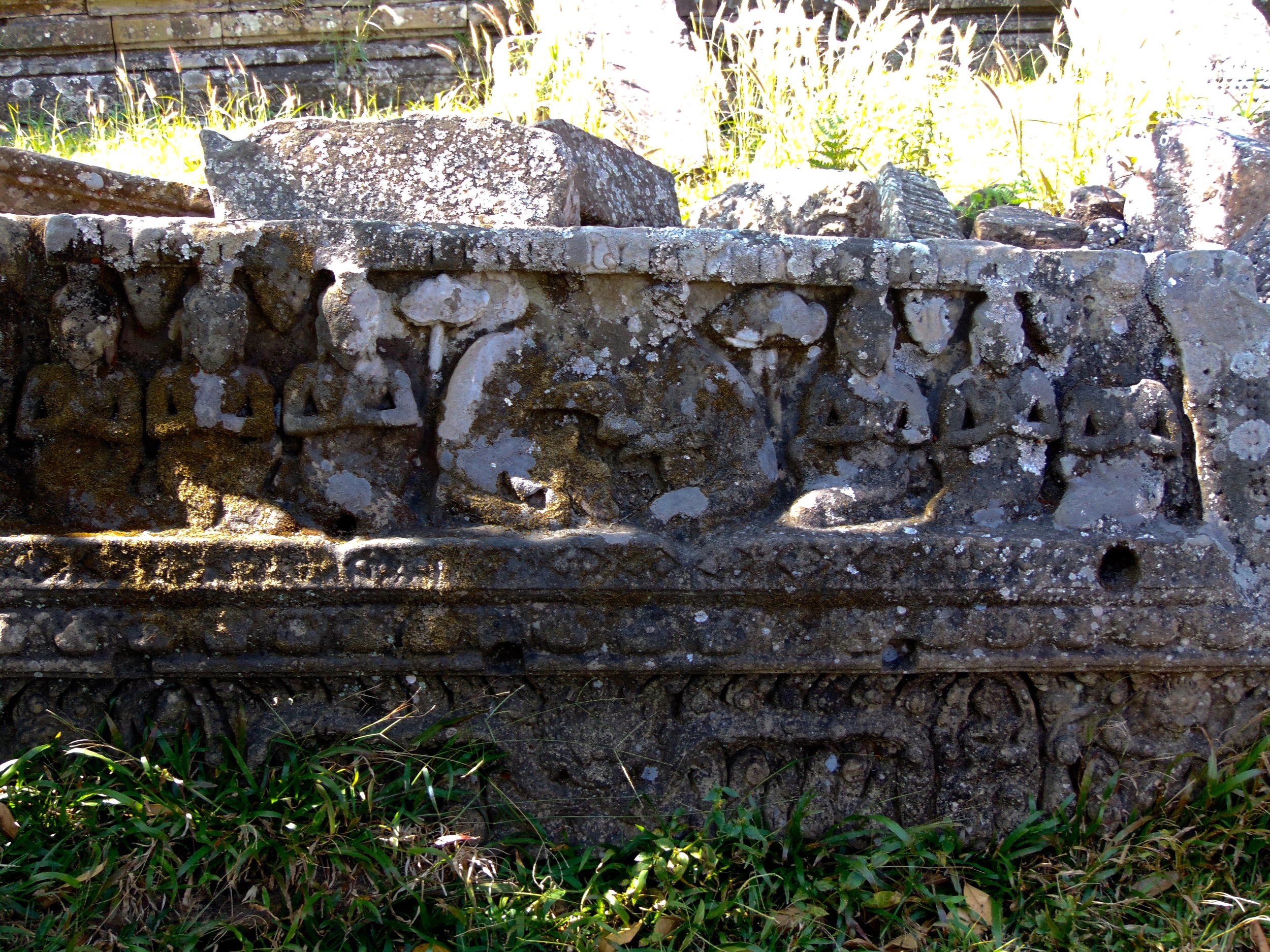
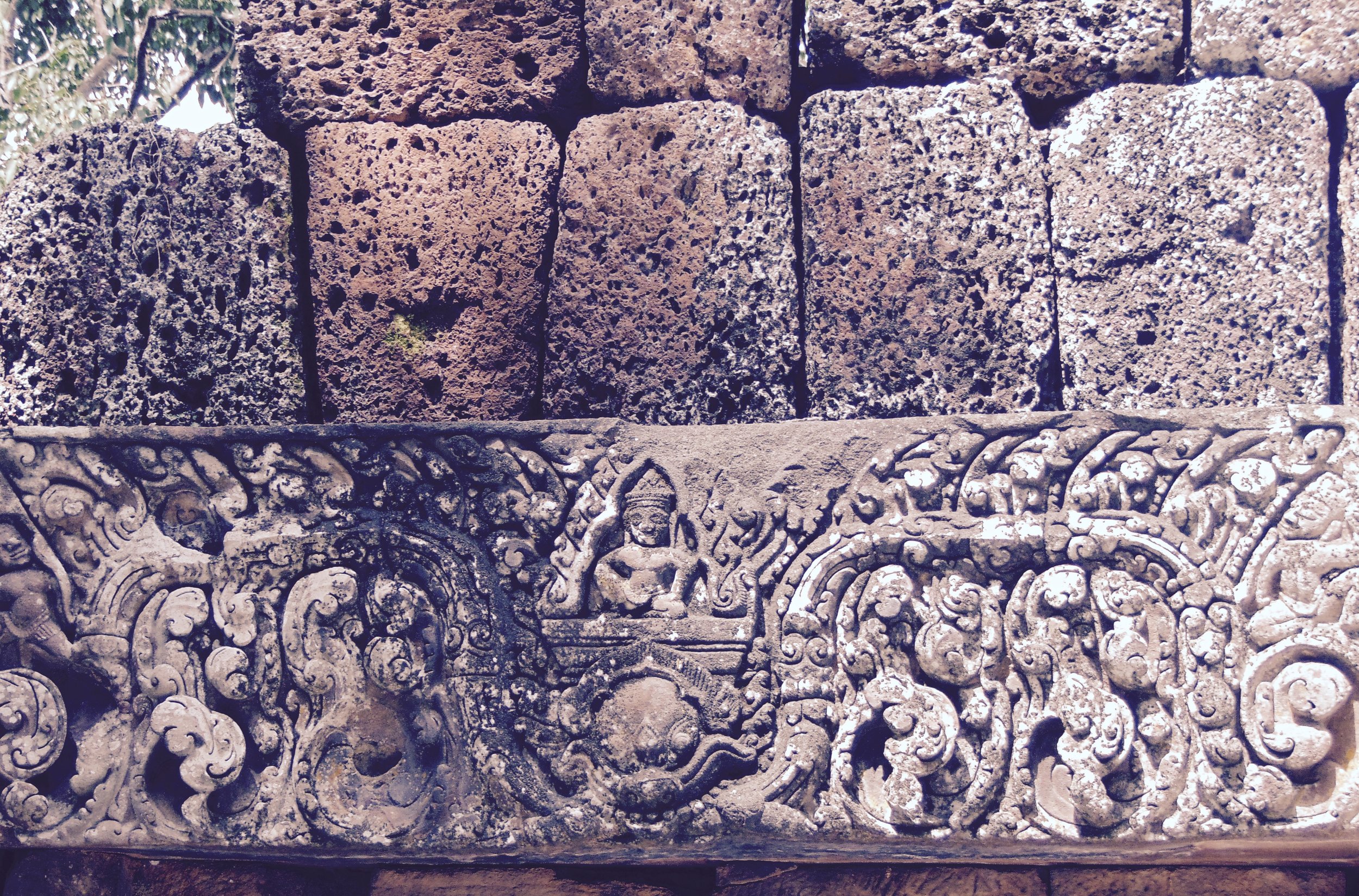
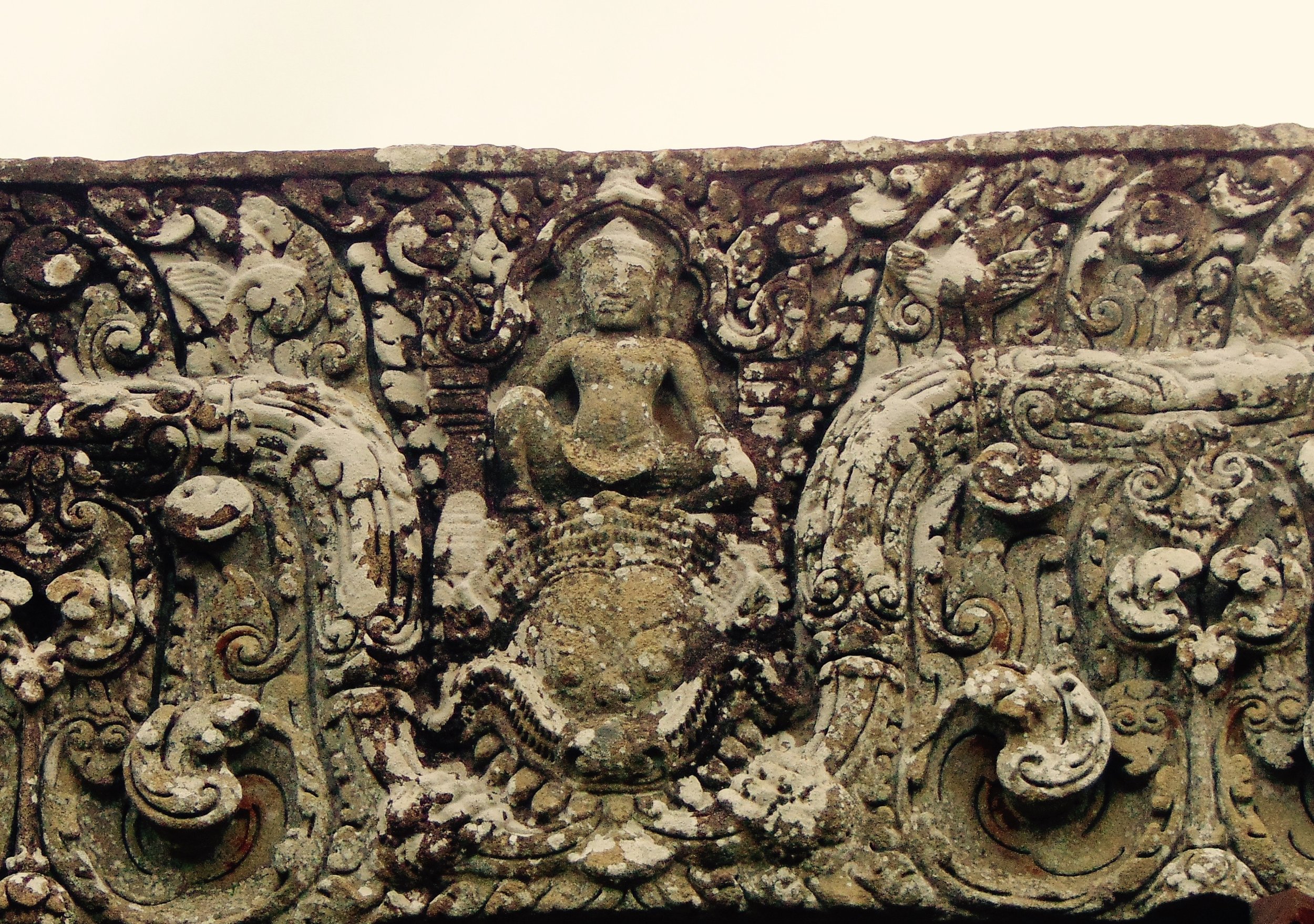
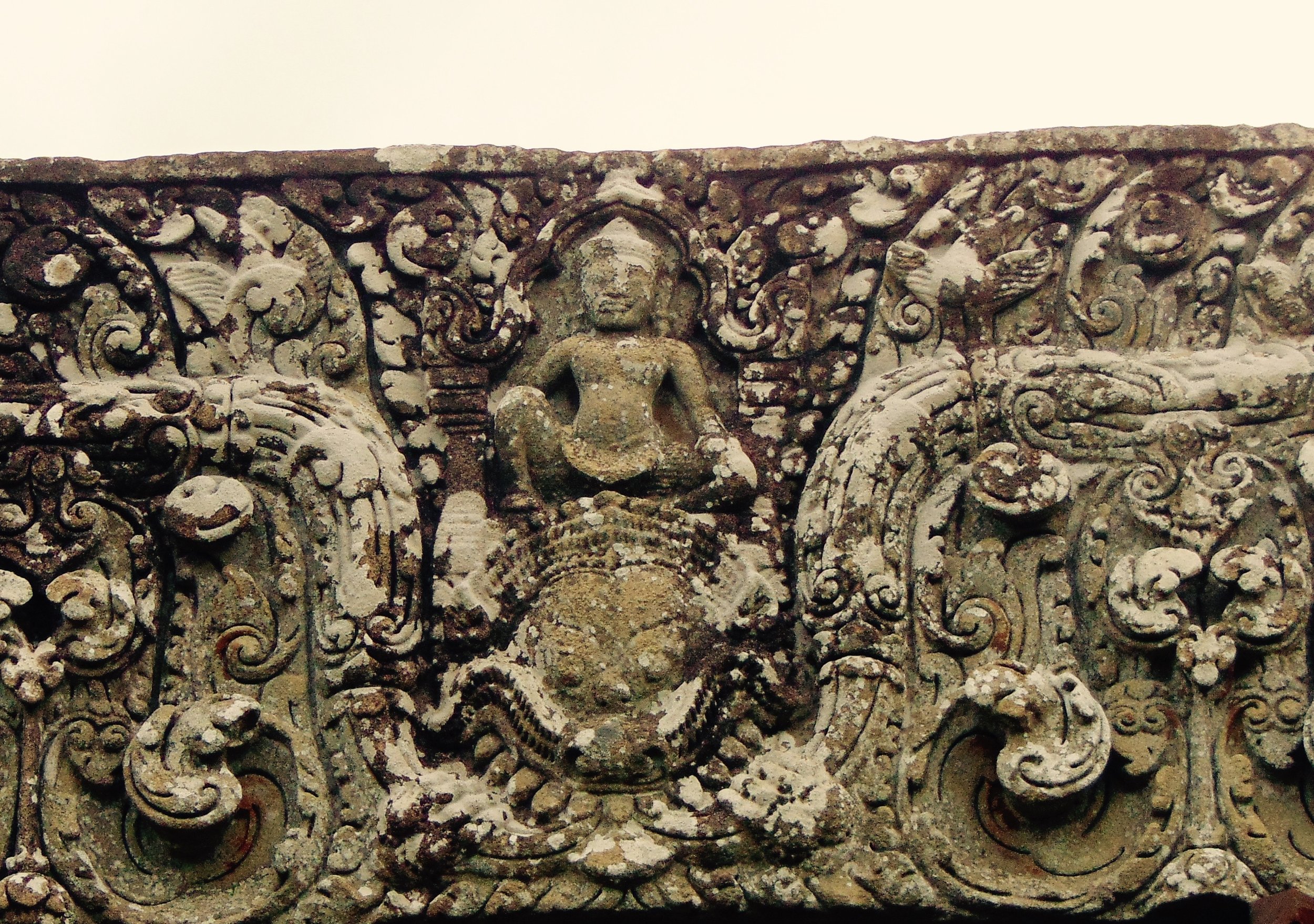
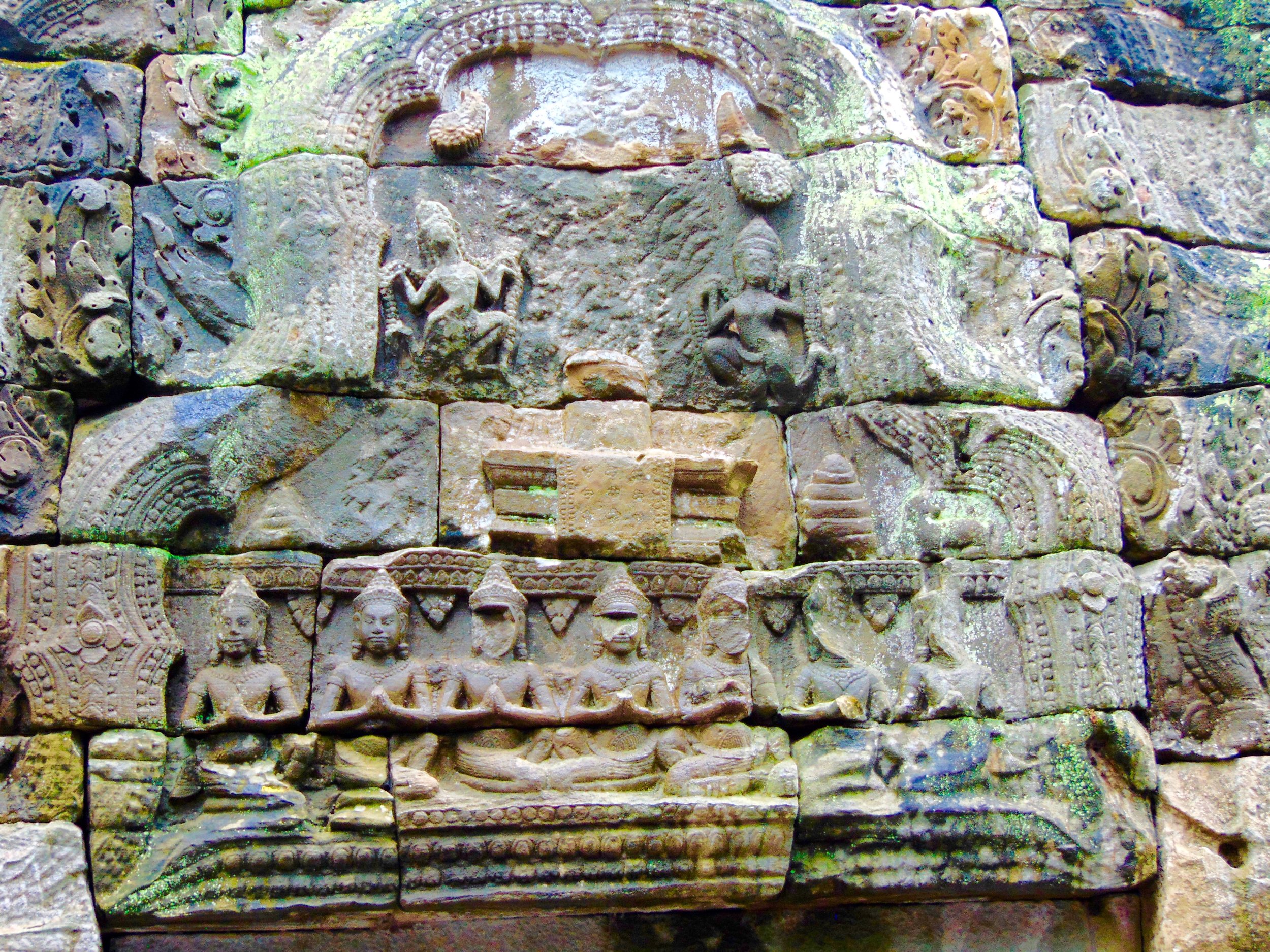
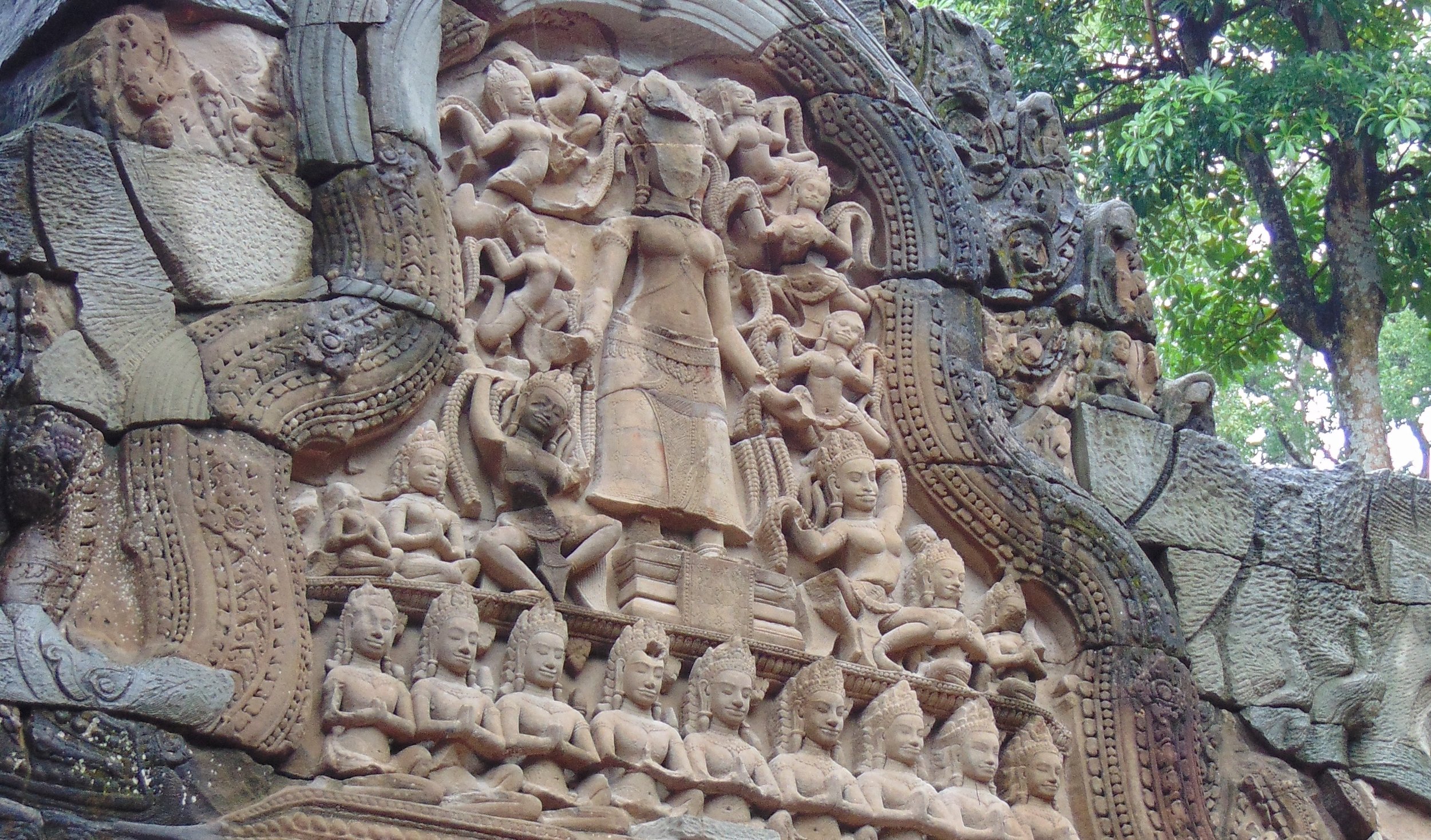
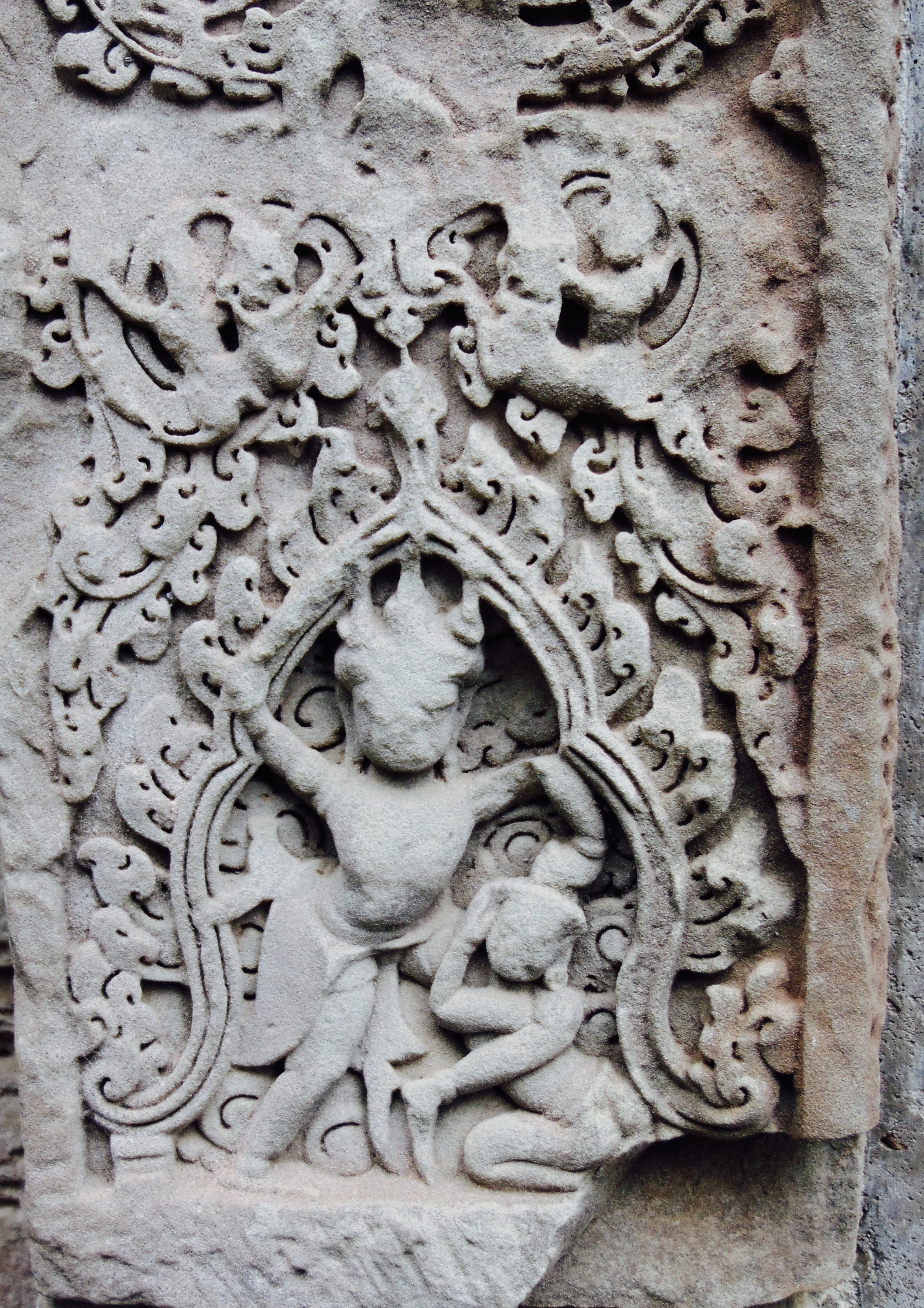
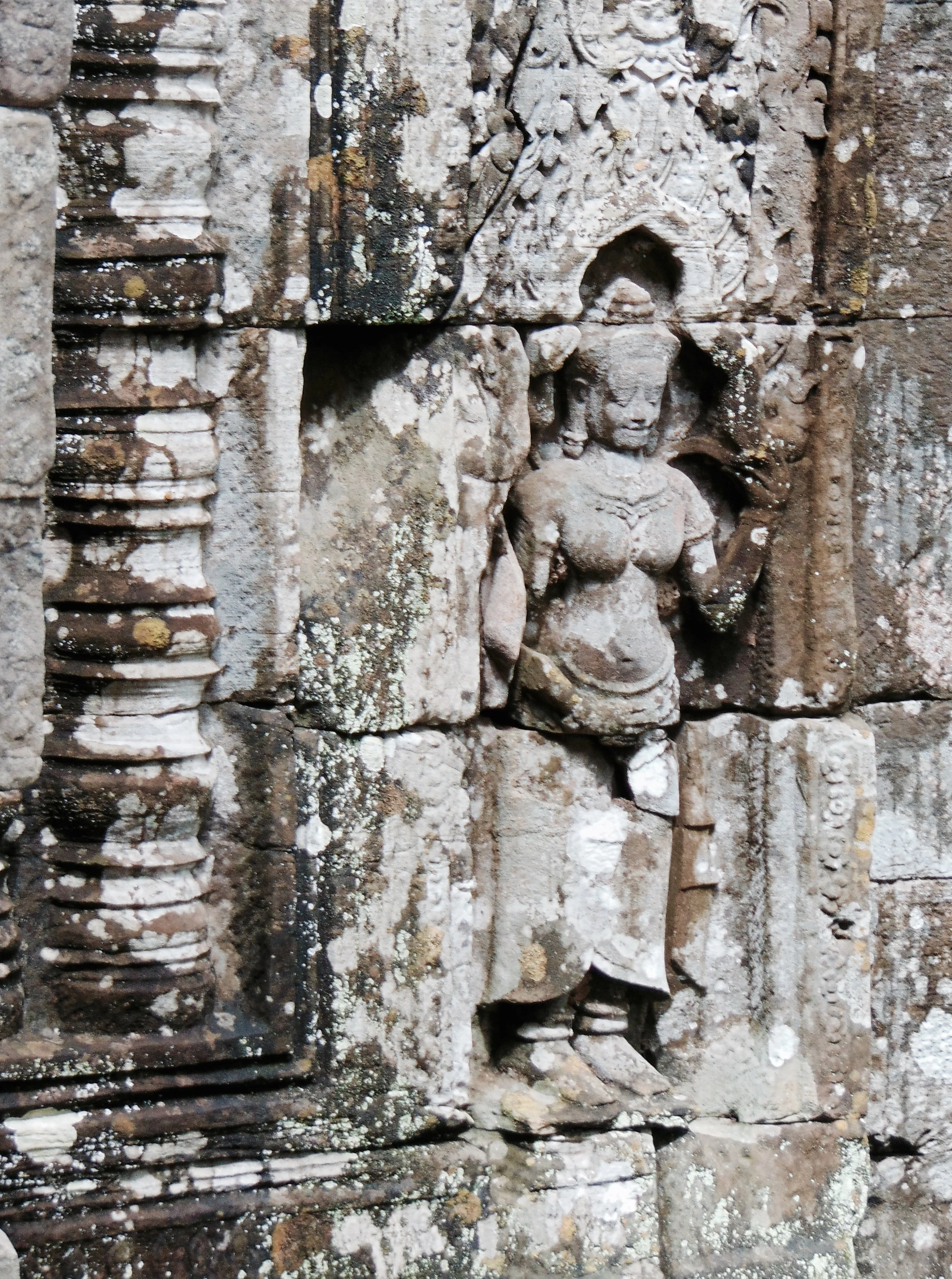
Image of an Apsara in the Angkor temple complex, Image courtesy of SKH, 2001.
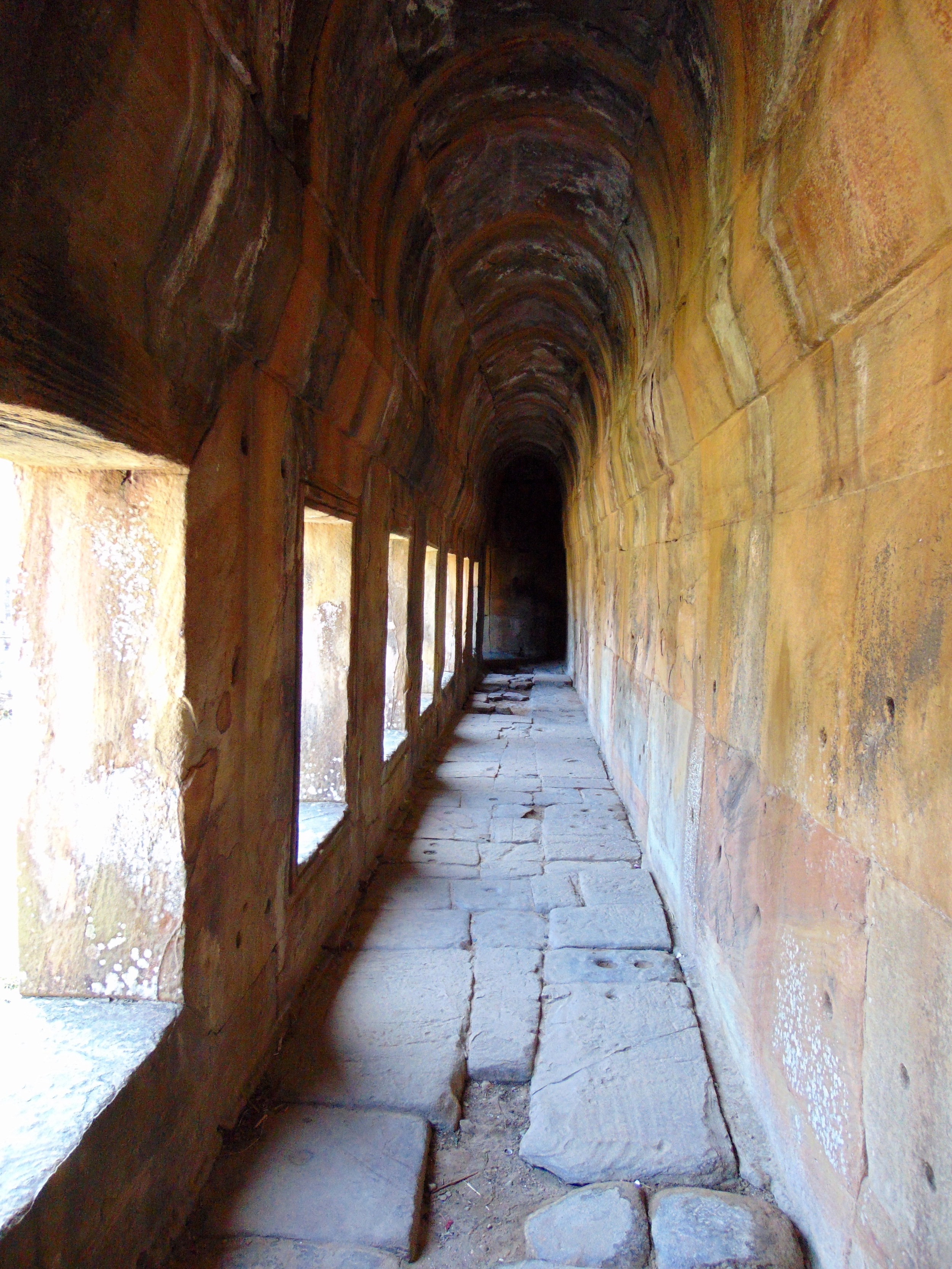
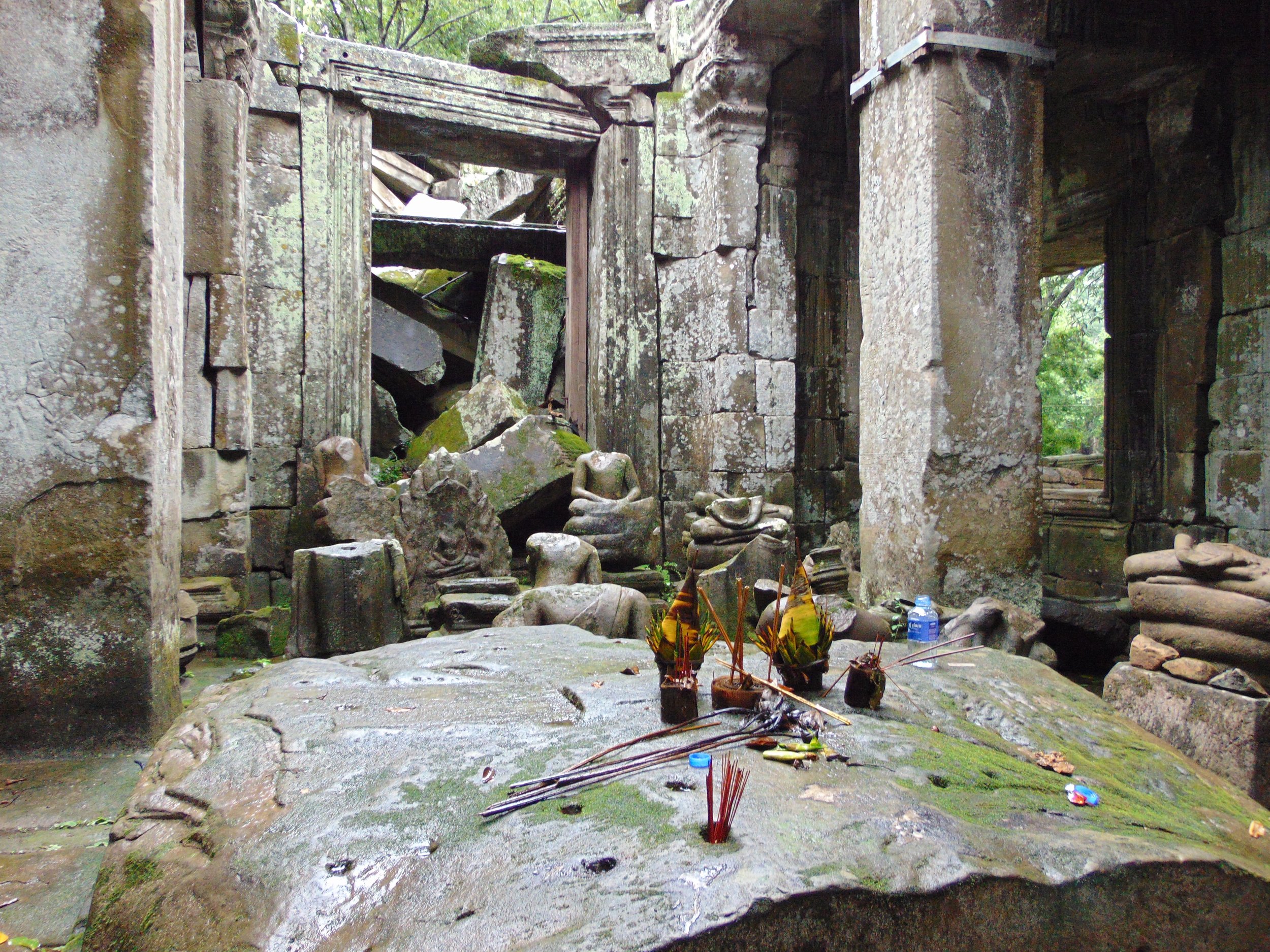
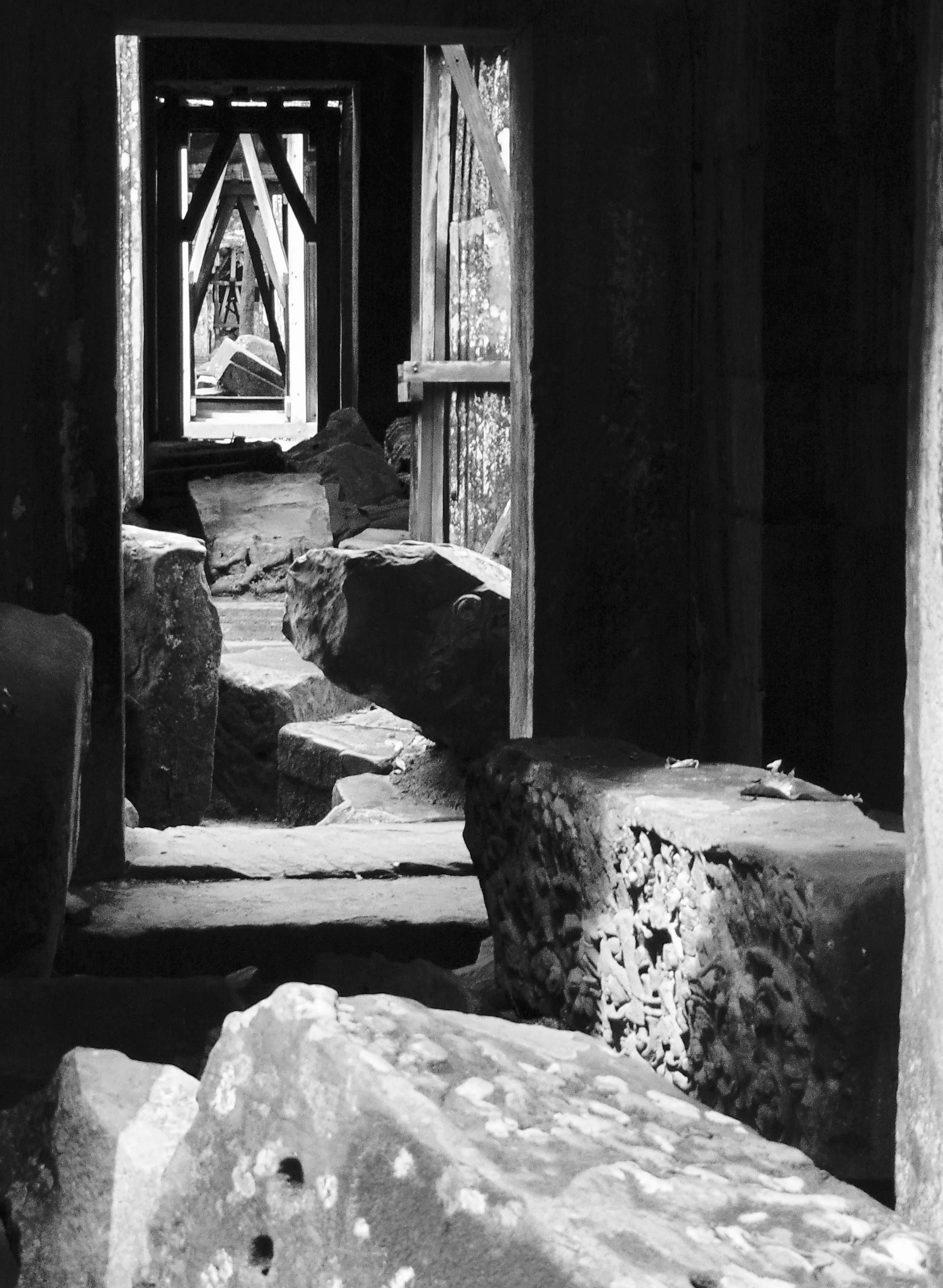
Image of temple conservation ongoing within the site. Courtesy of Francesco Bandarin, UNESCO.
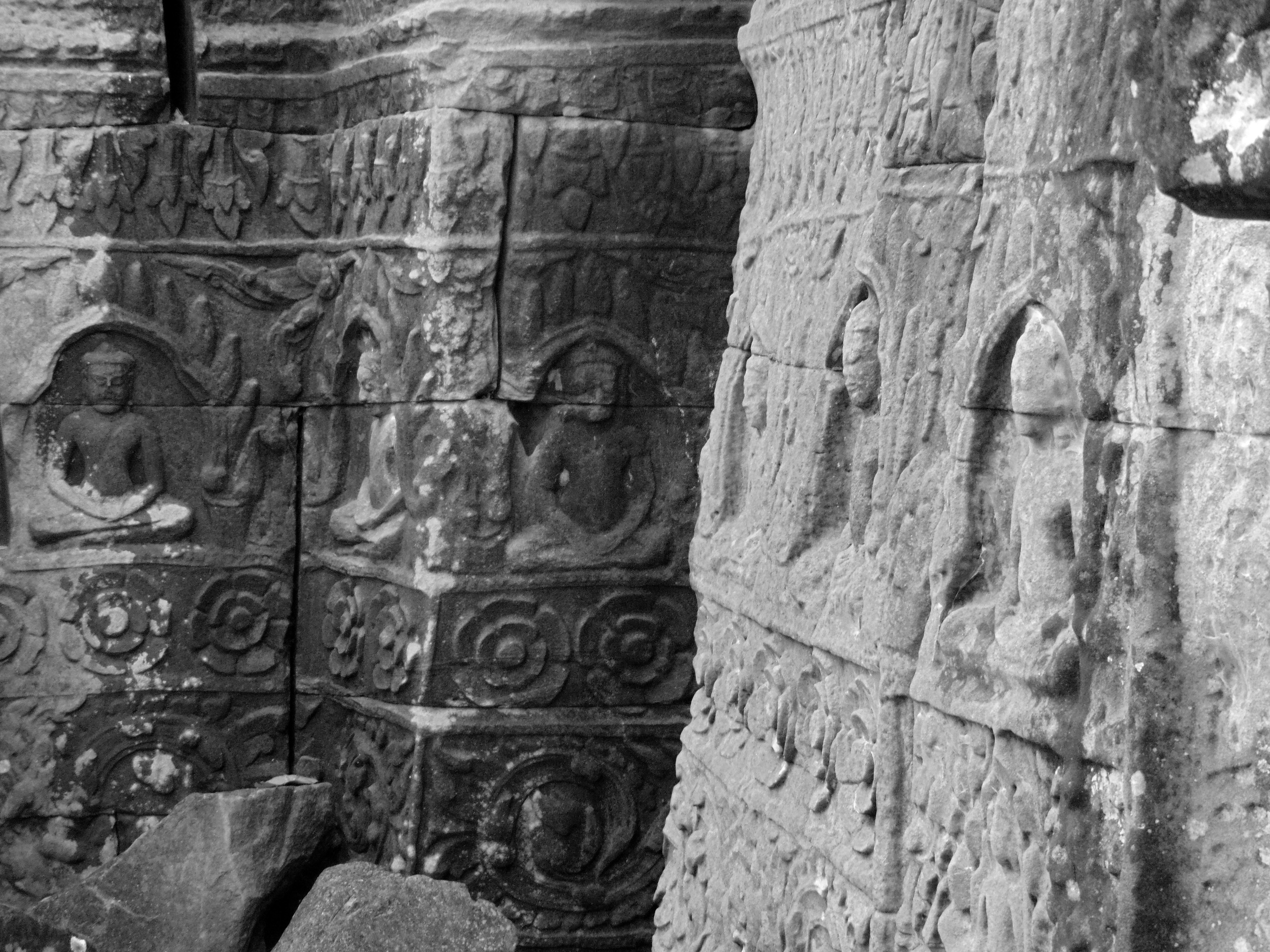
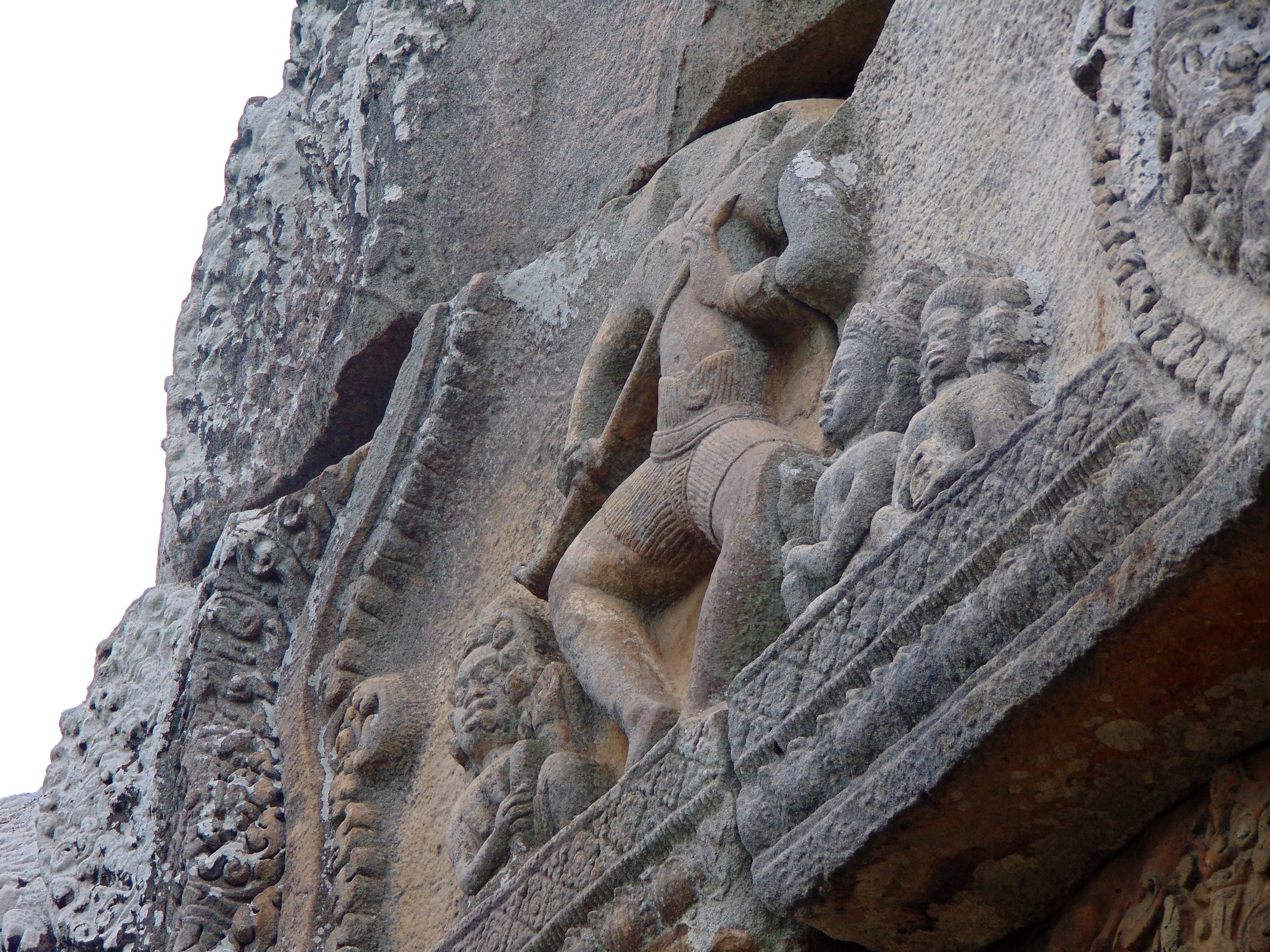
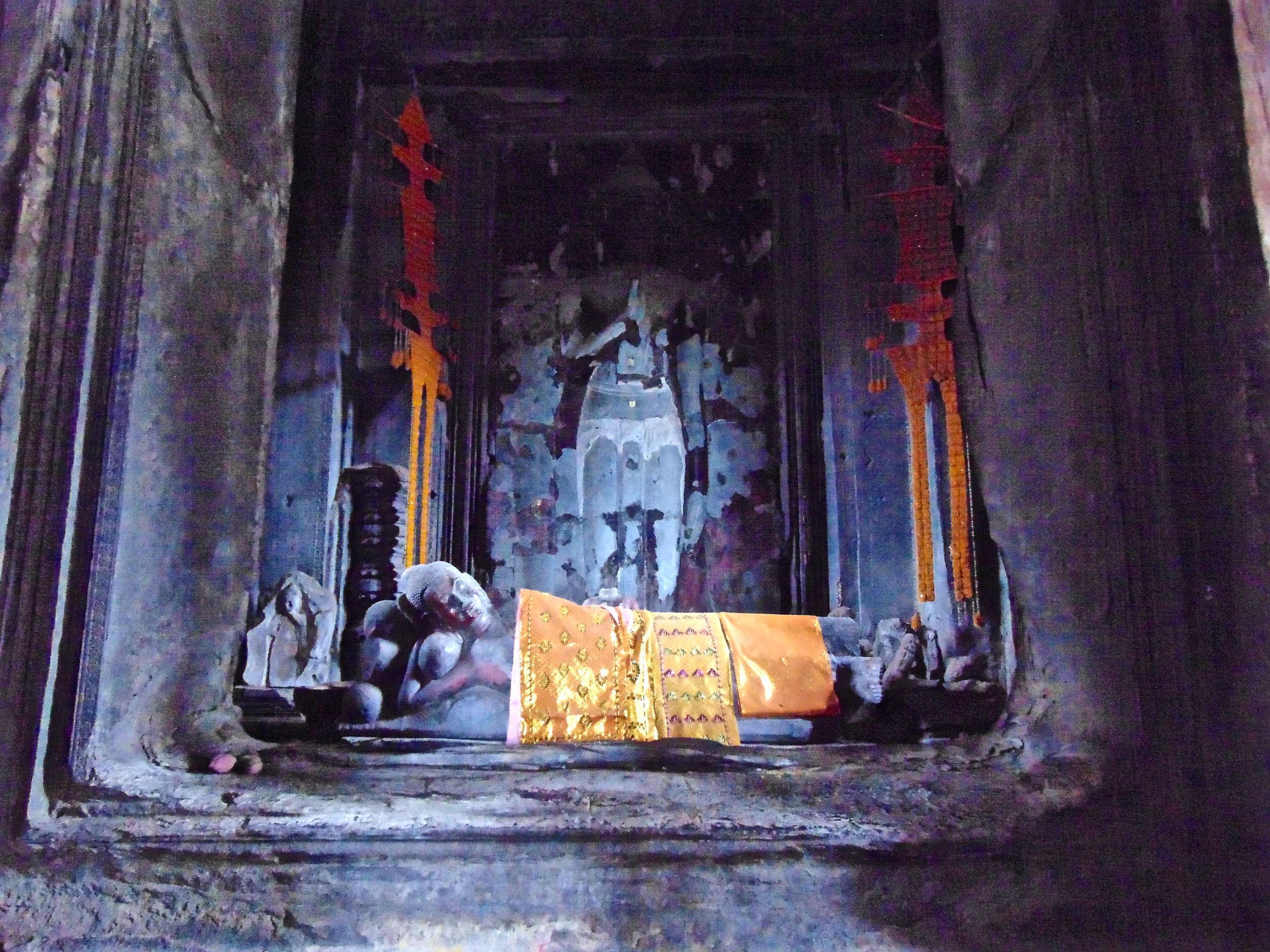
Visnu in Angkor Wat. Courtesy of SKH, 2001.